* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download World War II
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Greater East Asia Co-Prosperity Sphere wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Appeasement wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
End of World War II in Europe wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Home front during World War II wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
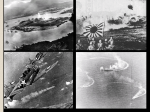
World War II Vocabulary • Appeasement – A policy where you meet the demands of an aggressor in order to preserve peace. • Aggression – A policy that means you launch attacks on other countries. • Dictator – A person that has total control over the people VOCABULARY • Fascism – A form of government that stresses the nation above the individual. • Genocide – The deliberate destruction of a group of people. • Propaganda – Planned spread of certain beliefs. Causes of WWIi • There were many causes to WWII. You should begin to notice a pattern within the causes. Many of these causes go back to issues connected with WWI. These unresolved issues or conditions of the Treaty of Versailles bring about WWII. Causes of WWIi • All of the countries were afraid to enforce the Treaty of Versailles. Causes of WWIi • Germany was forced to accept the blame. • This made Germany feel angry, bitter, and to have a lot of resentment toward the other countries, especially those that had defeated them in WWI. Causes of WWIi • Economic Depression around the world. • Germany was hit especially hard because they were also being forced to pay reparations for damages done during WWI. Causes of WWIi • Feelings of Desertion – No Jobs, No food, No Homes, No Businesses Causes of WWIi • Some countries turn to dictators • Dictators promised to change things in the country to improve the lives of the citizens. Causes of WWIi • Nationalism- Many people still experienced pride in their country. Many dictators played to the nationalism and used it to get the public on their side. Nationalism allowed fascist governments to come to power. Causes of WWIi • Militarism – The countries started to gather a collection of weapons U Boat – Can attack from a great distance, quiet, untraceable. Tanks – Heavier, Germans had radios installed for communication purposes. * Germany goes from 57 to 1,100 in 6 years. This causes Great Britain to become concerned. Turret – Mounted Machine Gun on Tanks. It can shoot all around the tank while shooter stays covered. Causes of WWIi Fighter Aircraft – Small and fast planes that are easy to maneuver. *The countries that controlled the sky would win the war. Blitzkrieg – “Lightening War” Very Big and Very Sudden. Causes of WWIi • Alliances Allies Axis Great Britain Germany Soviet Union Italy France, Poland,Canada Japan The United States stays neutral until it is drawn into the war. Then we joined the side of the Allies. Leaders of WWIi • Allied Powers– – Joseph Stalin – Soviet Union – Winston Churchill – Great Britain – Franklin Roosevelt – United States • Axis Powers – – Benito Mussolini – Italy (Dictator) – Adolf Hitler – Germany (Dictator) – Hirohito – Japan (Emperor) The Beginnings of WWII • Hitler takes over country after country. Hitler had a policy of aggression. • He says that he is taking over these countries to unite the Germans. • Great Britain and France appease Hitler and allow him to take over Austria. He doesn’t stop there. Next he takes over Czechoslovakia. The Beginnings of WWII • If Hitler wanted to take over Poland he would have to deal with the Soviets. He makes a deal that Germany and the Soviet Union would divide up Poland and not attack each other. • Hitler doesn’t want to split Poland so he makes it look like Poland attacked Germany and then he invades Poland. The Beginnings of WWII • Great Britain and France send an ultimatum to Hitler. War breaks out shortly after. • Russia joins the side of the Allies since Hitler broke his promise to Russia. Allied Powers Axis Powers Neutral Major Battles • Pearl Harbor – 12/7/41 – The United States had remained neutral up to this point. – Japan attacks a U.S. Base in Hawaii – The attack lasted less than 2 hours but damaged 21 ships and 300 airplanes. 