* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Population Ecology
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Two-child policy wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
The Population Bomb wikipedia , lookup
Human overpopulation wikipedia , lookup
World population wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
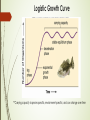
Population Ecology CP Biology What is Ecology? ´Ecology is the branch of biology that deals with how organisms interact with one another and their environment. Populations ´Population – a group of interbreeding individuals of the same species in a particular area ´Members of a population breed with one another ´Researchers study populations’ geographic range, density and distribution, growth rate and age structure Geographic Range ´ The area inhabited by a population ´ Can vary enormously in size w/different species ´ Ex: Bacteria in a rotting pumpkin – small range Cod in the Atlantic – Greenland to N. Carolina Density and Distribution ´Population density – The # of individuals per unit area ´Density is based on availability of resources ´Clumped – patchy distribution of resourced ´Near-uniform – limited resources, intense competition ´Random – uniformly distributed resources Age structure ´Number of females & males of each age a population contains ´Important to know reproductive potential of a population ´ Only females produce offspring (animals) ´ Important to know age at which organisms reproduce Population Growth ´Determined by the # of organisms that are added to or subtracted from the population ´ Populations increase with births and immigration (in) ´ Populations decrease with deaths and emigration (exit) ´How the population changes determines the type of growth you see in the population over time ´Exponential vs. Logistic Growth Exponential Growth ´When the size of each generation will be larger that the generation before it ´The larger a population gets, the faster it grow ´Happens under ideal conditions ´Examples: Bacterial growth, elephants over a long time, organisms in a new environment ´Produces a J-shaped curve Population Sampling ´ Two basic methods of sampling a population: ´ Plot sampling ´Gives an estimate of the # of individuals in a larger area based on actual #s in a smaller area ´Great for marine environments ´ Mark & recapture ´A group of animals are marked & captured, then turned loose ´Second capture (recapture) done ´Proportion of marked animals in recapture represent proportion of entire population ´Great for mobile populations Exponential Growth Example: Mice in a field ´ Imagine 2000 mice in a field ´ If 1000 mice are born each month… ´ And if 200 mice die each month… ´ The population will increase over time ´ But by how much? How fast? Exponential Growth Example: Mice in a field Logistic Growth ´ Happens when a population’s size grows then stops after exponential growth ´ Four stages: ´1. Exponential growth – resources are unlimited, population grows quickly, few individuals die ´2. Growth slows down – In reality, population growth slows down, can’t be sustained at an exponential rate ´3. Growth stops – Size of the population levels off, no more growth, will remain at this size indefinitely ´ Produces an S-Shaped curve ´ Growth levels off when the population reaches carrying capacity ´ Carrying capacity – the maximum # of individuals of a particular species that a particular environment can support Logistic Growth Curve **Carrying capacity is species specific, environment-specific, and can change over time Limiting Factors ´ Any factor that controls the growth of a population ´ Determine the carrying capacity of an environment for a species ´ Two kinds: ´ Density-independent ´ Density-dependent Density-Dependent Limiting Factors ´ Based on crowding of the population ´ Examples: ´Competition for limited resources, i.e. nesting sites, food, water, hiding places, sunlight, etc. ´Predation, herbivory, human predators ´Parasitism, disease ´ Density-dependent limiting factors produce competition between members of the same species ´More competition = organisms that don’t survive to reproduce ´ The result is logistic growth Density-Independent Factors ´ Factors that impact the size of a population that are unrelated to crowding in a population ´ Ex: Natural disasters & weather related events such as hurricanes, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, floods, etc. ´ In nature, density-dependent and density-independent factors often interact to determine a population’s size ´ Ex: Reindeer in Alaska