* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PRACTICE EXAM 1 for Midterm 1
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Negative mass wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
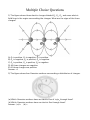
PRACTICE EXAM 1 for Midterm 1 solutions Multiple Choice Questions 1) The figure shows three electric charges labeled Q1, Q2, Q3, and some electric field lines in the region surrounding the charges. What are the signs of the three charges? A) Q1 is positive, Q2 is negative, Q3 is positive. B) Q1 is negative, Q2 is positive, Q3 is negative. C) Q1 is positive, Q2 is positive, Q3 is negative. D) All three charges are negative. E) All three charges are positive. Answer: A 2) The figure shows four Gaussian surfaces surrounding a distribtuion of charges. (a) Which Gaussian surfaces have an electric flux of +q/ε0 through them? (b) Which Gaussian surfaces have no electric flux through them? Answer: (a) b (b) c 3) Under electrostatic conditions, the electric field just outside the surface of any charged conductor A) is always parallel to the surface. B) is always zero because the electric field is zero inside conductors. C) is always perpendicular to the surface of the conductor. D) is perpendicular to the surface of the conductor only if it is a sphere, a cylinder, or a flat sheet. E) can have nonzero components perpendicular to and parallel to the surface of the conductor. Answer: C 4) Suppose you have two point charges of opposite sign. As you move them farther and farther apart, the potential energy of this system relative to infinity A) increases. B) decreases. C) stays the same. Answer: A 5) A negative charge is moved from point A to point B along an equipotential surface. Which of the following statements must be true for this case? A) The negative charge performs work in moving from point A to point B. B) Work is required to move the negative charge from point A to point B. C) No work is required to move the negative charge from point A to point B. D) The work done on the charge depends on the distance between A and B. E) Work is done in moving the negative charge from point A to point B. Answer: C 6) A conducting sphere contains positive charge distributed uniformly over its surface. Which statements about the potential due to this sphere are true? All potentials are measured relative to infinity. (There may be more than one correct choice.) A) The potential is lowest, but not zero, at the center of the sphere. B) The potential at the center of the sphere is zero. C) The potential at the center of the sphere is the same as the potential at the surface. D) The potential at the surface is higher than the potential at the center. E) The potential at the center is the same as the potential at infinity. Answer: C 7) The charge on the square plates of a parallel-plate capacitor is Q. The potential across the plates is maintained with constant voltage by a battery as they are pulled apart to twice their original separation, which is small compared to the dimensions of the plates. The amount of charge on the plates is now equal to A) 4Q. B) 2Q. C) Q. D) Q/2. E) Q/4. Answer: D 8) An ideal air-filled parallel-plate capacitor has round plates and carries a fixed amount of equal but opposite charge on its plates. All the geometric parameters of the capacitor (plate diameter and plate separation) are now DOUBLED. If the original energy stored in the capacitor was U0, how much energy does it now store? A) 4U0 B) 2U0 C) U0 D) U0/2 E) U0/4 Answer: D 9) Two cables of the same length are made of the same material, except that one cable has twice the diameter of the other cable. When the same potential difference is maintained across both cables, which of the following statements are true? (There may be more than one correct choice.) A) The same current flows through both cables. B) Both cables carry the same current density. C) The electrons have the same drift velocity in both cables. D) The current in the thin cable is twice as great as the current in the thick cable. E) The current in the thin cable is four times as great as the current in the thick cable. Answer: B, C 10) A narrow copper wire of length L and radius b is attached to a wide copper wire of length L and radius 2b, forming one long wire of length 2L. This long wire is attached to a battery, and a current is flowing through it. If the electric field in the narrow wire is E, the electric field in the wide wire is A) E. B) 2E. C) 4E. D) E/2. E) E/4. Answer: E PROBLEM A The capacitive network shown in the figure is assembled with initially uncharged capacitors. A potential difference, Vab = +100V, is applied across the network. The switch S in the network is initially open but is then closed. Assume that all the capacitances shown are accurate to two significant figures. What is the equivalent capacitance between ab (a) with the switch S open? (b) with the switch S closed? and what is potential difference Vcd across the switch S (c) when S is open? (d) when S is closed? Answer: (a) 14 µF (b) 17 µF (c) 40V (d) 0 V