* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Holt McDougal
Buddhist art wikipedia , lookup
Nirvana (Buddhism) wikipedia , lookup
Early Buddhist schools wikipedia , lookup
Triratna Buddhist Community wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Western philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Greco-Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism in Vietnam wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism in Myanmar wikipedia , lookup
Dalit Buddhist movement wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Women in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Enlightenment in Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Silk Road transmission of Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
History of Buddhism in India wikipedia , lookup
Pre-sectarian Buddhism wikipedia , lookup
Decline of Buddhism in the Indian subcontinent wikipedia , lookup
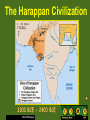
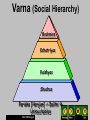
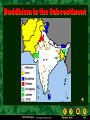
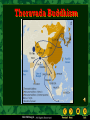
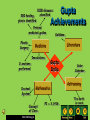
Ancient India Holt McDougal, Map of India Holt McDougal, Geography and Early India The Big Idea Indian civilization first developed on the Indus River. Main Ideas • The geography of India includes high mountains, great rivers, and heavy seasonal rain. • Harappan civilization developed along the Indus River. • The Aryan invasion of India changed the region’s civilization. Holt McDougal, Indian Geography Mountains • North: The Himalayas are the highest mountains in the world. • West: The Hindu Kush provide protection from enemies. Plains and Plateaus • Rivers and melting snow kept the plains fertile. • Both sides of the river thrived. Holt McDougal, Water • Monsoons • Heavy rainfall • Civilizations arose around seasonal rainfall. The Harappan Civilization 3300 BCE - 2400 BCE Holt McDougal, Harappan Civilization People Cities • Population grew in the Indus River Valley. • Harrapa • Growth came as irrigation and farming techniques improved. • Fortresses for defense against enemies • Mohenjo Daro • Well-planned public areas • Cities were built as surplus food was produced. Holt McDougal, Achievements • Wells and indoor plumbing • Pottery, cotton clothing, jewelry • India’s first writing system Citadel Of MohenjoDaro Holt McDougal, Aerial View of Mohenjo-Daro Holt McDougal, Wide View, Mohenjo-Daro Holt McDougal, The Great Bath, Mohenjo-Daro Holt McDougal, Bath Area, Mohenjo-Daro Holt McDougal, Well, Mohenjo-Daro Holt McDougal, Granery, Mohenjo-Daro Holt McDougal, pottery, Mohenjo-Daro Holt McDougal, Bison Seal, Mohenjo-Daro Holt McDougal, A Horned-God Seal, Mohenjo-Daro Holt McDougal, A Male Head, MohenjoDaro Dravidian Holt McDougal, A Priest-King, Mohenjo-Daro Holt McDougal, Necklace, Mohenjo-Daro Holt McDougal, Public Well, Harappa Holt McDougal, Drain, Harappa Holt McDougal, Unicorn Seal, Harappa Holt McDougal, Female Figures, Harappa Holt McDougal, Bull Figurine, Harappa Holt McDougal, Elephant Figurine, Harappa Holt McDougal, Burial Pottery, Harappa Holt McDougal, Male Skeleton, Harappa Holt McDougal, Female Skeleton with Child, Harappa Holt McDougal, Harappan Writing Undecipherable to date. Holt McDougal, Holt McDougal, Aryan Migration pastoral depended on their cattle. warriors horse-drawn chariots. Holt McDougal, Aryan Invasion Invaders from the West When the Harappan civilization dissipated in 1700 BC, Central Asians called Aryans began taking over territory. Religion The Aryans left behind vast collections of poems, hymns, myths, and rituals. They also had religious writings known as Vedas. Government No central government: small communities ruled by rajas Language Sanskrit is the root of many modern South Asian languages. Holt McDougal, Summary Harappan Civilization • Two major cities: Harappa, Mohenjo Daro • Advanced civilization that thrived between 2300 and 1700 BC • Culture, artistry, city planning Aryan Invasion • South Asian warriors pushed through the Hindu Kush mountains and settled in the Indus Valley • Oral tradition in religion and mythology resulted in the most important language of ancient India: Sanskrit. Holt McDougal, Sanskrit writing Holt McDougal, The Vedas 1200 BCE-600 BCE. written in SANSKRIT. Hindu core of beliefs: hymns and poems. religious prayers. Rig Veda oldest work. Holt McDougal, magical spells. lists of the gods and goddesses. Varna (Social Hierarchy) Brahmins Kshatriyas Vaishyas Shudras Pariahs [Harijan] -> Dalits Untouchables Holt McDougal, The Vedic Age The foundations for Hinduism were established! Holt McDougal, Origins of Hinduism