* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PHY102Lab2-HK
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
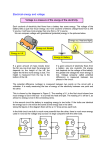
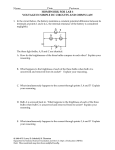
Physics 102 Mapping Electric Fields January 24th, 2006 Wai N. Man, HoKoon Yau Abstract: This experiment will introduce the idea of series and parallel of circuits, and using the oscilloscope and function generator. Equipment: 3 light bulbs Wires Power supply (AC) Digital voltmeter (VOM) Function generator Oscilloscope Procedure 1: 1. Using the light bulb board and wires, build a series circuit for all three bulbs and a power supply (4.5v). 2. Measure the voltage across each light bulb. 3. Remove one wire connecting the bulbs to the power supply (4.5v). And using the VOM set to DCA to replace it, and record the current. 4. Remove one light bulb and observe the result. 5. Wire only two bulbs in series with the power supply (4.5v) and observe. 6. Measure the voltage across each light bulb. 7. Wire three bulbs in parallel with the power supply (4.5v) and measure the voltage across each. 8. Remove one bulb and observe. 9. Remove one wire connecting the bulbs to the power supply (4.5v). 10. Use the VOM set to DCA to replace it and record the current with all three bulbs lit. 11. Wire two bulbs in series, and then wire the third in parallel with the other two. 12. Remove the first light bulb and observe, and then put it back. 13. Remove the second light bulb and observe, and then put it back. 14. Remove the third light bulb and observe. Data: Calculations 1: 1a. Do all three bulbs light? Yes, all the bulbs have lighted up in the series circuit. 1b. What happens if any one bulb is removed? All the bulbs will be off if any one bulb is removed. 2. Input 4.5v 1st bulb: voltage = 1.22v, current = 0.10A 2nd bulb: voltage = 1.71v, current = 0.09A 3rd bulb: voltage = 1.46v, current = 0.09A 3a. Are the two bulbs brighter, dimmer, or the same as they were when all three bulbs were wired? When only tow bulbs were wired, the bulbs became brighter than they were when all three bulbs were wired. 3b. 1st bulb: voltage = 2.3v 2nd bulb: voltage = 2.1v 4a. Do all three bulbs light? Yes, all three bulbs lighted. 4b. What happens if any one bulb is removed? There are several possibilities. The rest of the bulbs still lighted if any one bulb is removed. 4c. When one bulb is removed, what happens to the brightness of the remaining two bulbs? If one bulb is removed, the remaining two bulbs will be the same as they were and the voltage across each bulb is higher. 4d. 1st bulb: voltage = 4.28v 2nd bulb: voltage = 4.06v 3rd bulb: voltage = 3.50v 5a. Do all three bulbs light? Yes, all three bulbs have lighted up. 5b. What happens if any one bulb is removed? If the 1st or second bulb is removed, all the bulbs will be off. If the 3rd bulb is removed, the rest of the bulbs will stay on. 5c. When one bulb is removed, what happens to the brightness of the remaining two bulbs? If the 1st or second bulb is removed, all the bulbs will be off. If the 3rd bulb is removed, the rest of the bulbs will have the same brightness as before. Procedure 2: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Connect the function generator to the oscilloscope. Set the frequency dial on the function generator to about 0.9. Set the waveform to sine, and the multiplier to X100 Turn up the gain to about 3 o’clock, and set the offset to 0. Read the waveform on the oscilloscope. Find the period on the oscilloscope and calculate the frequency. Find the amplitude of the wave in volts. Turn the frequency dial on the Function Generator and record the effect on th oscilloscope. Calculation 2: 1. Period: 5.6x 2ms = 0.0112s 2. F = 1/T = 1/0.0112s = 89.29 Hz. If the function generator connected to a speaker, we could hear this frequency. 3. 2.3v x 1 = 2.3A Error Analysis Questions: 1. Are the circuits in your car connected in parallel or series? Why? The circuit in the car is connected in parallel, because if one of the head light is off, the other head light is still on. 2. Construct on your paper a single circuit that has two series branches and two parallel branches. There are many possible answers. 3. Note the three schematic diagrams below: Error Analysis: According to the first procedure we have done in the experiment, we found out that is impossible to get the precise number of the input voltage. We believed that is because the bad connection between the wire and the connector on the bulbs. Conclusion: After we have finished this experiment, we have found out that the series circuit has a constant current, and the parallel circuit has a constant voltage across each bulb. The light bulbs are actually brighter in the parallel circuit compare with the series circuit. Moreover, we have concluded that the circuit in the car is in parallel circuit. Since, even thou one of the head light is off, the other one is still working. Therefore, the circuit in the car can’t be the series circuit. (actually is a combination of series and parallel) Grade: 76/100