* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download History of American Political Parties
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
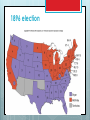
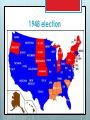
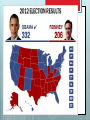
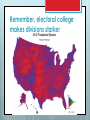
History of American Political Parties 1791-2014 FEDERALIST PAPER #10 ABRIDGED The Same Subject Continued The Union as a Safeguard Against Domestic Faction and Insurrection From the New York Packet. Friday, November 23, 1787. [written by James Madison] To the People of the State of New York: AMONG the numerous advantages promised by a well constructed Union, none deserves to be more accurately developed than its tendency to break and control the violence of faction…... The instability, injustice, and confusion introduced into the public councils, have, in truth, been the mortal diseases under which popular governments have everywhere perished . . . Thomas Jefferson and Providential Detection Political Parties NOT in the Constitution WHY? By a faction, I understand a number of citizens, whether amounting to a majority or a minority of the whole, who are united and actuated by some common impulse of passion, or of interest, adversed to the rights of other citizens, or to the permanent and aggregate interests of the community. . . . . The latent causes of faction are thus sown in the nature of man. . . . It is in vain to say that enlightened statesmen will be able to adjust these clashing interests, and render them all subservient to the public good. Enlightened statesmen will not always be at the helm. . . . The influence of factious leaders may kindle a flame within their particular States, but will be unable to spread a general conflagration through the other States. ….. A rage for paper money, for an abolition of debts, for an equal division of property, or for any other improper or wicked project, will be less apt to pervade the whole body of the Union than a particular member of it… 1796 Washington's Farewell Address The alternate domination of one faction over another, sharpened by the spirit of revenge, natural to party dissension, which in different ages and countries has perpetrated the most horrid enormities, is itself a frightful despotism. But this leads at length to a more formal and permanent despotism. … and sooner or later the chief of some prevailing faction, more able or more fortunate than his competitors, turns this disposition to the purposes of his own elevation, on the ruins of public liberty. Political parties developed immediately, however RED BLUE Business Owners Workers First Two-Party System Federalists v. Democratic- Republicans, 1780s - 1815 MAJOR ISSUE: strength of the national government Democratic-Republicans Emphasized states' rights. "Strict" interpretation of the Constitution. Preference for agriculture and rural life. Democratic- Republicans Strength in South and West. Foreign policy sympathized with French Revolution. Stressed civil liberties and trust in the people Thomas Jefferson born to wealth, champion of the common man “I have sworn upon the altar of God eternal hostility against every form of tyranny over the mind of man.” Thomas Jefferson Thos. Jefferson on Shay’s Rebellion >"I hold it that a little rebellion now and then is a good thing, and as necessary in the political world as storms in the physical. Unsuccessful rebellions, indeed, generally establish the encroachments on the rights of the people which have produced them. An observation of this truth should render honest republican governors so mild in their punishment of rebellions as not to discourage them too much. It is a medicine necessary for the sound health of the government." Patrick Henry Is life so dear or peace so sweet as to be purchased at the price of chains and slavery? Forbid it, Almighty God! I know not what course others may take, but as for me, give me liberty, or give me death! Federalists Favored strong central government. "Loose" interpretation of the Constitution. Encouragement of commerce and manufacturing. Federalists Strongest Favored in Northeast. close ties with Britain. Emphasized stability order and Alexander Hamilton bastard son of a barmaid in Barbados: champion of the rich In the general course of human nature, A power over a man's subsistence amounts to a power over his will. John Jay diplomat, 1st Chief Justice Those who own the country ought to govern it. Alexander Hamilton’s Financial Plan 1st Sec’y of the Treasury under George Washington "All communities divide themselves into the few and many. . the The first are the rich and the well-born; the other the mass of the people ... turbulent and changing, they seldom judge or determine right. Give therefore to the first class a distinct, permanent share in the Government ... Nothing but a permanent body can check the imprudence of democracy." Interpretation of the Constitution Elastic clause: The Congress shall have the power… To make all laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into Execution the foregoing Powers, and all other powers vested by this Constitution … Article I section 8 clause 18 “Loose” interpretation of the Elastic clause—doing things not delegated to the national government Federalists Creating the first national bank Democratic-Republicans Louisiana Purchase Era of good feelings 1815-1836 Second Two-Party System Whigs v. Democrats, 1836 – 1850 Major Issue: Infrastructure (sectionalism) Whigs 1.Wanted to use federal and state government to promote economic growth, especially transportation, protective tariffs and banks 2.Advocated reforms such as temperance and public schools, and prison reform. 3.Favored gradual territorial expansion over time and opposed the Mexican War. 4.Northerners, city dwellers, entrepreneurs DEMOCRATS 1.Opposed banks and corporations as state-legislated economic privilege. 2.Opposed state-legislated reforms and preferred individual freedom of choice, including the right to own slaves. 3. Supported the Mexican War. 4. Southerners and Westerners. Democrats First organized political party, with conventions and “bosses” who ran the party between elections. Created by Andrew Jackson and Martin van Buren Party Symbols – Jackson and his party was called “jackass”, or donkey because they were so stubborn. Mid-19th Century Political Crisis MAJOR ISSUE: SLAVERY Whigs would not take a clear position on this moral issue. Republicans were Anti-slavery Whigs. Abraham Lincoln was a Whig who became a Republican. AFTER CIVIL WAR, Republicans became the Elephant, which never forgets 19TH CENTURY ALIGNMENT Republicans Business Professionals (college) Nativists Isolationists (against war) For Civil Rights Most AfricanAmericans Democrats organized labor, urban voters immigrants Most Southerners Farmers For World War I Confused on Civil Rights 1896 election FD Roosevelt REALIGNMENT Republicans Business Professionals Farmers Nativists Against reform Anti-communist Isolationists (against World War II) Democrats organized labor, urban voters immigrants Farm laborers African Americans Intellectuals Pro reform Most Southerners More in favor of war 1948 election 1964 Civil Rights Act "We have lost the South for a generation.“ President Johnson Reagan Realignment Republicans Business owners Many working class Nativists Fundamental Christians Mid West South Democrats Union workers Professionals Immigrants African Americans North East West Coast 1992 Election Clinton/Bush Sr. Remember, electoral college makes divisions starker VOTING LAWS Elections are the responsibility of the states and national government. Section 4. Clause 1. The Times, Places and Manner of holding Elections for Senators and Representatives, shall be prescribed in each State by the Legislature thereof; but Congress may at any time make or alter such Regulations, except as to the Place of chusing Senators. MOST rules are made by the states. National Election Day has been the first Tuesday in November since 1845, but not in Constitution. Do convicted felons get to vote? Depends on the state. Voting history 1787– only European American men with property 1830s – European American men by state 1870 – 15th Amendment freed slaves; all men 1920 – 19th Amendment women 1924—Native Americans by Congress 1971 – 26th Amendment 18 year olds Not yet –citizens of territories can not vote at the national level