* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download P K P K K K P P
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
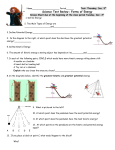
Name_____________________________ Period______ Science Test Review - KEY!!! : Forms of Energy 1. Define Energy: the ability to do work or cause change 2. Two Main Types of Energy are potential energy______and____kinetic energy 3. Define Potential Energy stored energy due to position or arrangement of particles 4. In the diagram to the right, at which point does the sled have the greatest potential energy?___A_______ 5. Define Kinetic Energy: energy of motion 6. The amount of Kinetic energy a moving object has depends on its_mass_____and _speed_____. 7. In each of the following pairs, CIRCLE which would have more kinetic energy rolling down a hill: A marble or a boulder A beach ball or bowling ball A Toy car or a Hummer Explain why you chose the ones you chose? they all have the greater mass 8. In the diagrams below, identify the greatest Kinetic and greatest potential energy P P P K K P K K 9. What is pictured to the left? pendulum 10. At which points does the pendulum have the most potential energy? A & E 11. At which point does the pendulum have the most kinetic energy? C A B C D 12. At which points on the pendulum are the kinetic and potential energy equal ? B&D E 13. If you place a block at point C, what would happen to the block? It would be moved Why? The pendulum has kinetic energy which would be transferred to block as motion energy Define the Forms of Potential Energy: 14. Chemical Energy: energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules Example: biomass, petroleum (gasoline), natural gas 15. Nuclear Energy: energy stored in the nucleus of an atom Example: the sun (fusion), nuclear (fission) in power plants List two ways nuclear energy is produced: fusion and fission 16. Gravitational Potential Energy: potential energy due to position or place (elevation) Example: cat on a fridge 17. Stored Mechanical: energy stored in objects by application of force Example: compressed spring, rubber band wind-up toy made in class Define the Forms of Kinetic Energy: 18. Radiant Energy: is electromagnetic energy that travels in transverse waves. Example: x rays, sun light List the different forms of Radiant Energy gamma rays & x-rays, UV rays, visible light, infrared, microwaves, radiowaves (GUVIMR) 19. Thermal Energy: heat energy Example: geothermal heat 20. Motion or Mechanical Energy: is the movement of objects and substances from one place to another. Example: bike riding 21. Sound Energy: is the movement of energy through substances in longitudinal waves Example: guitar string plucked 22. Electrical Energy: the movement of electrons Example: electricity 23. Energy of microwaves, radio waves, x-rays, ultraviolet rays, and light waves are all forms of _ electromagnetic _energy Energy Transformations (Conversions) 24. Define Energy transformation: begins with one energy and produces another type of energy 25. What does the law of conservation of energy state? The law of conservation of energy says that energy is neither created nor destroyed. Give an example: chemical energy transforming into motion/mechanical energy and also producing heat and sound energy 26. In every energy conversion, some energy is always converted into thermal (heat) energy., due to friction. 27. What is the energy transformation for a resource to produce electricity? Flashlight: __chemical__________ electrical _______thermal______ _radiant____________ (battery) (electricity) (resistor creates heat) (Light) 28. Using number 27, diagram the energy transformations that occur in the following: Hot Plate electrical thermal Windmill motion /mechanical electrical or mechanical Toaster electrical thermal Gas Stove Car Engine chemical thermal chemical mechanical/sound/thermal Hair Dryer electrical thermal/motion 29. chemical_______________energy in the sugars and starches of food fuels all your body functions and movements, and provides the thermal energy that keeps your body temperature constant. Heat/Thermal Energy Transfer DEFINE: 30. convection- heat transfer through fluids (liquids) and gases 31. conduction- heat transfer by particles touching 32. radiation- heat transfer through electromagnetic waves (example: sun’s light and heat) 33. Identify the following examples as convection, conduction or radiation: Ice in a soft drink melts due to ____conduction & convection____________________ Boiling an egg in water __ convection______________________________________ A pot touching a hot stove ___conduction_____________________ A small heater heating a bathroom ___radiation__________________ A cold blooded reptile warming itself from the sun ___radiation__________________ 34. Explain how heat moves through liquids during convection. Hot liquids circulate and rise to top as cold liquids circulate and sink to bottom—and this process repeats in a circular-type fashion. ~Draw a picture showing this.