* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrical Basics
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
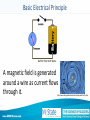
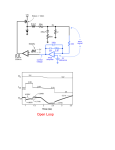
Shake Flashlight North Dakota State College of Science Applied Science and Technologies Electrical Basics • Current is the flow of electrons • Voltage is electrical pressure • Resistance is the opposition to the flow of electrons • Ohm’s Law: V = I x R (voltage = current x resistance) Closed Circuit Closed Circuit Basic Electrical Principle A magnetic field is generated around a wire as current flows through it. http://www.educypedia.be/electronics/javaelectricity.htm Shake Flashlight http://www.msscweb.org The basic principle of "moving magnet plus coil makes electricity" is the foundation for electrical generators, so in a sense this is old technology. Voltage Generation http://www.msscweb.org When a magnet passes through a tightly-wound coil of insulated wire, a voltage is generated. As the magnet changes direction, so does the polarity of the voltage. This action generates an AC voltage. Schematic The AC voltage is sent to a fullwave bridge to convert the AC to a pulsating DC voltage. This energy is stored in Capacitor C1. The switch turns on the LED. http://www.msscweb.org http://www.play-hookey.com/ac_theory/ps_rectifiers.html Components http://www.msscweb.org Full-wave Diodes Capacitor (Battery) www.ndscs.edu