The Big Idea Hinduism, the largest religion in India today, developed out of ancient Indian beliefs and practices. Main Ideas • Indian society divided into distinct groups under the Aryans. • The Aryans practiced a religion known as Brahmanism. • Hinduism developed out of Brahmanism and influences from other cultures. • The Jains reacted to Hinduism by breaking away to form their own religion. Holt McDougal, Indian Society Divides Varnas Social divisions in Aryan society Brahmins Priests Kshatriyas Rulers and warriors Vaisyas Farmers, craftspeople, and traders Sudras Laborers and non-Aryans Holt McDougal, Caste System Individuals • Place in society based on birth, wealth, or occupation • 3,000 castes once existed in India. • Individuals could rarely change castes. Holt McDougal, Caste Rules • Sutras (guides) listed all the rules for the caste system. • Breaking rules resulted in a transfer to a lower class. The Caste System WHO IS… Brahmins Kshatriyas The mouth? The arms? Vaishyas The legs? The feet? Shudras Holt McDougal, Brahmanism develops into Hinduism Brahmanism • Aryan priests were called Brahmins. • Wrote Vedic texts, which were their thoughts about the Vedas Evolving Beliefs The Vedas, Upanishads, and other Vedic texts began blending with beliefs from different cultures, creating Hinduism. Holt McDougal, Hinduism • Many gods • Reincarnation: could be reborn into new forms and castes • Men and women could both gain salvation, but women were inferior. Hinduism • Also known as The Sanatana Dharma • Hinduism is a way of life, not a religion. • Third most popular religion • Believe in one God reincarnated into different forms • Follow The Vedas Holt McDougal, Hinduism • A Hindu’s goal is to become free from continuous reincarnations. • Three ways to end the cycle of reincarnation 1. Be devoted to any of the Hindu God or Goddesses 2. Mediation. Acknowledge life as an illusion and realize that Brahman is the only real thing 3. Dedicate oneself to various religious ceremonies Holt McDougal, The Vedas • Religious text also called Shruti • Arranged into four parts 1. 2. 3. 4. The The The The Samhitas Brahmanas Aranyakas Upanishads Holt McDougal, Gods Hindus believe in only one God, Brahman, but they worship other reincarnations of Brahman. There are 300,000 different reincarnations of Brahman. Three Majors Gods Three Major Goddess • Brahma (Creator) • Vishnu (Preserver) • Shiva (Destroyer) Holt McDougal, • Saraswati (Knowledge) • Lakshmi (Wealth) • Parvati or Shakti (Power) Shiva Holt McDougal, Vishnu Hindu Gods Holt McDougal, Hindu Gods Holt McDougal, Jains React to Hinduism Origins of Jainism • 599 BC, established as an alternative to Hindu ritualism • Based on the teachings of Mahavira, who abandoned his life of luxury to become a monk Four Principles of Jainism • Injure no life. • Tell the truth. • Do not steal. • Own no property. Holt McDougal, Origins of Buddhism The Big Idea Buddhism began in India and became a major religion. Main Ideas • Siddhartha Gautama searched for wisdom in many ways. • The teachings of Buddhism deal with finding peace. • Buddhism spread far from where it began in India. Holt McDougal, Siddhartha Gautama Quest for Answers Enlightenment • Siddhartha was born a prince, but he questioned the meaning of life. • Found it under the Tree of Wisdom while meditating • Determined to find answers using: • Meditation • Fasting • Learning from different teachers Holt McDougal, • Called the Buddha (Enlightened One) • Spent the rest of his life traveling and teaching his ideas Teachings of Buddhism Four Noble Truths 1. Suffering and unhappiness are a part of human life. No one can escape sorrow. 2. Suffering comes from our desires for pleasure and material goods. 3. People can overcome desire and ignorance and reach nirvana, a state of perfect peace. People can overcome ignorance and desire by following an 4. eightfold path that leads to wisdom, enlightenment, and salvation. Holt McDougal, Challenging Hindu Ideas Ancient Ways • The Buddha taught that following the Vedic texts was unnecessary. • Challenged the authority of Hindu priests Changing Society • A more individualistic approach to enlightenment • Rebirth as a means to evolve Holt McDougal, Caste System • Opposed caste system • The Eightfold Path could lead any individual to nirvana. • The Buddha’s teachings reached all classes. Buddhism began in India and then became a major religion. Buddhism branches out • Asoka, one of the most powerful kings in India, became a Buddhist and spread Buddhism in India and foreign lands. • Buddhist missionaries traveled the world to teach enlightenment. Buddhism splits • Buddhism split into two main sects: Theravada and Mahayana. • Members of the Theravada followed the Buddha’s teachings exactly. • Members of the Mahayana believed that individual interpretation was important. Holt McDougal, Religions of South Asia Holt McDougal, Buddhism in the Subcontinent Holt McDougal, The Essence of Buddhism The “middle way of wisdom and compassion.” 