* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human body and disease
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
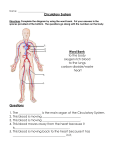
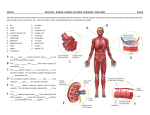
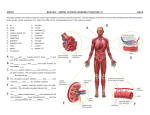
HUMAN BODY AND DISEASE Different Cells for Different Jobs Organisms that have many cells have specialized cells that work together. Tissue A group of cells that have a common structure and function Plants and animals have tissues that perform specific jobs. Types of Tissues Epithelial – sheets of cells that cover surfaces and line some body and blood vessels Connective tissue – includes bone, blood, and cartilage; these join other tissues together Muscle tissue – helps animals move their bodies Nervous tissue – produces electrical impulses and sends signals Organ Two or more types of tissue that work together to perform a function These tissues work together to perform more than one function. Tissue vs. Organ TISSUE Muscle tissue and nervous tissue are used to move the body. ORGAN Body functions are performed by organs. System a group of parts that work together Systems can work together to make up a larger whole. Many body systems work together to carry out all your body’s functions. Most animals have similar body systems. However, the organs that make up those body systems and how they work differ. Respiratory System A system that takes in oxygen from the air that your breathe Nose Mouth diaphragm Function of the Respiratory System 1) 2) 3) 4) The lungs are the main structure. When you breathe in, air moves down your throat and into your lungs. Oxygen is taken in through the thin lining of the lungs. Carbon dioxide is removed from your body. Then the air you breathe out has less oxygen, than the air you breathed in. It has more carbon dioxide. Diaphragm A thin sheet called the diaphragm lies below the lungs. The diaphragm and muscles attached to your ribs make your lungs breathe in and breathe out. These muscles are not part of the respiratory system, but they help it work. Digestive System A system that breaks down food so that it can be used by the body Function of the Digestive System The process begins when you chew. This breaks food into smaller pieces. In the stomach, the food is mixed with chemicals that help break it down. Then the food passes through the small intestines. More chemicals continue to break down food. Those chemicals are made by the liver and the pancreas. Nutrients are then absorbed by the body. Digestive System (cont.) In the large intestine, water is removed from food and taken into the body. Any remaining food that has not been digested becomes waste. Circulatory System carries oxygen, food, and wastes throughout the body The heart, blood vessels, and blood make up this system. The heart is the center of the circulatory system. The heart pumps blood through blood vessels called arteries. Circulatory System (cont.) The blood moves through the arteries into the capillaries. In the capillaries, oxygen and food move from the blood to the body cells. Carbon dioxide and other wastes move from cells to the blood. The blood moves through veins back to the heart. Nervous System The organ system – made up of the brains and other nerves – that controls movement and other organ systems The brain is the core of the nervous system. It collects information and makes decision. Your brain tells you when to breathe and tells the muscles of your digestive system when to move. The brain is connected to all parts of the body by nerves. Nervous System (cont.) The nerves carry instructions from your brain to the rest of your body. They also carry information from the body to the brain. Your sense organs are eyes, ears, nose, and skin. They gather information about the environment. Your brain reacts to what is going on around you and tells your body what to do. Skeletal System The basic framework of the body The human skeletal system is made of 206 bones that give the body structure and support. The bones also cover and protect the organs inside the body. The skull protects the brain. The ribs protect the heart and lungs. Muscular System Made up of all the body’s muscles Muscles that are attached to the bones move the body. How our Systems Work Together The circulatory system works with other systems. The respiratory system takes in oxygen from air in your lungs. The circulatory system carries oxygen to every cell of your body. The digestive system breaks food down into forms the body can use. The circulatory system absorbs those nutrients and carries them to the cells of the body. Skin Your skin is part of an organ system. The top layer (outside) of your skin is the epidermis. The inner layer (inside) of your skin is the dermis. The epidermis and dermis protect you from injury and keeps in moisture. Disease An illness caused by germs Some diseases, such as strep throat, are caused by living things. Germs are microscopic and can causes diseases. Pathogen An organism that causes a disease Pathogens are usually called germs. A disease caused by a pathogen is sometimes called an infection. Two Main Kinds: Bacteria Viruses – non-living; must be inside a cell and attacks the cell which makes you sick Antibiotic A substance that controls or kills harmful bacteria Antibiotic kill bacteria or stop them from reproducing. Antibiotic do not affect viruses. This is why your doctor does not give you an antibiotic for a cold or flu. These diseases are caused by viruses. Your doctor will give you an antiobiotic for strep throat. Alexander Fleming Studying bacteria Grew the mold in one of the dishes of bacteria There was a space around the mold where no bacteria grew. He experiment with the mold. He found that the mold made a chemical that stopped the growth of the bacteria. This chemical is penicillin, the first antibiotic. Vaccine A shot that contains a liquid made from the germ that causes an illness The vaccine will not give you the disease. It will cause your body to make antibodies that will give your body immunity. Immunity – the ability to fight off a disease caused by germs Louis Pasteur Pasteur made a vaccine to prevent rabies, a disease of the nervous system Rabies are spread by a bite from an animal who has the disease. Jonas Salk Salk made the vaccine that prevents polio. Polio is a disease caused by a virus. One form is like the flu and the other form is more serious! In the early 1900s, polio affected people, which were mostly children. It is a very rare disease. Immune System an organ system that fights disease and foreign agents This system produces specialized cells that help fight invading organisms and destroy damaged cells. Infectious Disease A disease caused by organisms or viruses Certain kinds of worms can get stuck in the intestines and muscles and cause serious diseases. Bacteria and some kinds of fungi can cause infectious disease. Some are contagious and some are not, and others are more dangerous and even deadly. Noninfectious Disease a disease caused by malfunction of an organ system Such a disease does not spread from person to person. Sometimes the disease is caused by a condition that is inherited (transferred by genes – from birth) from your family. Other times a disease appears as a person’s body ages.