* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulation ppt
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
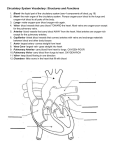
Circulation and Respiration Supplying Oxygen to the body through the bloodstream Blood Vessels • Blood vessels carry blood from your heart to all of your body parts, and then back again. • Blood vessel walls consist of muscle tissue and connective tissue that enable it to expand and contract as blood flows through it. • Red blood cells inside the vessel carry oxygen to all parts of your body. Circulatory System • Together, the organs of the circulatory system supply nutrients and oxygen to your body • They remove waste products that would be harmful to your health if they were not removed Heart • The human heart is the primary organ of the circulatory system • It is a 4-chambered organ • Blood is actually a type of connective tissue that circulates throughout the body carrying nutrients and oxygen Blood Vessels • Arteries – Blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart – This blood can be going to the lungs – Or to the body organs • Veins – Carry blood to the heart – From the lungs – From the body organs • Capillaries –Tiny blood vessels that allow for diffusion of oxygen and nutrients between the arteries and veins Blood Vessels Heart and Blood Flow • pulmonary circuit carries oxygen-poor blood from the heart to the lungs and oxygenrich blood back to the heart. • In the lungs the blood picks up oxygen which is used by the body organs Systemic Circuit • The Systemic circuit takes the oxygen rich blood TO the body organs and returns the oxygen depleted blood back to the heart • The blood is then brought back to the lungs (by the pulmonary system) to get oxygen Structures of the Heart High Oxygen Heart Structures • Aorta – Carries Blood to the rest of the body • Left Atrium – Oxygen-rich blood enters the left atrium through the pulmonary veins – Blood passes through the atrioventricular valves to the Left ventricle • Left Ventricle- Made of thick cardiac muscle is the pump. This chamber pumps oxygen-rich blood to the body through the aorta Low Oxygen Side of the Heart • Right Atrium – Oxygen-poor blood enters the right atrium from the body organs through the upper and lower vena cava (veins) – Blood passes through the right atrioventricular valves to the right ventricle • Right Ventricle –Blood is sent to the lungs through the pulmonary arteries • pulmonary Arteries carry oxygen-poor blood back to the lungs Blood Pressure • Systolic pressure measures the pressure of the heart when it is pumping blood • Diastolic pressure is the pressure of the heart “at rest” or taking in blood – Normal blood pressure is below 130/85