2,500 people died as a result of this attack. – This would be the start of the war between the United States and Japan. Japanese Internment Camps • Americans were angry toward the Japanese because of Pearl Harbor. • Roosevelt responded to pressure from the public and ordered all Japanese descent or relation to leave the west coast and go to camps in other U.S. states. • 50 years later Congress voted to give $20,000 to the surviving Japanese Americans who had been in the camps. Major Battles • Battle of Midway – 6/7/42 – Turning point in the war – Midway islands were northwest of Hawaii – Control of Midway would mean control over the Pacific – Japan lost many ships, aircraft carriers, and aviators. – The United States defeated Japan and gained control over the Pacific. Major Battles • Battle of Normandy – 6/6/44 – Also known as D-Day – Nazis vs. Allies – Largest Seaborne invasion in history – 3 million troops – Air and Sea attack that lasted 2 Months – Resulted in an Allied Victory – Less than a year later the Germans surrendered. Women in WWII • For the most part women are not allowed to fight in combat. • Ways women helped the war effort: – Worked in Defense plants and weapon factories – Nurses or Non Combat Army positions – WASP’s or other similar organizations. Women’s Air Force Service Pilots towed targets for training. They also moved aircrafts from factories to bases around the world. – Near the end of the war, due to a heavy loss of men, Great Britain drafted women but did not let them fight. Russia did the same however, they did let them fight U.S. Involvement • Prior to getting involved in war we allowed the Allied powers to buy supplies from us. • When we joined the war we were the only big power left that could stop Japan from taking over Asia. • We produced 86,000 Tanks/297,000 Airplanes • Our country took a leading position in the war with U.S. General, Dwight D. Eisenhower, leading the D-Day attack and U.S. General Douglas MacArthur’s leadership in the Pacific. Victory in Europe • August 25th U.S. and French troops drive the Germans out of Paris. • The Soviets are advancing from the east pushing the Germans out of the Soviet Union. • The Allied forces began closing in on the Axis Powers. • As they are closing in, Hitler gets married on April 29, 1945. One day later he and his wife take their own lives. • Eventually Berlin was surrounded and on May 7, 1945 the Germans surrendered. Victory in Japan • While the U.S. was mobilizing to war Japan took over more of Asia. • General Douglas MacArthur was giving the Japanese a lot of resistance in the Philippine Islands, however, the island surrendered forcing the General out. MacArthur promises to return and after a few Allied victories and 2 years time he makes it back to the Philippines to defeat the Japanese. Japan fought back with a new deadly weapon – Kamikazes! • The war against Japan raged on until the United States decided to take serious measures in the war. The Atomic Bombs • A top secret government program called the Manhattan Project developed the Atomic Bomb. • New U.S. President Harry Truman (took office after Roosevelt died) had to make the decision of whether or not to drop the bomb on Japan. • He decided to use it and on August 6, 1945 the U.S. dropped the atomic bomb on Hiroshima, Japan. The bomb devastated the city; however, Japan would not surrender. • So on August 9, 1945 the U.S. dropped a second Atomic bomb on Nagasaki. The emperor convinced the government to surrender. • WWII was now over. The Tragedies of War • Death Toll – 40 to 50 million people were killed worldwide • Refugees – Millions forced to leave their homes now flooded Europe and China • Atomic Bomb Effects – 100, 000 died instantly, others died later and even more developed cancer and other diseases. • Concentration Camps – Millions of people were put to death or died under the horrible camp conditions. Holocaust • “The Final Solution” • Concentration camps held people of a particular ethnic group or people with particular religious or political beliefs. • Nazi Germany put millions of people, not just Jews, to death in these camps. The Holocaust was a genocide of people with different beliefs than the Nazis. • Forced work, little food, no medical attention, research experiment subjects, and many other terrible fates awaited those who were placed into Concentration Camps. New Beginnings • United Nations- 1945 – International Peacekeeping Organization – Headquarters in New York City – Stronger Version of the League of Nations – Eleanor Roosevelt was the United States Delegate to the UN New Beginnings • Marshall Plan – 1948 – Secretary of State, George Marshall, and President Truman worked to come up with a plan to help the economy of Europe. – The United States sent $13 billion in aid to Europe – The plan was a success in Eastern Europe. Western Europe was under Soviet, Communist control and they were forced to turn down the U.S. offer of help. WWII Toward The Cold War • Following WWII the United States and Russia become rivals. • Both wants to be the superpower • We both have different government structures – Democracy vs. Communism. • These things create a lot of tension which gives this time period the name – The Cold War.