* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Wizard Test Maker
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum operator wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
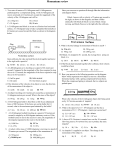
MOMENTUM AND IMPULSE WORKSHEET 1. What is the momentum of a 30-kilogram cart moving with a speed of 10 meters per second? 1) 20 kg-m/sec 3) 3 kg-m/sec 2) 40 kg-m/sec 4) 300 kg-m/sec 2. If the direction of the velocity of an object is west, the direction of the momentum of the object is 1) north 3) east 2) west 4) south NAME__________________ 8. Base your answer to the following question on the information and diagram below. Block A moves with a velocity of 2 meters per second to the right, as shown in the diagram, and then collides elastically with block B, which is at rest. Block A stops moving, and block B moves to the right after the collision. 3. If a 3.0-kilogram object moves 10. meters in 2.0 seconds, its average momentum is 1) 60. kg-m/sec 3) 15 kg-m/sec 2) 30. kg-m/sec 4) 10. kg-m/sec 4. Two rocks weighing 5 Newtons and 10 Newtons, respectively, fall freely from rest near the Earth's surface. After 3 seconds of free-fall, compared to the 5-newton rock, the 10-newton rock has greater 1) speed 3) momentum 2) acceleration 4) height 5. Momentum may be expressed in 1) joules 3) watts 2) kg-m/s 4) N-m 6. Which object has the greatest momentum? 1) a 12-kg mass moving at 1 m/sec 2) a 5-kg mass moving at 2 m/sec 3) a 9-kg mass moving at 3 m/sec 4) a 4-kg mass moving at 4 m/sec 7. Cart A has a mass of 2 kilograms and a speed of 3 meters per second. Cart B has a mass of 3 kilograms and a speed of 2 meters per second. Compared to the inertia and magnitude of momentum of cart A, cart B has 1) the same inertia and the same magnitude of momentum 2) the same inertia and a smaller magnitude of momentum 3) greater inertia and the same magnitude of momentum 4) greater inertia and a smaller magnitude of momentum If block A is stopped in 0.1 second, the average force acting on block A is 1) 50 N 3) 200 N 2) 100 N 4) 400 N 9. A 15-newton force acts on an object in a direction due east for 3.0 seconds. What will be the change in momentum of the object? 1) 0.20 kg-m/sec due west 2) 5.0 kg-m/sec due east 3) 45 kg-m/sec due east 4) 45 kg-m/sec due west 10. A 1.0-kilogram mass changes speed from 2.0 meters per second to 5.0 meters per second. The change in the object's momentum is 1) 9.0 kg-m/sec 3) 3.0 kg-m/sec 2) 21 kg-m/sec 4) 29 kg-m/sec 11. A 20.-kilogram mass moving at a speed of 3.0 meters per second is stopped by a constant force of 15 Newtons. How many seconds must the force act on the mass to stop it? 1) 0.20 sec 3) 5.0 sec 2) 1.3 sec 4) 4.0 sec 12. A net force of 12 Newtons acting north on an object for 4.0 seconds will produce an impulse of 1) 48 kg-m/sec north 3) 3.0 kg-m/sec north 2) 48 kg-m/sec south 4) 3.0 kg-m/sec south 13. A 5.0-kilogram cart moving with a velocity of 4.0 meters per second is brought to a stop in 2.0 seconds. The magnitude of the average force used to stop the cart is 1) 20. N 3) 10. N 2) 2.0 N 4) 4.0 N 16. A 0.025-kilogram bullet is fired from a rifle by an unbalanced force of 200 Newtons. If the force acts on the bullet for 0.1 second, what is the maximum speed attained by the bullet? 1) 800 m/s 3) 5 m/s 2) 20 m/s 4) 400 m/s 14. A 5.0-newton force imparts an impulse of 15 Newton- seconds to an object. The force acted on the object for a period of 1) 0.33 s 3) 3.0 s 2) 20. s 4) 75 s 17. A force of 20. Newtons is exerted on a cart for 10. seconds. How long must a 50.-newton force act to produce the same impulse? 1) 10. s 3) 5.0 s 2) 2.0 s 4) 4.0 s 15. A force of 10. Newtons acts on an object for 0.010 second. What force, acting on the object for 0.050 second, would produce the same impulse? 1) 1.0 N 3) 5.0 N 2) 2.0 N 4) 10. N 18. A student drops two eggs of equal mass simultaneously from the same height. Egg A lands on the tile floor and breaks. Egg B lands intact, without bouncing, on a foam pad lying on the floor. Compared to the magnitude of the impulse on egg A as it lands, the magnitude of the impulse on egg B as it lands is 1) less 3) the same 2) greater Answer Key [New Exam] 1. 4 2. 2 3. 3 4. 3 5. 2 6. 3 7. 3 8. 3 9. 3 10. 3 11. 4 12. 1 13. 3 14. 3 15. 2 16. 1 17. 4 18. 3