* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Forces
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
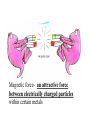
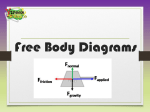
Forces What is a force? • Forces are what makes things move, like a push or a pull. • When you kick a football your foot applies a force to the ball. • Forces can – start motion – stop motion – change directions • The engine of a train uses a pulling force to make the carriages move along the track. Forces are either balanced or unbalanced • The more energy used to create force, the stronger the force will be. • Forces cause Energy to be transformed or transferred. Forces cause motion to occur. Balanced Forces • All forces acting on an object are equal • When forces are balanced, there is no change in motion. (If the object is not moving, there will be no movement. If the object is moving, its speed will not change; no slowing down or speeding up. – It will remain constant. Unbalanced Forces • An unbalanced force changes the motion of an object. An unbalanced force will have acceleration. • All forces acting on an object are not equal • One or more force is stronger than others • Motion occurs Net Force • The sum of all forces acting on an object – A net force of 0 • No motion – A net force of more than 0 • Motion occurs • AND has direction Mass is a measure of how much matter is in an object. Unit of mass is grams (g) Weight is the force of gravity on an objects mass. Weight is measured in Newtons (N). A spring scale is used to measure a force. It measures a force in Newtons. Kinds of Forces Friction • Force that slows down motion or opposes motion – The force of friction is affected by the type of surfaces involved – The greater the load or mass the more force needed to overcome friction – The force of friction does NOT depend on the amount of surface area Three types of Friction • Sliding- when two solid surfaces slide past each other. Example pushing a box across the floor • Rolling- involving wheels or round objects. Reduces sliding friction. Example: wheels on a car • Fluid- involving liquids or gases. Reduces both sliding and rolling friction. Example: Air resistance or use of a lubricant such as grease • Air resistance creates friction in most situations Attractive Forces • A force between two mass – Types of Attractive Forces • Gravity • Magnetic • Electrical Gravityis an attractive force . • More mass = more gravity • Gravitational force is the force of attraction between two different masses. • The larger the mass, the Larger the effect of the gravitational force has on a body. • Acceleration because of gravity is 9.8 m/s/s • All objects accelerate at the same rate Law of Universal Gravitation states: That all objects in the universe attract each other by the force of gravity and the size of the forces depends on the mass of the objects and the distance between them. Magnetic force- an attractive force between electrically charged particles within certain metals Electrical force is an attractive force between electrical charges Applied force • refers to a force that is applied to an object such as when a person moves a piece of furniture across the room or pushes a button on the remote control. A force is applied. Normal Force • A book resting on a table has the force of gravity pulling it toward the Earth, but the book is not moving or accelerating, so there must be opposing forces acting on the book. This force is caused by the table and is known as the normal force. . Normal Force is the force of an object pushing back. • You can "see" the normal force in some situations. If you place a ruler so that it is supported by both ends and place a small heavy object in the center, the ruler will bend. Of course it wants to straighten out so it exerts an upward force on the object. This upward force is the normal force. You can feel the force yourself if you push down in the center of the ruler. The harder you push, the more the ruler bends and the harder it pushes back Tension Force -the force created by a stretched wire, rope or cable Spring Force- the force created by the compression of a spring Buoyancy • An upward pushing force in a fluid. A fluid is a liquid or a gas. Newton’s Laws • Mechanical forces obey three laws called Newton’s Laws of Motion. • Motion is a change of position in a certain amount of time. – To stop a motion, we must have an opposing force • Describe motion and changes in motion First Law of Motion • Law of inertia – Inertia: a property of all objects that is related to its mass - moving objects tend to stay moving and motionless objects remain motionless – An object at rest [not moving] will stay at rest until a force acts on it. – An object in motion will stay in motion until a force acts on it. – Objects with more mass have more inertia • Bigger objects are harder to start and stop …If there are no forces acting on an object which is not moving, it will stay at rest. or ….. if it was already moving at a steady state in a straight line, it will continue to move in a straight line as before. So to start something moving ... …or speed it up, slow it down or stop it ... …or change its direction... A force must be applied. The Second Law Law of acceleration • A force applied to an object will change its speed in the same direction as the force. • Objects accelerate in the direction of the force • The more force applied, then more acceleration • There is a RELATIONSHIP between mass of object and the force needed to move an object. • The more mass an object has, the more force is needed to accelerate the object. Which can be expressed: F = ma A big force will give a bigger acceleration than... …a small force applied to the same mass. • Acceleration is the change of speed of an object. It means the object is speeding up or slowing down. • Speed is the rate of motion of an object. The speed of an object is equal to the distance the object travels divided by the time it takes to travel that distance. Speed = distance divided by time The third law Third Law often called the Law of action-reaction • For each force there is another force acting in the opposite direction with the same strength. • (For every action there is an equal but opposite reaction) – Forces occur in pairs – The forces are equal and opposite – One force is an action force – The other force is a reaction force • So if you push against the wall, the wall pushes you back with the same force, otherwise the wall would fall over! • This also explains how a rocket works. The force of the gases rushing out of the end of the rocket produces a force in the opposite direction pushing the rocket forward.