2,500 year old tradition. The 3 jewels of Buddhism: Buddha, the teacher. Dharma, the teachings. Sangha, the community. Holt McDougal, Siddhartha Gautama (563-483 BCE) Born in NE India (Nepal). Raised in great luxury to be a king. At 29 he rejected his luxurious life to seek enlightenment and the source of suffering. Lived a strict, ascetic life for 6 yrs. Rejecting this extreme, sat in meditation, and found nirvana. Became “The Enlightened One,” at 35. Holt McDougal, What is the fundamental cause of all suffering? Desire! Therefore, extinguish the self, don’t obsess about oneself. Holt McDougal, Four Noble Truths 1. There is suffering in the world. To live is to suffer. (Dukkha) The Buddha found this out when he was young and experienced suffering and death in others. Holt McDougal, Four Noble Truths 2. The cause of suffering is selfcentered desire and attachments. (Tanha) Holt McDougal, Four Noble Truths 3. The solution is to eliminate desire and attachments. (Nirvana = “extinction”) Holt McDougal, Four Noble Truths 4. To reach nirvana, one must follow the Eightfold Path. Holt McDougal, Eightfold Path Nirvana The union with the ultimate spiritual reality. Escape from the cycle of rebirth. Holt McDougal, Buddhist Altar Holt McDougal, Types of Buddhism Therevada Buddhism (traditional type) Mahayana Buddhism (modern type) Tibetan Buddhism Zen Buddhism Holt McDougal, Theravada Buddhism The oldest school of Buddhism. The “Way of the Elders” or the “Small Vehicle.” Found in southern Asia. The monastic life is the best way to achieve nirvana. Focus on wisdom and meditation. Goal is to become a “Buddha,” or “Enlightened One.” Over 100,000,000 followers today. Holt McDougal, Theravada Buddhism Holt McDougal, Mahayana Buddhism The “Great Vehicle.” Founded in northern Asia (China, Japan). Buddhism “for the masses.” Seek guidance from Boddhisatvas, wise beings. Goal: Not just individual escape from the wheel, but the salvation of all humanity through self-sacrifice of those enlightened few. Holt McDougal, Mahayana Buddhism Holt McDougal, Boddhisatva Holt McDougal, Tibetan Buddhism The “Diamond Vehicle.” [Vajrayana] Developed in Tibet in the 7c CE. A mix of Theravada and Mahayana. Boddhisatvas include Lamas, like the Dalai Lama. The Tibetan Book of the Dead [Bardo Thodol]. Holt McDougal, The Dalai Lama Holt McDougal, Zen Buddhism The “Meditation School.” Seeks sudden enlightenment [satori] through meditation, arriving at emptiness [sunyata]. Use of meditation masters [Roshi]. Beauty, art, and aesthetics: Gardens. Archery. Tea ceremony. Calligraphy. Holt McDougal, Buddhism in America Holt McDougal, Relieve Stress & Meditate: Get a Mantra ! Ohm...mani...padme...hung... Hail to the jewel in the lotus! Holt McDougal, Indian Empires The Big Idea The Mauryas and the Guptas built great empires in India. Main Ideas • The Mauryan Empire unified most of India. • Gupta rulers promoted Hinduism in their empire. Holt McDougal, Mauryan Rule Candragupta Maurya Asoka (304 – 232 BCE) (321 BCE-298 BCE) • The grandson of Candragupt extended Mauryan rule over most of India. • Candragupta seized control of northern India and created a society dominated by war. • Candragupta became a Jainist monk and gave up his throne. Holt McDougal, • Asoka converted to Buddhism and stopped waging war, choosing instead to rebuild cities and spread Buddhist teachings. Asoka’s law code Edicts scattered in more than 30 places in India, Nepal, Pakistan, & Afghanistan. Written mostly in Sanskrit, but one was in Greek and Aramaic. 10 rock edicts. Each pillar [stupa] is 40’-50’ high. Buddhist principles dominate his laws. Holt McDougal, The Mauryan Empire 321 BCE – 185 BCE Holt McDougal, Turmoil & a power Vacuum: 220 BCE – 320 CE The Maurya Empire is divided into many kingdoms. Holt McDougal, Gupta Empire • After the decline of the Mauryan Empire, India remained primarily Buddhist for 500 years. • Under the rule of Candra Gupta I, India became unified and prosperous again. • Gupta rulers spread Hinduism in their empire through the building of temples and the promotion of Hindu writings and rituals. • Widespread religious tolerance was encouraged for Buddhists and Jainists. Holt McDougal, Gupta Rulers Chandra Gupta I r. 320 – 335 CE “Great King of Kings” Chandra Gupta II