* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The structure of the rainforest
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
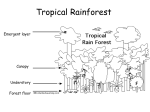
The structure of the rainforest Rainforests occur in a belt around the Equator. They forests have a warm climate with a mean monthly temperature that is always greater than 18°C. The rainfall is never less than 168 cm and can exceed 1,000 cm in a year. Student tasks 1. Copy the sketch below of ‘A typical rainforest landscape.’ A typical rain forest landscape 2. Copy out the paragraphs below. Use the word box to fill in the blanks: Rainforest trees The warm and wet climate of the tropical rainforest creates perfect conditions for the growth of plants. Most of the trees are h ................. with names like, M ............... Teak and Rosewood. These trees are excellent for making f ................. and are highly sought after because of this. As there are no s ................ in the rainforest, trees lose their leaves whenever they need to. Many sp.................. of rainforest trees, plants, insects and animals have yet to be discovered by scientists. How the rainforest is structured. The rainforest is organised in ................... distinct layers. The ............. .............. does not receive much sunlight as the dense canopy blocks out most of the sunlight reaching the forest floor. The trees of the under canopy grow .................................. as they do not receive much light. In an area where a canopy tree falls down, sunlight ...... reaches the under canopy trees and they literally race each other until they close the gap in the canopy. The tallest trees are called ..................... and can reach heights of up to . .............. high. slowly hardwoods 40 metres furniture four shrub layer seasons species suddenly Mahogany warm and wet emergents © www.teachitgeography.co.uk 2016 24169 Page 1 of 3 The structure of the rainforest Extension tasks 3. Look at the image below. Use the diagram of ‘a typical rainforest landscape’ to estimate how high the walkway is off the ground. Rainforest walkway, Sarawak © Bernard Dupont, 2007 flic.kr/p/dPNnrg 4. Copy out the paragraph below. Use the word box to fill in the blanks: Soils in the Rain Forest The enormous supply of dead leaves, fruit and animals falling from the canopy keeps the soil .................... They decay rapidly in the h .............. conditions and add n ................ to the poor quality soil. The rainforest soil near rivers is fertile because river water contains lots of m ............. from the rocks contained in the rivers. nutrients minerals humid fertile 5. Use the diagram of ‘a typical rainforest landscape’ and the paragraph above to answer the questions: a. What is leaf litter? b. Why is the soil near the river more fertile than the other soil? c. Most of the rainforest is growing on poor soil – how does this soil keep fertile enough to allow trees to grow? © www.teachitgeography.co.uk 2016 24169 Page 2 of 3 The structure of the rainforest Teaching notes Rainforest Trees The hot and wet climate of the tropical rainforest creates perfect conditions for the growth of plants. Most of the trees are hardwoods with names like, Mahogany, Teak and Rosewood. These trees are excellent for making furniture and are highly sought after because of this. Because there are no seasons, trees lose their leaves whenever they need to. There are still many species of trees, plants, insects and animals in the World’s rain forests that scientists have yet to discover. How the rainforest is structured. The rainforest is organised in four distinct layers. The shrub layer does not receive much sunlight as the dense canopy blocks out most of the sunlight reaching the forest floor. The trees of the under canopy grow slowly as they do not receive much light. In an area where a canopy tree falls down, sunlight suddenly reaches the under canopy trees and they literally race each other until they close the gap in the canopy. The tallest trees are called emergents and can reach heights of up to 40 meters high. Soils in the rainforest The enormous supply of dead leaves, fruit and animals falling from the canopy keeps the soil fertile. They decay rapidly in the humid conditions and add nutrients to the poor quality soil. The rainforest soil near the rivers is fertile because river water contains many minerals from the rocks contained in the rivers. Extension tasks 3. The image shows the ‘Canopy Walk’ at the Mulu National Park in Sarawak. This is the longest tree-based canopy walk in the world and is 480 meters long. In the image, the walkway is approximately 20 metres above ground level, i.e. just below the canopy level. a. What is leaf litter? Leaf litter is dead plant material, such as leaves, bark, needles and twigs that have fallen to the ground. b. Why is the soil near the river more fertile than the other soil? Soil near rivers is fertile because river water contains many minerals from the rocks contained in the rivers. c. Most of the rainforest is growing on poor soil – how does this soil keep fertile enough to allow trees to grow? The enormous supply of dead leaves and animals falling from the canopy keeps the soil fertile. They decay rapidly in the humid conditions and add nutrients to the poor quality soil. © www.teachitgeography.co.uk 2016 24169 Page 3 of 3