* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SECTION 10.3 LECTURE NOTES
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
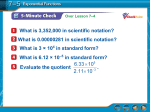
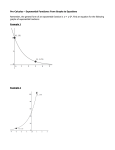
Lecture Notes, Detailed Comments, and Additional Explorations 253 Lecture Notes, Detailed Comments, and Additional Explorations 253 SECTION 10.3 LECTURE NOTES Math098 Lecture (10.3) SECTION 10.3 LECTURE NOTES Objectives 1. Sketch the graph of an exponential function. Objectives 1. the graphical graph of an exponential 2. Sketch Know the significance offunction. a and b for a function of the form f (x) = abx . x 2. significance of athe and b for a function of the form f (x) and = ab 3. Know Know the the graphical base multiplier property, increasing or decreasing property, the. reflection property. 3. Know base multiplier property, the increasing or decreasing property, and the reflection property. 253 Lecture Notes,the Detailed Comments, and Additional Explorations Main point: Graph exponential functions. SECTION 10.3 LECTURE NOTES Main point: Graph exponential functions. OBJECTIVE 1 x OBJECTIVE 1 1. Create a table Objectives of solutions of f (x) = 2 and graph f by hand. ✓ ◆x 1. Create a table solutions f (x) = 2xfunction. and 1 graph f by hand. 1. Sketch theof graph of an of exponential 2. Create a table of solutions of g(x) = 8✓ ◆x and graph g by hand. 12 2. Know the graphical significance b forgraph a function of the form f (x) = abx . 2. Create a table of solutions of g(x) =of 8 a and and g by hand. Use a graphing calculator to verify your graphs2in Problems 1 and 2. 3. Know the base multiplier property, the increasing or decreasing property, and the✓reflection property. ◆x Use a graphing calculator to verify your graphs in Problems 1 and 2. 1 OBJECTIVES 2 and 3 Refer to your tables of solutions of f (x) = 2x and g(x) = 8✓ ◆ to motivate the x 12 x base Main multiplier property. OBJECTIVES 2 and 3 Refer to your tables of solutions of f (x) = 2 and g(x) = 8 to motivate the point: Graph exponential functions. 2 base multiplier property. OBJECTIVE 1 Base Multiplier Property Multiplier 1. Create a table of solutions of f (x) =Base 2x and graph f Property by hand. For an exponential function of the form y = abx , if the value of the independent variable increases by 1, the ✓ ◆ x value of the dependent variable variable is multiplied b. 1 x theby For exponential function of the form= y= value gofby thehand. independent variable increases by 1, the 2. an Create a table of solutions of g(x) 8 ab , ifand graph 2 value of the dependent variable variable is multiplied by b. Describe the base multiplier property as applied to the given function. Use a graphing calculator to verify your graphs in Problems 1 and 2. 3. given function. ✓ 2 ◆x Describe base x multiplier property as applied to the f (x) =the 5(4) ✓ ◆x 4. g(x) = 7✓ ◆ 3= x2x and g(x) = 8 1 to motivate the x 2 and 3 Refer to your tables of solutions of f (x)2 OBJECTIVES 3. f (x) = 5(4) 2 4. g(x) = 7 3 base multiplier Use the base OBJECTIVE 2property. multiplier and 3 property to explain the following connections: Use the base property to explain • f (x) = 2xmultiplier is an increasing function and the b =following 2 > 1 (seeconnections: Problem 1). Base Multiplier Property ✓ ◆x x • f (x) = 2 is 1 an increasing function and b = 2 > 1 (see Problem 1). • g(x) = 8✓ ◆ is a decreasing function and xb = <value 1 (see 2). For an exponential of Problem the independent variable increases by 1, the 2 x function of the form y = ab , if the 2 1 1 value of the dependent variable variable is multiplied by b. • g(x) = 8 is a decreasing function and b = < 1 (see Problem 2). 