* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The causes of hearing loss are varied and their impact
Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Auditory system wikipedia , lookup
Lip reading wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of mammalian auditory ossicles wikipedia , lookup
Hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Sensorineural hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
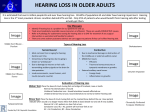
Causes of Hearing Loss The causes of hearing loss are varied and their impact on hearing is variable. Sometimes the cause or etiology is readily apparent, such as a wax build-up in the external ear canal or an ear infection. At other times, the cause of the hearing loss is presumed or indefinite given current levels of technology and the information they provide, such as in cases of sudden onset or non-syndromic Sensorineural. Genetic factors account for 50% of infant hearing loss. Together, disease, side effects of treatment and environment account for 25% of infant hearing loss. The cause of the remaining 25% of infant hearing loss is unknown. Genetic The part of the body that controls the unique characteristics of a person is a gene. Genes determine eye and hair color. A genetic hearing loss is caused by information or the ‘code’ carried by the genes. Disease An illness, infection, or sickness is a disease. A disease affects the way the body functions. There are several diseases that can cause hearing loss. Some diseases are transmitted from mother to baby during pregnancy or birth. Other diseases are contracted after birth. Side Effects of Treatment Some babies are very sick at birth. Medication or other types of treatment are needed in order for the baby to get well. Sometimes medication and other treatments are needed in order to save the baby’s life. Some of these medications and treatments can cause hearing loss. Environmental Factors Environmental factors are events that occur in the baby’s ‘living space’ either before or after birth. There are many events that can cause hearing loss. Conductive - External Ear - Congenital malformation where pinna and ear canal fail to form - Blockage in ear canal - foreign body or accumulated cerumen (ear wax) - Middle ear - Perforation in tympanic membrane (ear drum) from trauma or disease - Otitis media (ear infection) - Broken ossicular chain due to head trauma or trauma to the ear Sensorineural - Sensory - Neonatal risk indicators - Genetic disorders causing non-syndromic sensorineural hearing loss - Ototoxic drugs such as some antibiotics - Cancer treatments - chemotherapy and radiation therapy - Head trauma - fractured temporal bone - Excessive noise expose - Diseases of the vascular system such as sickle cell anemia - Kidney disease - Congenital infections such as toxoplasmosis, rubella, CMV, herpes, other bacterial infections like syphilis - Acquired infections such as influenza, meningitis, labyrinthitis, mumps, syphilis - Neural - Acoustic neuroma or other tumor of or near the nerve of hearing and balance Phonak acknowledges the permission and assistance of the following organizations for their expertise in this portion of our website: - The Better Hearing Institute (http://www.betterhearing.org) - The Infant Hearing Guide (Arkansas Children’s Hospital Audiology Department, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences)