* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Junior Cert Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
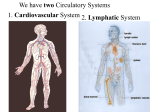
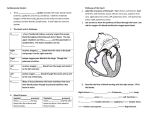
Learning Outcomes On completion of this chapter students should be able to: • OB13 describe the function and composition of blood, and know that blood contains white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets in a liquid called plasma • OB14 understand the structure and function of the heart, identify the four chambers of the heart, and explain the difference between the left and right ventricles • OB15 describe the passage of blood through the heart and lungs via arteries and veins, identify the pulmonary artery and vein, aorta and vena cava, and distinguish between arteries, veins and capillaries Learning Outcomes contd.. • OB16 demonstrate the effect of exercise and rest on pulse rate and understand that a balance of each promotes good health • OB17 recall that the average pulse rate for an adult at rest is 70 beats per minute, and explain why exercise results in increased pulse and breathing rates Lesson 1 Composition of Blood What is the circulatory system? The Circulatory System is responsible for transporting materials to and from different places in the body. It is made up of: Blood consists of: Red Blood Cells Most numerous cell in the body Small doughnut shape Contain haemoglobin which transports oxygen around the body White Blood Cells Larger than red blood cells but also much fewer in number Fights infection by destroying bacteria and viruses that have invaded the body Platelets Tiny fragments of cells Cause blood to clot by producing tiny fibrinogen fibres These stretch across a cut to stop bleeding Plasma It also contains useful things like: A strawcoloured liquid that carries the cells and the platelets which help blood clot. • carbon dioxide • glucose • amino acids • proteins • minerals • vitamins • hormones • waste materials Functions of Blood To transport food, oxygen and wastes To transport heat to the skin to keep the body temperature at 37°C. To fight infection Lesson 2 Blood Vessels Blood vessels There are 3 types of blood vessels found in our body: Veins Veins carry blood towards the heart They have thin walls and a wide inner cavity which allows blood flow to the heart easily They also contain valves which stops the blood flowing backwards Wide inner cavity (lumen) veins with valves Arteries Arteries carry blood away from the heart They have thick elastic walls which allows them to stretch and recoil at each heartbeat These muscles contract to push the blood along No valves present Narrow inner cavity (lumen) Thick muscular walls Capillaries Capillaries link arteries and veins Have very thin walls-just one cell thick Materials can be exchanged from the blood to other body cells and vice versa via capillaries Wall just one cell thick Lesson 3 The Structure of the Heart The Heart The heart is a muscular pump that transports blood around the body It consists of 4 chambers: Right atrium Right ventricle Left atrium Left ventricle YouTube video The Heart Ventricles The lower chambers Receives blood from the atria Pumps blood out through arteries Left ventricle has thick walls (more strength required to pump blood around the body) Atria The upper chambers Receives blood from veins Pumps blood into ventricles Have thin walls Structure of the Heart Pulmonary artery Vena Cava Right Atrium Right Ventricle Aorta Pulmonary vein Left Atrium Left Ventricle How does the heart work? 1. Deoxygenated blood enters right atrium via vena cava 2. Blood is pumped to right ventricle and then to the lungs via the pulmonary artery 3. Oxygenated blood enters left atrium via pulmonary vein 4. Blood is pumped to left ventricle where it leaves via the aorta Pulmonary artery Vena cava Aorta Pulmonary Vein Tips for remembering VEAL Veins Enter, Arteries Leave LORD Left=Oxygenated, Right=Deoxygenated Pulmonary = related to lungs e.g. Pulmonary vein enters from lungs Lesson 4 The Pulse & How to demonstrate the effect of exercise on the pulse The Pulse Every time the heart contracts, the blood surges forward in the arteries. By placing your fingers over an artery, you can feel this pulse The Pulse For an adult the average pulse rate is 70 beats per minute (b.p.m.). Children have faster heartbeats than adults. What happens to our pulse rate when we exercise? Mandatory Practical Title: to demonstrate the effect of exercise on the pulse rate Beats per minute at rest vs. Beats per minute after exercise Results Beats per minute At rest Immediately after exercise 3 minutes after exercise 6 minutes after exercise Person 1 Person 2 Conclusions When a person exercises, the muscles need more oxygen to get more energy from food. A faster heartbeat delivers oxygen to the muscles quicker. Exercise increases the pulse rate. Why we need exercise Exercising the heart makes it stronger and reduces the likelihood of heart disease. To prevent heart disease we should: Take regular exercise Never smoke Eat only small amounts of saturated (animal) fats Assessment The circulatory system is made up of blood, blood vessels and the _____. Arteries _____ the heart and ______ enter the heart. The capillaries ______ arteries and veins. Blood is made up of red blood cells which carry _____, white blood cells which fight _______, platelets which causes blood to _____ and ______ which is the liquid part of blood. The heart is made up of _____ chambers, 2 atria and 2 ventricles. Solutions The circulatory system is made up of blood, blood vessels and the heart. Veins enter the heart; arteries leave the heart and The capillaries link arteries and veins. Blood is made up of red blood cells which carry oxygen, white blood cells which fight infection, platelets which causes blood to clot and plasma which is the liquid part of blood. The heart is made up of four chambers, 2 atria and 2 ventricles. Bibliography http://library.thinkquest.org/5777/images/circulatory.gif http://images.encarta.msn.com/xrefmedia/sharemed/targets/images/pho/35a5c/35A5C 297.jpg http://www.fi.edu/learn/heart/blood/images/blood-platelets.gif http://www.clipartheaven.com/clipart/outdoor_recreation/cycling/mountain_biking_-_cartoon.gif http://www.worldofteaching.com/ http://www.clarian.org/ADAM/doc/graphics/images/en/19432.jpg http://www.artie.com/valentines_day/arg-beating-heart-sfx-url.gif http://www.bradfitzpatrick.com/character_design/images/full/DancingHeart.gif http://whttp://www.son.jhmi.edu/images/content/blood.jpgww.pamf.org/images/shutterstock /HM_SH001-W.jpg http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/ks2bitesize/science/revision_bites/keeping_healthy2.shtm l