2 2 Increasing or Decreasing Property x Describe the base multiplier property as applied to the given function. 1 fIncreasing ( x) = 6 ⎛⎜ ⎞⎟ or Decreasing Property x ✓ ◆x = ab , xwhere a > 0. Then ⎝ 2 ⎠ Let 3. ff (x) (x) Consider 2 = 5(4) the function, 4. g(x) = 7 x Let f• (x) 3 , where > 0. Then If b=>ab 1, then theafunction f is increasing. We say the function grows exponentially. By the base multiplier property, as the value of x increases by 1, the value of y is multiplied by one half. Values are ••in If > then function f to is increasing. say function growsdecays exponentially. If <t1, b< 1,bthe then the function f is decreasing. Wethe say the function exponentially. Use the base multiplier property explain the We following connections: shown tb0he able elow. If 0 = < 2bx<is1,anthen the function f isand decreasing. sayProblem the function • •f (x) increasing function b = 2 > We 1 (see 1). decays exponentially. Draw graphs to illustrate this property. ✓ ◆x 1 1 Draw graphs this property. • g(x) = 8 to illustrate is a decreasing function and b = < 1 (see Problem 2). 2 2 c 2015 Copyright Pearson Education, Increasing or Decreasing PropertyInc. c 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. Let f (x) = ab x , where a > 0. Copyright Then • If b > 1, then the function f is increasing. We say the function grows exponentially. • If 0 < b < 1, then the function f is decreasing. We say the function decays exponentially. Draw graphs to illustrate this property. BasexMultiplier Property For anan exponential function ofof thethe form y y==abab ,xif, if thethe value ofof thethe independent variable increases For exponential function form value independent variable increasesbyby1,1,thethe value of the dependent variable variable is multiplied by b. value the dependent variable variable multiplied b. of the independent variable increases by 1, the For anofexponential function of the form yis= abx , if thebyvalue value of the dependent variable variable is multiplied by b. Describe thethe base multiplier property asas applied toto thethe given function. Describe base multiplier property applied given function. ✓✓◆x◆ Describe the xbase multiplier property as applied to the given function. 22 x x 3. 3.f (x) = 5(4) f (x) = 5(4) 4.4.g(x) g(x)==7 7 ✓ 3 32 ◆x 3. f (x) = 5(4)x 4. g(x) = 7 3 Use the base multiplier property to explain the following connections: Use the base multiplier property to explain the following connections: the base property to explain the followingProblem connections: x multiplier • •Use f (x) == 2x2is anan increasing function and b= 1).1). f (x) is increasing function and b =2 2>>1 (see 1 (see Problem ✓ ◆ x x • f (x) = 2✓ x increasing function and b = 2 > 1 1is◆an 1 11 (see Problem 1). • •g(x) = 8 is a decreasing function and b= < 1 (see Problem 2). ◆ g(x) = 8 ✓ is a decreasing function and b = x 2 21 2 21 < 1 (see Problem 2). • g(x) = 8 is a decreasing function and b = < 1 (see Problem 2). 2 2 Increasing oror Decreasing Property Increasing Decreasing Property Increasing or Decreasing Property x x Let f (x) == abab , where a a>>0.0.Then Let f (x) , where Then x Let =1,abthen , where a > 0. fThen • •fIf(x) b> thethe function increasing. say thethe function grows If b> 1, then function fis is increasing.We We say function growsexponentially. exponentially. • If b > 1, then the function f is increasing. We say the function grows exponentially. • •If If 0< b< 1, 1, then thethe function f fis is decreasing. say thethe function 0< b< then function decreasing.We We say functiondecays decaysexponentially. exponentially. • If 0 < b < 1, then the function f is decreasing. We say the function decays exponentially. Draw graphs toto illustrate this property. Draw graphs illustrate this property. 