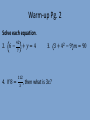* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Algebra 1
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Abuse of notation wikipedia , lookup
Functional decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Structure (mathematical logic) wikipedia , lookup
Big O notation wikipedia , lookup
Dirac delta function wikipedia , lookup
Continuous function wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard calculus wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Function of several real variables wikipedia , lookup
Function (mathematics) wikipedia , lookup
1.6: Relations
Agenda
1) Check HW/Warm-Up
2) 1.6 Notes
3) Exit Slip
Target: Represent and interpret graphs of relations
Warm-up Pg. 1
1. A car is currently 300 miles from its destination and is
traveling against the wind. The car travels 60 miles per
hour (mph) when there is no wind. The car’s distance from
its destination is given by the formula
𝐷 = 300 − ℎ(60 − 𝑐).
Given: D = distance in miles, h = number of hours, c = speed
of the wind in mph. What is a correct formula for the car’s
distance from its destination after 4 hours?
A) 𝐷 = 17400 − 290𝑐
C) 𝐷 = 60 − 𝑐
B) 𝐷 = 17400 − 𝑐
D) 𝐷 = 60 + 4𝑐
Warm-up Pg. 2
Solve each equation.
2. 6 −
42
7
4. If 8 =
+𝑦 =4
112
,
𝑥
3. 3 + 42 − 9 𝑚 = 90
then what is 3𝑥?
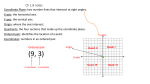
Coordinate System: The grid formed by the
intersection of two number lines, the horizontal axis
and the vertical axis.
Ordered pair: a set of numbers or coordinates
used to locate any point on a coordinate plane,
written in the form (x, y).
x-coordinate: the first number in an ordered
pair.
y-coordinate: the second number in an ordered
pair.
Relation: a set of ordered pairs
Mapping: illustrates how each
element of the domain is paired with
an element in the range.
Domain: the set of first numbers of
the ordered pairs in a relation.
Range: the set of second numbers of
the ordered pairs in a relation.
In the relation above, the domain is {-2, 1, 0} and
the range is {-3, 2, 4}
Example 1
a) Express {(4, 3), (-2, -1), (2, -4), (0, -4)} as a
table, a graph, and a mapping.
b) Determine the domain and range of the
relation.
Independent variable: the variable in a relation
with a value that is subject to choice.
Dependent variable: the variable in a relation
with a value that depends on the value of the
independent variable.
Example 3
Identify the independent and the dependent
variable for each relation.
a) In warm climates, the average amount of
electricity used rises as the daily average
temperature increases and falls as the daily
average temperature decreases.
b) The number of calories you burn increases as
the number of minutes that you walk increases.
Example 3
A relation can be graphed without a scale on
either axis. These graphs can be interpreted by
analyzing their shape.
Describe what is happening in each graph.
a)
b)
Homework
<6> p.43 #12, 16, 18, 20, 34, 36
Don’t let this happen…
Brain Break
Red in the Face
Ice Cube
Blanket
Section 1.7 Warmup
1.) Draw a graph that represents you taking a
dog for a walk. Let your labels be distance and
time. You stopped twice to talk to two
different neighbors and you ran the last half
block to your house.
2.) 1. Express the relation
−1, 0 , 2, −4 , −3, 1 , 4, −3 as a
table, a graph, and a mapping. Then
determine the domain and range.
Warmup Problem 2:
Algebra 1
Unit 1
Section 1.7 Notes: Functions
Function: a relationship between input and
output. In a function there is exactly one output
for each input.
Example 1:
Determine whether each relation is a function. Explain.
a)
b)
Example 1:
Determine whether each relation is a function. Explain.
c)
Discrete function: a
function of points that are
not connected.
Continuous function: a
function that can be
graphed with a line or a
smooth curve.
Example 2
Circle the continuous functions below.
B
A
D
C
E
Example 3: There are three lunch periods at a
school. During the first period, 352 students
eat. During the second period 304 students eat.
During the third period, 391 students eat.
a) Make a table showing the number of students
for each of the three lunch periods.
b) Determine the domain and range of the
function.
Example 3 Continued:
c) Write the data set of ordered pairs then graph
the data.
d) State whether the function is discrete or
continuous. Explain your reasoning.
Vertical line test: if any vertical line passes
through no more than one point of the graph of
a relation, then the relation is a function.
*Use when you are given a graph.
Example 4: Determine whether the following
graphs represent functions.
a)
b)
c)
A function can be represented in different ways.
Function Notation: A way to name a function
that is defined by an equation. In function
notation, the equation 𝑦 = 3𝑥 − 8 is written
𝑓 𝑥 = 3𝑥 − 8.
It is said “f of x”. If a number is inside the
parenthesis than that is the number you
substituted in for x.
Example 5: For 𝑓 𝑥 = 3𝑥 − 4, find each value.
a) 𝑓(4)
b) Find the missing values in
the table using the function
above.
Nonlinear function: a function with a graph that
is not a straight line.
Example 6: If ℎ 𝑡 = 1248 − 160𝑡 + 16𝑡 2 , find
each value.
a) ℎ(3)
b) ℎ(2𝑧)
Brain Break
A Walk in the Park
Down to Earth
All Mixed Up
Algebra 1
Unit 1
Section 1.8 Notes: Interpreting Graphs of Functions
y-intercept: the y – coordinate of a point where
a graph crosses the y – axis.
x-intercept: the x – coordinate of a point where
a graph crosses the x – axis .
Example 1: The graph shows the cost at a
community college y as a function of the
number of credit hours taken x.
a) Identify the function as linear or nonlinear.
b) Estimate and interpret the intercepts of the
function.
c) Approximate the cost of
a student taking 4 credit
hours.
Line Symmetry: if a vertical line is drawn and
each half of the graph on either side of the line
matches exactly.
Example 2: The graph shows the cost y to
manufacture x units of product. Describe and
interpret any symmetry.
Brain Break
Q: What word becomes shorter when you add two letters to
it?
A: Short
Q: What can you catch but not throw?
A: A cold.
Q: Forward I am heavy, backward I am not. What am I?
A: A ton
Example 3: The graph shows the population y of
deer x years after the animals are introduced on an
island.
Estimate when the deer population is:
A) positive
B) negative
C) increasing
D) decreasing
E) at its maximum population (relative maximum)
F) at its minimum population (relative minimum)
Example 3: The graph shows the population y of deer x
years after the animals are introduced on an island.
• Describe the end behavior of the graph.
• How many deer will there be after
0.5 years?
5 years?
• The deer population started
at about 80 deer. When will
the deer population be at
80 again?
Exit Slip
1. Where do you find intercepts?
2. Using the graph below, estimate what will
the companies maximum revenue be.
Homework
p.52 #20, 22, 24, 26, 30, 34, 46, 48
p.59 #4, 6, 8, 12, 14, 16, 18
Don’t let this happen…