r. 375 - 415 CE Profitable trade with the Mediterranean world! Hindu revival. Huns invade – 450 CE Holt McDougal, Candra Gupta II Growth Under Candra Gupta II, the Gupta Empire reached the height of its power. It spread across northern India and prospered. Economy and Culture The economy boomed, allowing citizens the time and money to create great works of art and literature. The Caste System It was believed that keeping citizens under strict caste rule would stabilize the empire. Social Ramifications Women in the caste system were not seen as equals and had few basic rights. Holt McDougal, Gupta Empire: CE Holt McDougal, 320 CE – 647 Chandra Gupta II Holt McDougal, International Trade Routes during the Guptas Holt McDougal, Extensive Trade: 4c spices gold & ivory Holt McDougal, Kalidasa The greatest of Indian poets. His most famous play was Shakuntala. During the reign of Chandra Gupta II. Holt McDougal, Gupta Art Greatly influenced Southeast Asian art & architecture. Holt McDougal, 500 healing plants identified Printed medicinal guides Plastic Surgery Gupta Achievements 1000 diseases classified Kalidasa Literature Medicine Inoculations Gupta India C-sections performed Decimal System Mathematics Concept of Zero Holt McDougal, PI = 3.1416 Solar Calendar Astronomy The earth is round The Decline of the Guptas Invasion of the White Huns in the 4c signaled the end of the Gupta Golden Age, even though at first, the Guptas defeated them. After the decline of the Gupta empire, north India broke into a number of separate Hindu kingdoms and was not really unified again until the coming of the Muslims in the 7c. QUESTION: Is the best literature and art written as the civilization is on the rise, at its height, or in its decline? Holt McDougal, Time Line • 320 BC Candragupta Maurya becomes the first Mauryan emperor. • 301 BC Candragupta Maurya relinquishes the throne to become a Jainist monk. • 270 BC Asoka becomes the second Mauryan emperor. • 261 BC Asoka’s empire gains great power, and he leaves to become a Buddhist. • AD 375 Candra Gupta I invades and conquers northern India and brings Hinduism, prosperity, and a strict caste system back into popular culture. Holt McDougal, Indian Achievements The Big Idea The people of ancient India made great contributions to the arts and sciences. Main Ideas • Indian artists created great works of religious art. • Sanskrit literature flourished during the Gupta period. • The Indians made scientific advances in metalworking, medicine, and other sciences. Holt McDougal, Religious Art: Temples • Both Hindu and Buddhist temples began flourishing under Gupta rule. • Once simply constructed meeting places, Hindu temples became complex towers covered with intricate carvings. • Buddhist temples were large and impressive, some carved out of mountainsides. Most famous Buddhist cave temple is located at Ajanta. • Buddhist stupas were built to house sacred objects from the life of the Buddha. They were covered with detailed carvings. Holt McDougal, The Taj Mahal Holt McDougal, Religious Art: Paintings and Sculpture • Great artists were commissioned by rich and powerful members of society. • Paintings offered a perspective on the daily life and religious belief of the ancient Indians; many of these paintings could be found on the walls of temples. • Indian sculptors carved columns, statues, and entire temples in the likenesses of the Buddha and Hindu gods. Holt McDougal, Sanskrit Literature Mahabharata Ramayana • One of the world’s longest literary works • The story of a god, Vishnu, who has taken human form • The story of two Indian families struggling for control of a kingdom • Written long after the Mahabharata; contains models for the ideal ruler (Rama) and the ideal mate (Sita) • Many long passages of Hindu beliefs and practices Holt McDougal, Sanskrit Literature Other Works • Chadra Gupta II hired a famous writer named Kalidasa to write plays for the royal court. • The Panchatantra, a book of stories intended to teach moral lessons and quick thinking, was translated into many languages. Holt McDougal, Scientific Advances Metalworking Pioneers of metallurgy, the Indians created tools and weapons by mixing iron and other metals together. Mathematics The Indians invented the concept of zero and developed a sophisticated number system, the Hindu-Arabic numerals. Medicine Using plants and minerals, Indian doctors made advances in medicinal science. They were among the first to practice inoculation and perform surgery. Astronomy Indian astronomers knew of seven about the nine planets in the solar system and could predict eclipses of the sun and moon. Holt McDougal,