* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Nerve guidance conduit wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Central nervous system wikipedia , lookup
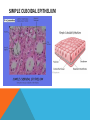
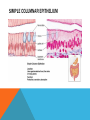
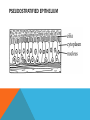
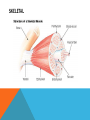
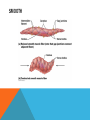
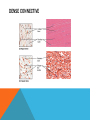
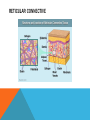
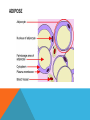
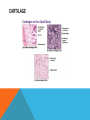
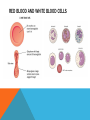
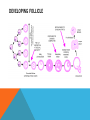
SIMPLE SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM SIMPLE SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM • Description: • Function as mediators of filtration and diffusion • Allow for easy transmembrane movement • Located in: • Kidney glomeruli, air sacs of lungs, lining of heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels; lining of ventral body cavity • Unique features: • Thin and flat • Scale-like in appearance • Larger elliptically-shaped nuclei • Wider than they are tall SIMPLE CUBOIDAL EPITHELIUM SIMPLE CUBOIDAL EPITHELIUM • Description: • Provide a layer of protection from abrasion and excessive water loss • Aid in the absorption and transportation of filtered substances • Located in: • Lines the surface of small excretory ducts in various organs and glands • Compose some of the kidney tubules • Create covering of ovary • Unique features: • May have microvilli on surface • Only a single layer of cells • Hexagonal surfaces • Equally tall and wide SIMPLE COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM SIMPLE COLUMNAR EPITHELIUM • Description: • Main function is protection • Can also be specialized to provide sensory input • Absorbing and transporting nutrients • Located in: • Throughout body’s organ system • Respiratory system • Line ears and buccal cavity • Unique features: • Longer than they are wide • Nuclei usually found at base of cell • Cells connected by tight junctions STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM STRATIFIED SQUAMOUS EPITHELIUM • Description: • Provide protection against mechanical friction and chemical damage • Located in: • Alveoli • Lining of the esophagus • Unique features: • Flat, scale-like • Multiple layers of simple squamous epithelium • Selectively permeable PSEUDOSTRATIFIED EPITHELIUM PSEUDOSTRATIFIED EPITHELIUM • Description: • Secretion • Absorption • Located in: • Linings of the trachea • Upper respiratory tract • Membranous part of male vas deferens (non-ciliated) • Unique features: • Although it has a single layer of cells, cell nuclei makes it look stratified • May have cilia HEART HEART • Description: • Have structural and functional characteristics of smooth and skeletal muscle cells • Highly coordinated to contract together with each heartbeat • Located in: • The heart • Unique features: • Rectangular shaped • Connected by intercalated discs • Under involuntary control SKELETAL SKELETAL • Description: • Allow muscle contraction • Located in: • Muscles attached to the skeleton • Unique features: • Striated in appearance • Under voluntary control • Bound together • Formed in myogenesis SMOOTH SMOOTH • Description: • Control slow, involuntary movements like the contraction of smooth muscle tissue in the walls of the stomach • Located in: • Walls of blood vessels • Lymphatic vessels • Bladder • Uterus • Unique features: • Involuntary • Non-striated LOOSE CONNECTIVE LOOSE CONNECTIVE • Description: • Principal site of rapid fluid and gas exchange between blood and local tissue • Located in: • Beneath epithelial membranes and glandular epithelium • Contributes to formation of organs • Unique features: • Consists of: • • • • “An abundance of amorphous ground substance” “A loose, multidirectional weave of extracellular fibers” “An abundance of different types of fixed and wandering connective tissue” http://histologyolm.stevegallik.org/node/99 DENSE CONNECTIVE DENSE CONNECTIVE • Description: • Forms strong, rope-like structures such as tendons and ligaments • Located in: • Arranged in sheets in Dermis • Tendons and ligaments • Unique features: • Mainly composed of type I collagen • Fibers as its main matrix element • Fibroblasts between collagen fibers ELASTIC CONNECTIVE ELASTIC CONNECTIVE • Description: • Important in recoil of organs (like arteries) • Located in: • Large arteries • Unique features: • Very rare • Elastic fibers present in high concentrations RETICULAR CONNECTIVE RETICULAR CONNECTIVE • Description: • Form stroma, which supports the lymphoid organs • Located in: • Kidney • Spleen • Lymph Nodes • Bone Marrow • Unique features: • Has reticular fibers • Fibers made of type III collagen • Reticular fibers synthesized by reticular cells ADIPOSE ADIPOSE • Description: • Store energy as fat • Cushions and insulates body • Located in: • Beneath skin • Around internal organs • In bone marrow • Around muscles • In breast tissue • Unique features: • Lipid droplets fill the middle of the cell • Anchored by collagen fibers CARTILAGE CARTILAGE • • • Description: • Can bear weight • Lubrication • Repair capabilities • Holds tubes open in the body Located in: • Joints between bones • Rib cage • Ear • Nose • Intervertebral discs Unique features: • Flexible • Composed of chondrocytes • Three types of cartilage—elastic, hyaline, and fibrocartilage BONE BONE • Description: • Makeup skeleton of vertebrates • Develop new bones and bone remodeling • Located in: • Within bone tissue • Unique features: • Several types: • Osteoclasts—break down bone tissue • Osteoblasts—build new bone tissue • Osteocytes—hold bone together RED BLOOD AND WHITE BLOOD CELLS RED AND WHITE BLOOD CELLS RED • Description: • • Location: • • Organism’s principal means of delivering oxygen to body’s tissue • • • • • Cytoplasm rich in hemoglobin Flexible Oval biconcave disks Lack organelles • Protect body against infections and invaders Location: • • Within blood Unique Features: • WHITE • Description: Throughout body Blood and lymphatic system Unique Features: • • • Have nuclei May or may not have granules Five main types BRAIN TISSUE BRAIN TISSUE • Description: • Gray matter: areas of nerve connections and processing • White matter: connect regions of gray matter to each other and rest of the body; transmits nerve signals faster • Located in: • The brain • Unique features: • Myelinated vs. unmyelinated neurons NEURON NEURON • Description: • Processes and transmits information through electrical and chemical signals • Located in: • Core components of the brain and the spinal cord • Ganglia of the PNS • Unique features: • Synapses • Specialized types: • Sensory neurons • Motor neurons • Interneurons SPERMATOGONIUM SPERMATOGONIUM • Description: • Undifferentiated male germ cell • Located in: • Testicles • Unique features: • Originates in a tubule • Divides into two spermatocytes DEVELOPING FOLLICLE DEVELOPING FOLLICLE • Description: • Secretes hormones that influence stages of the menstrual cycle • Located in: • Ovaries • Unique features: • Spheroid • Contain a single oocyte • Continually grow and develop until ovulation