254 CHAPTER LectureNotes, Notes,Detailed DetailedComments, Comments,and andAdditional AdditionalExplorations Explorations 254 CHAPTER 2 2 Lecture Draw graphs to illustrate this property. 254 CHAPTER 2 Lecture x Notes, Detailed Comments, and Additional Explorations x Notes, Substitute0 0for forxxininthe theCHAPTER generalequation equation show thefollowing following property. 254Substitute 2 Lecture Detailed Comments, and Additional Explorations general y y==abab totoshow the property. c 2015 Copyright Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2015 Pearson Inc. Substitute 0 for x in the general equationcy of = abxExponential to showEducation, the following y-Intercept an Function property. x Exponential Function y-Intercept of an Substitute 0 for x in the general Copyright equation y c= 2015 ab toPearson show the followingInc. property. Education, Forananexponential exponentialfunction functionofofthe theform form y-Intercept of an Exponential Function For y-Intercept of an Exponential Function x x, y y==abab , Fory-intercept an exponential function of the form the (0, a). the y-intercept isis(0, a). For an exponential function of the form y = abx , y = abx , the the y-intercept is (0, Find they-intercept y-intercept ofa). thegraph graphofofthe thefunction. function. Find of the the y-intercept is (0, a). ✓✓ 2◆x◆x x x y==8(5) 8(5) 2 the y-intercept of the graph of the function. 5.5.yFind 6.6.y y== 4 4 7 Find the y-intercept of the graph of the function. 7✓ ◆x 5. y = 8(5)x ✓ ◆2xx 6. y = 4 Warning: x 2 xb is (0, 1), not (0, b). They-intercept y-interceptofofthe thegraph graphofofa afunction functionofofthe the formy y== 5.Warning: y = 8(5) The 6. yform = 4 b 7 is (0, 1), not (0, b). Warning: The y-intercept of the graph of a function of the form y = b7x is (0, 1), not (0, b). xbase multiplier property to Find they-intercept y-intercept thegraph graph ofthe thegiven function. Then use thebbase graphthe the Warning: The y-intercept of theofgraph ofgiven a function of Then the form ythe = is (0, 1), not property (0, b). to graph Find the ofofthe function. use multiplier x Warning: The y-intercept of the graph of a function of the form y = b is (0, 1), not (0, b). function hand. function bybyhand. Find the y-intercept of the graph of the given function. Then use ◆base multiplier property to graph the ✓✓the xx 1◆base xx the= y-intercept of the graph of the given function. Then use the multiplier property to graph the 7.f f(x) (x) 2(3) 1 function by= hand. 7.Find 2(3) g(x)==1212 8.8.g(x) function by hand. 3✓3 ◆x 7. f (x) = 2(3)x ✓ ◆1x 8. g(x) = 12 x x x x1x 7. f (x) = 2(3) Sketchand andcompare comparethe thegraphs graphsofoff f(x) (x)== 4(2) 4(2) and andg(x) g(x)= 9.9.Sketch 8. g(x) ==4(2) 124(2). 3. 3 x 9. Sketch and compare the graphs of f (x) = 4(2) and g(x) = 4(2)x . 9. Sketch and compare the graphs of f (x)Reflection = 4(2)x Property and g(x) = 4(2)x . Reflection Property x x x and g(x) = ab Thegraphs graphsofoff f(x) (x)== abab arereflections reflections eachother otheracross acrossthe thex-axis. x-axis. Reflection Property The and g(x) = abx are ofofeach Reflection Property The graphs of f (x) = abx and g(x) = abx are reflections of each other across the x-axis. Graph thefunction function hand. Graph the byby hand. The graphs of f (x) = abx and g(x) = abx are reflections of each other across the x-axis. ✓✓ ◆x◆x xx 1 1 10. f (x) = 3(4) 10. fGraph (x) =the3(4) function by hand. 11.g(x) g(x)== 1616 11. Graph the function by hand. 4✓4 ◆x x 10. f (x) = 3(4) ✓ ◆1x 11. g(x) 16 x x where a > 0 and do the x and Discuss domain andrange rangeofofananexponential exponentialfunction function the= form (x) Discuss ofofthe form f1f(x) a > 0 and do the 10. f (x) the =thedomain 3(4) 4 ==abab where 11. g(x) = 16 samewhere wherea a<<0.0. same 4 Discuss the domain and range of an exponential function of the form f (x) = abx where a > 0 and do the same Find Discuss Find where the domain the domain a domain < 0. and and range range range of of the the function. an exponential a > 0 and do the function. and of function of the form f (x) = abx where the same where a < 0. ✓✓ ◆x◆x xx 11 12.fFind f(x) (x)= =3(2) 3(2) 12. the domain and range of the function. 13.g(x) g(x)== 1010 13. 22 Find the domain and range of the function. For an exponential function of the form 9. Sketch and compare the graphs of f (x) = the y-intercept is (0, a). 3 y = abx , 4(2)x and g(x) = 4(2)x . Reflection Property Find the y-intercept of the graph of the function. ✓ ◆x 2 across the x-axis. abx and g(x) = abx are reflections of each other 6. y = 4 7 Graph the function by hand. Warning: The y-intercept of the graph of a function of the form y = bx is (0, 1), not (0, b). ✓ ◆x 1 10. f (x) = 3(4)x 11. g(x) = 16 Find the y-intercept of the graph of the given function. Then use the 4 base multiplier property to graph the function by hand. x For all eDiscuss xponential functions, the xof -‐axis is a horizontal asymptote. the domain and range an exponential function of the form ✓ f (x) = ab where a > 0 and do the ◆x x 1 f (x)where = 2(3) a < 0. 7. same 8. g(x) = 12 3 Find the domain and range of the function. x 9. Sketch and compare the graphs of f (x) = 4(2)x and g(x) = 4(2) ✓ ◆x. x 1 12. f (x) = 3(2) 13. g(x) = 10 2 Reflection Property x of f (x) = graphs 5. y The = 8(5) SHORTofHW 5, 11, 15, x21, 27, 29, 33, 37, x41, 45, 47, 63, 71, 77, 85 The graphs f (x) = ab and g(x) = ab are reflections of each other across the x-axis. MEDIUM HW 1, 5, 11, 15, 17, 21, 23, 27, 29, 33, 37, 41, 45, 47, 61, 63, 71, 75, 77, 85, 87, 99, 101, 103 Graph the function by hand. ✓ ◆x x 1 10. f (x) = 3(4) The domain of any exponential function f(x) = abx is t11. he sg(x) et of = real 16 numbers. 4 The range of an exponential function f(x) = abx is the set of all positive real numbers if a > 0, and the range is the set of all negative real and numbers f an exponential function of the form f (x) = abx where a > 0 and do the Discuss the domain range iof a < 0where . same a < 0. Find the domain and range of the function. Copyright c 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. ✓ ◆x 1 12. f (x) = 3(2)x 13. g(x) = 10 2 SHORT HW 5, 11, 15, 21, 27, 29, 33, 37, 41, 45, 47, 63, 71, 77, 85 MEDIUM HW 1, 5, 11, 15, 17, 21, 23, 27, 29, 33, 37, 41, 45, 47, 61, 63, 71, 75, 77, 85, 87, 99, 101, 103 The graph of an exponential function f is shown below. Copyright c 2015 Pearson Education, Inc. 1. Find f(2). Ans: f(2) = 8 2. Find x when f(x) = 2. Ans: x = –2 when f(x) = 2. 3. Find x when f(x) = 0. Ans: there is no value of x where f(x) = 0. Because the graph of an exponential functions gets close to, but never reaches, the x-‐axis. <Homework 10.3> 𝒇 𝒙 = 𝟐𝒙 + 𝟑𝒙 #51. Find 𝑓(2) #52. Find 𝑓(0) #53. Find 𝑓(−2) #54. Find 𝑓(−1) 𝒇 𝒙 = 𝟑𝒙 #55. Find x when 𝑓 𝑥 = 3. #56. Find x when 𝑓 𝑥 = 9. #57. Find x when 𝑓 𝑥 = 1. 1 #58. Find x when 𝑓 𝑥 = 3. #75. Use an equation of the form 𝑓 𝑥 = 𝑎𝑏 ! , where a and b are constants you specify. What equation works?