* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Solve 2x2 Sys
Cubic function wikipedia , lookup
Quartic function wikipedia , lookup
Quadratic equation wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Linear algebra wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Intermediate Algebra Worksheets
By O. Pauline Chow
HACC
Math 051 Intermediate Algebra
Lecture Notes for chapter 3.1-3.5 (audio dated 8/17/07 at 10:03 pm, 29 minutes long)
Solve 2x2 Systems of Linear Equations by Graphing
Solve 2x2 Systems of Linear Equations by Substitution
Solve 2x2 Systems of Linear Equations by Addition Methods
Applications of Systems of Linear Equations
Solve 3x3 Systems of Linear Equations
Solve 2x2 Systems of Linear Equations by Graphing
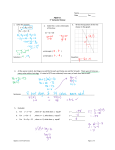
Ex 1.
Solve the system by graphing.
1
y = x+2
2
5
y = x−2
2
For each equation, we set up a table of values and graph.
x
y=
1
x+2
2
0 2
–4 0
4 4
x
y=
5
x−2
2
0
–2
0.8 0
2
3
The solution to the system is the point of intersection of the two lines: (2, 3).
Ex 2.
Solve the system by graphing.
Intermediate Algebra, by Miller, O’Neill, Hyde, 2nd edition, McGraw Hill
Intermediate Algebra Worksheets
By O. Pauline Chow
HACC
x=4
y = 2x − 3
For each equation, we set up a table of values and graph.
x y
4 2
4 0
x
0
1.5
2
Y = 2x – 3
–3
0
1
The solution to the system is the point of intersection of the two lines: (4, 5).
Solve 2x2 Systems of Linear Equations by Subsitution
Ex 1. Solve the system using substitution.
x = 2 y − 10
2x + 3 y = 8
Using equation 1, we substitute 2y – 10 for x into equation 2.
2(2y – 10) + 3y = 8
Now we solve for y.
4y – 20 + 3y = 8
7y – 20 = 8
7y = 28
y=4
We substitute 4 for y into equation 1 and solve for x.
Intermediate Algebra, by Miller, O’Neill, Hyde, 2nd edition, McGraw Hill
Intermediate Algebra Worksheets
By O. Pauline Chow
HACC
x = 2(4) – 10 = 8 – 10 = –2
So, the solution to the system is (–2, 4).
Ex 2. Solve the system using substitution.
5x – y = 19
2x + 7y = –22
Before we can use the substitution, we shall solve for y in equation 1.
5x – y = 19
–y = –5x + 19
y = 5x – 19
(3)
Now we substitute 5x – 19 for y into equation 2.
2x + 7(5x – 19) = –22
2x + 35x – 133 = –22
37x = 111
x=3
Next we substitute 3 for x in equation 3 to solve for y.
y = 5(3) – 19 = –4
The solution to the system is (3, –4).
Ex 3.
Solve the system using substitution.
4x + 5y = 3
3x – 2y = 8
We use equation 1 to solve for x.
4x + 5y = 3
4x = –5y + 3
5
3
x=− y+
4
4
Now substitute −
(3)
5
3
y + for x into equation 2 and solve for y.
4
4
Intermediate Algebra, by Miller, O’Neill, Hyde, 2nd edition, McGraw Hill
Intermediate Algebra Worksheets
By O. Pauline Chow
HACC
3
5
3 − y + − 2 y = 8
4
4
15
9
− y + − 2y = 8
4
4
−15 y + 9 − 8 y = 32
We multiply 4 to the equation.
−23 y + 9 = 32
−23 y = 23
y = −1
Now we substitute –1 for y into equation 3 to solve for x.
5
3 8
x = − (−1) + = = 2
4
4 4
The solution to the system is (2, –1)
Solve 2x2 Systems of Linear Equations by Addition
Ex 1: Solve the system using Addition.
5x – 3y = 15
2x + 7y = 56
We need to multiply each equation by an appropriate constant to make the coefficients of x or y
opposite to each other. We shall multiply equation 1 by –2 and equation 2 by 5.
–2(5x – 3y = 15)
5(2x + 7y = 47)
–10x + 6y = –30
10x + 35y = 235
Now add the two equations.
–10x + 6y = –30
10x + 35y = 235
41y = 205
y=5
Now substitute 5 for y in equation 1 to solve for x.
5x – 3(5) = 15
5x – 15 = 15
5x = 30
x=6
Intermediate Algebra, by Miller, O’Neill, Hyde, 2nd edition, McGraw Hill
Intermediate Algebra Worksheets
By O. Pauline Chow
HACC
The solution to the system is (6, 5).
Ex 2. Solve the system using Addition.
x – 3y = 15
2x – 6y = 31
We multiply equation 1 by –2.
–2x + 6y = –30
2x – 6y = 31
0 = 1 No solution!
There is no solution to the system. This means the lines are parallel to each other.
