* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
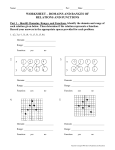
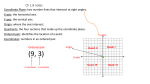
KUD Organizer Course: Pre-Algebra Unit: Functions and Coordinate Geometry Approximate Days: STANDARDS: CC.2.2.8.C.1 Define, evaluate, and compare functions. CC.2.2.8.C.2 Use concepts of functions to model relationships between quantities. UNDERSTAND: Relations and functions are mathematical relationships that can be represented and analyzed using words, tables, graphs, and equations. Mathematical functions are relationships that assign each member of one set (domain) to a unique member of another set (range), and the relationship is recognizable across representations. KNOW: Define, evaluate, and compare functions displayed algebraically, graphically, numerically in tables, or by verbal descriptions. Represent or interpret functional relationships between quantities using tables, graphs, and descriptions. How to plot, locate or identify ordered pairs on a coordinate plane (the point may be a vertex of a polygon). How to determine the value of an algebraic expression by simplifying and/or substituting a value for the variable. How to identify the domain or range of a relation (may be presented as ordered pairs, a graph, or a table). DO: Determine whether a relation is a function. Compare properties of two functions each represented in a different way (i.e., algebraically, graphically, numerically in tables, or by verbal descriptions). Example: Given a linear function represented by a table of values and a linear function represented by an algebraic expression, determine which function has the greater rate of change. Interpret the equation y = mx + b as defining a linear function whose graph is a straight line; give examples of functions that are not linear. Construct a function to model a linear relationship between two quantities. Determine the rate of change and initial value of the function from a description of a relationship or from two (x, y) values, including reading these from a table or from a graph. Interpret the rate of change and initial value of a linear function in terms of the situation it models and in terms of its graph or a table of values. Describe qualitatively the functional relationship between two quantities by analyzing a graph (e.g., where the function is increasing or decreasing, linear or nonlinear). Sketch or determine a graph that exhibits the qualitative features of a function that has been described verbally. How to identify, describe, and/or use constant rates of change. Continue a numeric or algebraic pattern. The formulas for distance and midpoint. Find missing elements in numeric or geometric patterns and/or functions. The different types of transformations and how to apply a transformation. Determine the rule of a function. Graph a linear function based on an x/y table and using slope-intercept form. Match the graph of a linear function to its x/y table and/or equation. Match the linear equation to the x/y table. Plot, locate, or identify ordered pairs on a coordinate plane. Determine the value of an algebraic expression by simplifying and/or substituting a value for the variable. Identify the domain or range of a relation. Apply the concept of linear rate of change (slope) to solve problems. Draw, identify, and/or find a line of best fit for a scatter plot. Calculate the distance and midpoint between two points. Apply the transformations of translation, reflection, rotation, and dilation to lines and figures in a coordinate plane. KEY VOCABULARY: Coordinate plane, ordered pair, x-axis, y-axis, origin, quadrant, ordered pair, x-coordinate, y-coordinate, relation, domain, range, input, output, function, vertical line test, equation in two variables, solution of an equation in two variables, graph of an equation in two variables, linear equation, function form, x-intercept, y-intercept, slope, rise, run, slope-intercept form, line of best fit, function notation, linear systems of equations, solutions of a linear system of equations, linear inequality in two variables, solution of a linear inequality in two variables, graph of a linear inequality in two variables, half-plane, quadratic functions, non-linear function, minimum value, maximum value, expontial function, exponential growth, exponential decay