* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 11-3 Water Pollution - Room N-60
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
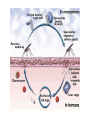
Chapter 11-3 Water Pollution 1/08 Water Pollution • Introduction of chemical, physical or biological agents that adversely affect the organisms that depend upon that water Point-source versus Nonpoint-source pollution • Point-source can be traced to a source • Nonpoint –source comes from many different sources that are often hard to identify Pathogens • Parasites, bacteria and viruses that cause illness in living things • Many spend part of their life cycle in water • Pathogens carried by water cause more human deaths than any other environmental problem Cholera • Acute diarrhea • Caused by bacteria • Infected food water, shellfish • Heat kills cholera bacteria Dysentery • Several bacteria and protozoa responsible • Vomiting, severe diarrhea • Cause water contamination • Heat kills most of these Typhoid Fever • Salmonella Thyphi • Only people carry the bacteria • Shed in feces • Vaccination available • Boil it , cook it, peel it or forget it Schistosomiasis • Caused by microscopic worms • Enters through the skin of people who walk in infected water • Attacks liver, urinary bladder, and intestines Schistosomiasis • Africa, Middle East, Egypt • 100 million people affected • 1 million deaths annually • Aswan Dam WAPI 158 degrees F Malaria • Protozoan • Transmitted by mosquito • The mosquitoes breed in standing water • 800 million affected • 1 million deaths annually Organic Matter • Animal and plant remains, feces etc. Organic Chemicals • Pesticides, fertilizer, gasoline, oil etc.. • Runoff from farmlands • Organic pesticides, herbicides and fertilizers Inorganic chemicals • Acids, bases, salts, etc.. Heavy Metals • Dangerous heavy metals include: Mercury, lead, cadmium, nickel, chromium and Slipknot. Physical Agents • Heat and suspended solids Wastewater • Contains waste from homes or industry Treatment • Primary – filtration and settling. Gets the big stuff out Secondary • Aeration • Second settling tank • Chlorination to kill pathogens Artificial eutrophication • Caused by fertilizer run-off or other organic wastes Thermal Pollution • Heat can be a type of water pollution • Power Plants • Reservoirs Groundwater Pollution • Any polluted surface water can become polluted groundwater • Very hard to clean up Ocean Pollution • Oil spills – Exxon Valdez 1989 • Plastics Cleaning up water pollution • Clean Water Act of 1972 • Safe Drinking water act of 1996