Ex 3. Solve the system using Addition.
2x – 3y = 4
4x – 6y = 8
We multiply equation 1 by –2.
–4x + 6y = –8
4x – 6y = 8
0 = 0 An identity!
This means the lines are the same and the equations are equivalent. So, we write the solution in set
notation, {(x, y) | 2x – 3y = 4}.
Applications of Systems of Linear Equations
Ex 1. A fruit punch that contains 25% fruit juice is combined with a fruit drink that contains 10%
fruit juice. How many ounces of each should be used to make 48oz of a mixture that is 15%
fruit juice?
To solve this problem, we let x and y be the number of ounces of 25% and 10% fruit juice,
respectively. Since the total number of ounces of the mixture is 48, x + y = 48. We use the percent to
find the number of ounces of fruit in each juice.
Juice I
% of fruit
25%
# of oz of juice
x
# of oz of fruit in each juice (25%)(x)
Juice II
10%
y
(10%)(y)
Mixture
15%
48
x + y = 48
(15%)(48) 0.25x + 0.10y = 7.2
Now we solve the 2x2 system using substitution method. We shall solve the equation 1 for x and
substitute into equation 2.
Intermediate Algebra, by Miller, O’Neill, Hyde, 2nd edition, McGraw Hill
Intermediate Algebra Worksheets
By O. Pauline Chow
HACC
x = 48 – y
0.25(48 – y) + 0.10y = 7.2
12 – 0.25y + 0.10y = 7.2
12 – 0.15y = 7.2
–0.15y = –4.8
y = 32
x = 48 – 32 = 16
16 oz of 25% fruit juice and 32 oz of 10% fruit juice.
Ex 2. Jack cruised 42 miles downriver in 45 minutes. His return trip upriver took 1 hour. Determine
the speed of his motorboat in still water and the speed of the river’s current.
We let x mph be the speed of the motorboat in still water and y mph be the speed of the river’s current.
When the boat is going upriver, its speed is (x – y) mph. When the boat is going downriver, its speed
is (x + y) mph.
distance Speed
time
d = st
Downriver 42 miles (x + y) mph
42 = 0.75(x + y)
45
45 minutes =
= 0.75 hour
60
Upriver
42 miles (x – y) mph 1 hour
42 = 1(x – y)
Now we have a 2x2 system. We will divide 0.75 into equation 1 to make the system easier.
x + y = 56
x – y = 42
Now we just add the equations and solve for x.
2x = 98
x = 49
We substitute 49 for x into equation 2 to solve for y.
49 – y = 42
–y = –7
y=7
Speed of the boat in still water is 49 mph and current is 7 mph.
Ex 3. A rectangle has the perimeter of 42 m. The length is 1 m longer than the width. Find the
dimensions of the rectangle.
Let x m be the width and y m be the length. We set up the two equations:
length is 1 m longer than the width y = 1 + x
Intermediate Algebra, by Miller, O’Neill, Hyde, 2nd edition, McGraw Hill
Intermediate Algebra Worksheets
By O. Pauline Chow
HACC
Perimeter is 42 m 2x + 2y = 42
y=1+x
2x + 2y = 42
We will substitute 1 + x for y into equation 2.
2x + 2(1 + x) = 42
2x + 2 + 2x = 42
4x = 40
x = 10
y = 11
The dimensions of the rectangle are 10 m by 11 m.
Solve 3x3 Systems of Linear Equations
Ex 1
Solve the 3x3 system.
2x + 3y – z = –6
3x – y + 2z = 11
x + 4y – 5z = –15
We shall apply the addition method. First we use equations 1 and 2 to eliminate x.
3(2x + 3y – z = –6)
–2(3x – y + 2z = 11)
6x + 9y – 3z = –18
–6x + 2y – 4z = –22
11y – 7z = –40
(4)
Next we use equations 1 and 3 to eliminate x.
2x + 3y – z = –6
–2(x + 4y – 5z = –15)
2x + 3y – z = –6
–2x – 8y +10z = 30
–5y + 9z = 24
(5)
Now we have a 2x2 system. We shall apply the addition method.
5(11y – 7z = -40)
11(–5y + 9z = 24)
55y – 35z = -200
–55y + 99z = 264
64z = 64, z = 1
We will use back substitution to solve for y and x. Substitute 1 for z into equation 4 to solve for y.
11y – 7(1) = –40
11y = –33
y = –3
We will substitute –3 for y and 1 for z into equation 3 to solve for x.
Intermediate Algebra, by Miller, O’Neill, Hyde, 2nd edition, McGraw Hill
Intermediate Algebra Worksheets
By O. Pauline Chow
HACC
x + 4(–3) – 5(1) = –15
x – 12 – 5 = –15
x – 17 = –15
x=2
The solution to the system is (2, –3, 1).
Intermediate Algebra, by Miller, O’Neill, Hyde, 2nd edition, McGraw Hill