* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry B Date: ______ 5.5-5.6 Triangle Inequality in One and
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Penrose tiling wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Apollonian network wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Incircle and excircles of a triangle wikipedia , lookup
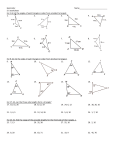
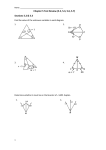
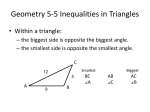
Geometry B Date: _____________ 5.5-5.6 Triangle Inequality in One and Two Triangles Objective: To apply triangle inequalities in one and two triangles Key Concepts: The longest side in a triangle is across from the ___________________ angle. The shortest side in a triangle is across from the __________________ angle. Ex. 1: Ordering Triangle Side Lengths and Angle Measures Write the sides and angles in order from smallest to largest. a. b. Sides: _______, _________, ________ Angles: _______, _________, ________ Angles: _______, _________, ________ Sides: _______, _________, ________ Triangle Inequality A triangle is made of 3 segments, but not every set of 3 segments can form a triangle. The sum of the two smallest sides must be __________________________________ If this is not true, then ___________________________________________________ To Test: Add the two smallest sides. Ex. 1: State whether it is possible to form a triangle with the given side lengths. a. 3 in, 3 in, 8 in b. 7 in, 4 in, 4 in c. 6 in, 6 in, 12 in d. 9 in, 5 in, 11 in Ex. 2: Find the possible lengths of the 3rd side of the triangle described below. a. A triangle has one side of 10 cm and another of 14 cm. Option 1: 14 is the largest side. Find the smallest side (Subtract 14 – 10) Option 2: 10 and 14 are the smaller sides. Find the largest side (add 14 +10) Answer: The 3rd side could be between _____ and ____ cm long. b. A triangle has one side of 8 cm and another of 17 cm. Option 1: Option 2: Answer: Hinge Theorem: If two triangles have 2 pairs of congruent sides but the included angles are not congruent, then the longer 3rd side will be across from the _________________________________. Compare the measures of BAC and DAC. Find the range of values for the variable k. Compare the lengths of sides EF and FG. Find the range of values for the variable z. HW: 5.5-5.6 Worksheet