* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tetralogy of Fallot
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
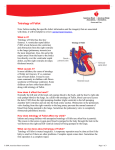
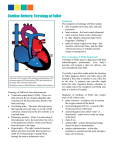
DR. PUNEET GARG B.H.M.S., M.D.(Paed.) Tetralogy of Fallot 1. A large Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) 2. Pulmonary stenosis 3. Right ventricular hypertrophy 4. An overriding aorta Ventricular Septal Defect A VSD is a hole in the septum between the heart's two lower chambers, the ventricles. The hole allows oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle to mix with oxygen-poor blood from the right ventricle. Pulmonary Stenosis This defect involves narrowing of the pulmonary valve and the passage from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery. Normally, oxygen-poor blood from the right ventricle flows through the pulmonary valve and into the pulmonary artery. From there, the blood travels to the lungs to pick up oxygen. Pulmonary Stenosis(cont.) In pulmonary stenosis, the pulmonary valve cannot fully open. Thus, the heart has to work harder to pump blood through the valve. As a result, not enough blood reaches the lungs Right Ventricular Hypertrophy With this defect, the muscle of the right ventricle is thicker than usual. This occurs because the heart has to work harder than normal to move blood through the narrowed pulmonary valve. Overriding Aorta This defect occurs in the aorta, the main artery that carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the body. In a healthy heart, the aorta is attached to the left ventricle. This allows only oxygen-rich blood to flow to the body. Overriding Aorta(cont.) In tetralogy of Fallot, the aorta is located between the left and right ventricles, directly over the VSD. As a result, oxygen-poor blood from the right ventricle flows directly into the aorta instead of into the pulmonary artery. Outcome With tetralogy of Fallot, not enough blood is able to reach the lungs to get oxygen, and oxygenpoor blood flows to the body. Causes Some factors that occur during pregnancy may raise risk of having a child who has tetralogy of Fallot. These conditions and factors include: German measles (rubella) and some other viral illnesses Causes(cont.) Poor nutrition Alcohol use Age (being older than 40) Diabetes Heredity Causes(cont.) Children who have certain genetic disorders, such as Down syndrome and DiGeorge syndrome (history of recurrent infection, heart defects, and characteristic facial features), often have congenital heart defects, including tetralogy of Fallot. Symptoms Cyanosis. Cyanosis is a bluish tint to the skin, lips, and fingernails. Low oxygen levels in the blood cause cyanosis. Symptoms(cont.) Babies who have unrepaired tetralogy of Fallot sometimes have "tet spells." These spells happen in response to an activity like crying or having a bowel movement. A tet spell occurs when the oxygen level in the blood suddenly drops. This causes the baby to become very blue. The baby also may: Symptoms(cont.) Have a hard time breathing Become very tired and limp Not respond to a parent's voice or touch Become very fussy Pass out children would get very tired during exercise and could faint. Signs Heart murmur The sound occurs because the heart defect causes abnormal blood flow through the heart. Babies tire easily while feeding. Not gain weight or grow as quickly as children who have healthy hearts. Clubbing It is the widening or rounding of the skin or bone around the tips of the fingers. Signs(cont.) Clubbing It is the widening or rounding of the skin or bone around the tips of the fingers. Diagnosis Echocardiography Chest X Ray- shows whether the heart is enlarged or whether the lungs have extra blood flow or extra fluid. Diagnosis(cont.) Pulse Oximetry- a small sensor is attached to a finger or toe (like an adhesive bandage). The sensor gives an estimate of how much oxygen is in the blood. Diagnosis (cont.) Cardiac Catheterization- a thin, flexible tube called a catheter is put into a vein in the arm, groin (upper thigh), or neck. The tube is threaded to the heart. Special dye is injected through the catheter into a blood vessel or one of the heart's chambers. The dye allows to see the flow of blood through the heart and blood vessels on an x-ray image. Diagnosis(cont.) cardiac catheterization also done to measure the pressure and oxygen level inside the heart chambers and blood vessels. Treatment Tetralogy of Fallot is repaired with open-heart surgery, either soon after birth or later in infancy. The goal of surgery is to repair the four defects of tetralogy of Fallot so the heart can work as normally as possible. THANKS DR. PUNEET GARG, M.D.(Hom.) Lecturer, Dept. of Medicine, Bakson Homoeopathic Medical College & Hospital, Greater Noida, (U.P)- 201306