* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ohm`s Law - Glasgow Science Centre
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
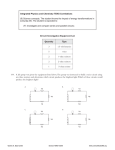
Circuits and Ohms Law Through Investigation, I understand the relationship between current, voltage and resistance. I can apply this knowledge to solve practical problems. SCN 4-09a. Today we are going to find out… • • • • What the term ‘resistance’ means in the context of electricity. What factors influence the resistance of a conducting material What the relationship is between current, voltage and resistance How resistors behave in series and parallel circuits. And we will be able to… • • • • Provide a definition of resistance State and describe the factors influencing resistance Carry out numerical problems involving resistance Describe how resistors work in series and parallel circuits. Memory Review… What do we mean when we talk about a ‘conducting material’? Like this copper penny… …Or this copper wire! All conducting materials oppose electrical current in some way. This opposition to electrical current is called resistance. Resistance is given the symbol R and is measured in Ohms. The symbol for ohms is Ω (Omega) The resistance of the conducting material is determined by various factors: - Thicker diameter wires have less resistance - Think - about how think electricity pylon cables are! Length – Shorter cables have less resistance than longer cables Material – copper has quite a low resistance Temperature – heat causes resistance to increase All conducting materials oppose current in some way. This includes circuit components such as lamps. If you wanted to increase the resistance in a circuit therefore, you could add in more lamps and in turn, this would… Try experimenting with this now! What happens to the current when you add in more bulbs to the circuit? What happens when you take them away? You can limit the current flowing through the circuit in other ways, too. You can do this using circuit components called resistors. These are some examples of circuit symbols for different resistors. Why do you think they look different? There are different types of resistors. Each type has a different symbol to represent what controls the level of resistance. This is a ‘standard’ resistor. This is a variable resistor. This is a ‘thermistor’ - a resistor with resistance controlled by temperature. This is a ‘light dependent resistor or LDR’ - a resistor with resistance controlled by light. Can you think of an example of when you would want to use… Thinking this through… there must be a relationship between current, voltage and resistance. This relationship is called Ohms Law Ohms Law… Voltage = Current X Resistance V=IR V I R Calculating Resistance in Series Circuits… R1 R2 R3 R4 In a series circuit the total resistance is the sum of the individual resistors R5 Rt = R1+R2+R3+R4+R5 Calculating Resistance in Parallel Circuits… R1 R2 R3 In a parallel circuit the total resistance is the given by… 1/Rt = 1/R1 + 1/R2 + 1/R3 Today we have… • Learnt what the term ‘resistance’ means • Discovered what properties influence the resistance of a conductor • Learnt about various different kinds of resistor and what potential uses these may have • Discovered the relationship between Voltage, Current and Resistance and know that this relationship is called Ohms Law. • Learnt how to calculate resistance in series and parallel circuits.