* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download red shift blue shift
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Drake equation wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
Hawking radiation wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
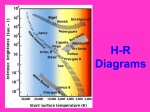
1446 Introduction to Astronomy II – Quiz Study Guide I. From the Labs: Lab Study for the Quiz Solar Spectrum Lab Unit 8.3: The Doppler Effect Sun’s core is extremely hot, and is as dense as lead. Continuum (continuous spectrum) produced in the core. Sun’s outer layers (photosphere) are much cooler than the core. Spectral lines produced in the outer layers of the sun. See blue shift when light source approaches you. See red shift when light source recedes/moves away. Know the equation for the amount of Doppler shift: Also know the equation for the final (shifted) wavelength: red shift blue shift Unit 7.2: The H-R Diagram Review the locations of main sequence stars, supergiants, giants, and white dwarf stars on the H-R Diagram. Spectral class order from hottest to coolest: O, B, A, F, G, K, M. M-K classes: supergiant (I), normal giant (III), and main sequence (V) Stars evolve and do NOT last forever. Absolute magnitude and spectral classification are useful in figuring out how a star will evolve. Parallax is used to measure the distances to nearby stars. Know the equation for parallax: d = distance in parsecs, p = parallax in arc seconds: Conversion from parsecs (pc) to light-years (ly), 1 pc = 3.26 ly. Unit 7.1: Parallax Unit 7.4: Hierarchy of Distances Unit 8.4: Black Holes = m + 5 – (5 log D) The Hubble constant can be used to find the age of the universe. A black hole can result from the death of a supergiant star. The event horizon is the boundary that marks the “point of no return” for a black hole. Also thought of as the size of the black hole. There is a super-massive black hole at the center of the Milky Way. II. Apparent magnitude is how bright something appears in the sky. Absolute magnitude is the apparent magnitude a star would have if it were 10 parsecs away. Know the relationship between apparent magnitude (m), absolute magnitude (M) and distance (D): From the Round House Concept Constellations Study for the Quiz Know at least 5 constellations on your study guide. This includes astronomical name, common name, main star, main star color, and main star M-K class.