* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Balanced and Unbalanced Forces
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
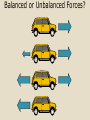
Balanced and Unbalanced Forces Force • A force is a push or pull that causes an object to move, stop, or change direction • Has a size and a direction • In physics a force is anything that makes an object accelerate (remember: acceleration in science can mean speed up, slow down, change direction or change speed & direction!) How do we measure force? • A spring scale is used to measure force. • The units of measurement for force, are called Newton. Mass Vs. Weight • Mass is the amount of matter in an object. • The tool we use to measure mass is the Triple beam balance. • The units used to measure mass are grams (g). • Weight is the measure of gravitational force on an object. • The tool we use to measure weight is the spring scale. • The unit for weight is the gram (g). Balanced and Unbalanced Forces • Forces occur in pairs and they can be either balanced or unbalanced. Balanced Forces • Balanced forces do not cause change in motion • They are equal in size and opposite in direction Examples of Balanced Forces Unbalanced Forces • Unbalanced forces are NOT equal in size. • An unbalanced force always causes a change in motion! This can be a change in speed, direction or both. • When unbalanced forces act in opposite directions you can find the net force. To find the net force, you • Calculate the Magnitude of the force. This is the difference between the two forces, so you subtract the smaller force from the larger one. • Determine the direction of the net force. The direction of the largest force is the direction of the force (IF they are going in opposite). Examples of Unbalanced Forces Unbalanced Forces 3 N, right – 6 N, left = 3N, left Unbalanced Forces 4 N, left – 10 N, right = 6N, right Unbalanced Forces 5 N, right + 10 N, right = 15N, right Balanced or Unbalanced Forces? Types of Forces • Gravitional Force (Gravity) – is the force of attraction between objects due to their masses. • Friction – the force that exists when there is contact between 2 surfaces (It opposes motion) • Applied force – force that is applied to an object by a person or another object. Types of Forces (continued) • Net force – the combined effect of all forces acting on an object. • Balanced – Forces are balanced when they act on an object in opposite directions and are equal in size (no change in the position, speed, or direction of motion of the object). • Unbalanced – opposing forces that are not equal (causes change in position, direction, or speed).