* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Example Example - Solution
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Recurrence relation wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
9/2/2009
Vocabulary
Linear Equations in Two
Variables
Objectives: To determine if a given
ordered pair is a solution, to define the
coordinate plane and plot ordered pairs.
Vocabulary (continued)
Ordered pair – identifies the location of a
point
Coordinates – the numbers of a point on
graph;
p ; in the form ((x,y)
,y)
the g
x-coordinate – tells how far to move right
(positive) or left (negative) from the origin;
always first in an ordered pair
y-coordinate –tells how far to move up
(positive) or down (negative); always second
in an ordered pair
Example
Complete the given ordered pairs.
a) 3x – y = 5 (0, ___), (1, ___), ( ___, 5)
coordinate plane – an area defined by two
axes (number lines) that intersect at right
angles
x-axis – the horizontal (left to right) number
liline
y-axis – the vertical (up and down) number
line
origin – point where the axes intersect
quadrants – the four regions of the
coordinate plane
Vocabulary (continued)
solution -- an ordered pair (x,y) that “works”
in the equation
To complete a solution: Substitute the given x
or y value into the equation and solve for the
remaining variable.
Example - Solution
Complete the given ordered pairs.
a) 3x – y = 5 (0, -5), (1, -2), (10/3, 5)
3(0) – y = 5
3(1) - y=5
3x – 5 = 5
-y = 5
3–y=5
3x = 10
y = -5
-y = 2
x = 10/3
(0, -5)
y = -2
(10/3, 5)
(1, -2)
1
9/2/2009
Example
Example - Solution
b) Complete the table for the
equation y = -5x.
b) Complete the table for the
x
y
3
0
-2
-20
Example
Find the solution set for each equation given the
replacement set by substituting for x and y.
c) {(-5,0), (-3,-2), (2,13)} for y = 7 + 3x.
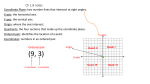
Recognizing Ordered Pairs
Name the coordinates of each point in the
graph.
d P
d.
Q
W
P
V
e. T
f. Q
g. W
T
h. V
equation y = -5x.
We must substitute each given
value and find the other
value.
y=-5(3) = -15
0 = -5(x)
0=x
y=-5(-2) = 10
-20=-5x
4=x
x
y
3
-15
0
0
-2
10
4
-20
Example - Solution
Find the solution set for each equation given the replacement
set by substituting for x and y.
c) {(-5,0), (-3,-2), (2,13)} for y = 7 + 3x.
We must substitute each given ordered pair to find which ones
work or give us true statements.
“work”
(-5,0) Æ 0 = 7 + 3(-5)
(-3,-2) Æ -2 = 7 + 3(-3)
0 = 7 – 15
-2 = 7 - 9
0 = -8 (false)
-2 = -2 (true)
(2,13) Æ 13 = 7 + 3(2)
13 = 7 + 6
So the solution set is (-3,-2)
13 = 13 (true)
and (2, 13).
Recognizing Ordered Pairs
Solution
Name the coordinates of each point in the
graph.
d P (-4,2)
d.
( 4 2)
Q
W
P
V
e. T (3,-2)
f. Q (0,3)
g. W (4,2)
T
h. V (-1,2)
2
9/2/2009
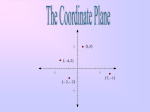
QUADRANTS in the Coordinate Plane
Plotting Points
y
5
II
((-,+)
+)
I
(+ +)
(+,+)
1. Start at the origin.
2. The first number tells you how much
x
III
(-,-)
IV
(+,-)
-5
(x,y)
-5
to move left or right on the horizontal
number line.
3. From there, the second number tells
you how much to move up or down.
4. Draw a dot & label it.
5
Examples
Examples - Solutions
Plot each point. In
which quadrant
or on which axis
would you find
each point?
5
i) (-4, 2)
Plot each point. In
which quadrant
or on which axis
would you find
each point?
5
i) (-4, 2)
y
y
i
j) (3, -2)
j) (3, -2)
l
x
k) (0, -5)
l) (-3, 0)
x
j
k) (0, -5)
-5
-5
5
l) (-3, 0)
-5
-5
k
5
3