* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download full ISN XI - Northbrook District 28
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
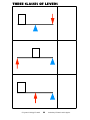
name:_________________________________________________per___ ISN X: WORK, POWER, MACHINES Point Value Check-in 1-2 Table of Contents/Things 2 Know text Reading & Text Questions on 67-73 ☜ no check for this ✌ --------------------* 2 3 Eureka Work Video Guide 2 4 Work and Power Worksheet 2 text Reading & Text Questions on 74-75 2 5-6 Lab: Work and Power 35 text Reading & Text Questions on 76-79 2 7 Simple Machines Pre-Test 1 8 Reference: Simple Machines Overview 1 9 EdHeads Simple Machines Interactive Web Site 2 text Reading & Text Questions on 80-83 2 10 Eureka! Simple Machines Notes 1 11 Reference: Three Classes of Lever 1 text Reading & Text Questions on 84-91 4 12 Notes: Mechanical Advantage Calculations 1 13-14 Lab: Mechanical Advantage 26 text Reading & Text Questions on 92-97 4 15-16 Lab: Lego Madness 22 17 Simple Machines Matching 2 text Study Guide on 98-101 4 18 Mind Map 10 19 Parent Signature & date day before quiz 5 *MAke up A,N & I work asap *A = absent N= Not Handed in i= incomplete If it’s green, it’s biology. If it smells Points Lost 1 TOTAL: 131 its chemistry. If it doesn’t work its physics. Parent signature ____________________________________________date_____ Item page # Updated Things 2 Know 1. SAFETY FIRST!! (lab walk, fragile things, P.A.S.S., etc) 2. You are required to have a pencil or erasable pen, ISN with cover, calculator, ruler, and red or green pen everyday. 3. on-line textbook my.hrw.com, username: nbjh3 password: science 4. Satoʼs email address: [email protected] 5. Matter is anything with mass and volume. 6. Matter is made of tiny particles that are always in some motion. 7. Matter can exist in several states(or phases), the most common are solid, liquid, gas and plasma. 8. Temperature is how fast the particles are vibrating and ... 9. Heat is how many particles there are and how fast they are moving. 10. An element is the most basic type of matter that is still unique. 11. Atoms are composed of protons, neutrons and electrons. 12. The number of protons(atomic number) determines the identity of an element 13. Matter is described by its physical and chemical properties. 14. The periodic table is organized on several levels, including by: atomic number, electron configuration, similar properties. 15. Elements can bond together to form chemicals other than elements. 16. There are three types of bond: ionic, covalent and metallic. 17. The valence electrons determine how an substance bonds. 18. We studied 4 types of reactions: synthesis, decomposition, single replacement and double replacement. 19. Chemical equations are balanced using coefficients. 20. pH levels of acids are less than 7, bases are greater than 7, neutral is 7. 21. Polymers are composed of many monomers linked together. 22. Speed = Distance÷Time 23. Velocity is speed with a direction. 24. Slope can be a useful tool to understand information. 25. Newtonʼs 1st law: Things do what they are doing unless acted on by unbalanced force. 26. Newtonʼs 2nd law: Force= mass x acceleration 27. Newtonʼs 3rd law: every action force has an equal and opposite reaction force. 28. Weight is different than mass. Mass units are grams. 29. Force is any push or pull. 30. Buoyancy is caused by the weight of the fluid displaced 31. Pressure is Force ÷ area If it’s green, it’s biology. If it smells 2 its chemistry. If it doesn’t work its physics. Eureka Video Guide: Work The Story So Far... 1. _____________ refers to how much “stuff”a thing contains. 2. _____________refers to the rate at which that amount of stuff is being accelerated towards the earth (or force of gravity) 3.An objectʼs _________________ never varies, but its ______________ can go up or down depending on the force of ______________ acting on it in various parts of the universe. 4. The barbell weighs ______________ newtons so it would take _______________ newtons to hold it up? 5.WORK = ______________ x ________________ 6.Work is measured in ___________________ named for James Prescott _____________ 7. How much work is done to lift the barbell 2 m up? Show Work. 8. How much work is done to lift the barbell 1 m up? Show Work. If it’s green, it’s biology. If it smells 3 its chemistry. If it doesn’t work its physics. its chemistry. If it doesn’t work its physics. Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. work ! Force " distance W!F"d W ! 16 N " 1.5 m W ! 24 J MATH SKILLS FOR SCIENCE 3. A 150 N boy rides a 60 N bicycle a total of 200 m at a constant speed. The frictional force against the forward motion of the bicycle equals 35 N. How much work does the boy do? Explain your answer. (Hint: Remember that work is only done when the motion is in the same direction that the force is applied.) 2. A rope is thrown over a beam, and one end is tied to a 300 N bundle of lumber. You pull the free end of the rope 2 m with a force of 400 N to lift the lumber off the ground. How much work have you done? 1. A deflated hot-air balloon weighs a total of 8000 N. Filled with hot air, the balloon rises to a height of 1000 m. How much work is accomplished by the hot air? Based on what you know about work, answer the following questions. Be sure to show your work. Work It Out! you lift the sack 1.5 m? SAMPLE PROBLEM: How much work is done on a 16 N sack of potatoes when The SI unit for work is the newton-meter (N # m), also known as a joule ( J). You can calculate the amount of work accomplished with the equation above. Let’s see how it’s done! EQUATION: As you sit and read this worksheet, are you doing work? You might say, “Yes, of course.” But are you doing work in the scientific sense? Scientists use the word work to describe a very specific concept. In physics, work is a force applied over a distance. Use the equations for work and power. Part 1: An Equation for Work Work and Power Addition Multiplication Division D ecim als Scientific Notation MATH IN SCIENCE: P HYSICAL S CIENCE 51 Class M ATH S KILLS U SED Date WORKSHEET N ame 79 Work and Power, continued Date Class W P!# t work power ! # time Power! Power! 80 HOLT SCIENCE AND TECHN OLOGY b. How much power does the crane produce? a. How much work is done by the crane? 4. A crane lifts a load of steel that weighs 9.3 " 105 N a distance of 100 m. It takes 5 minutes to complete the task. Challenge Yourself! Work! Work! Power ! Work ! Step 1: A 50 N girl climbs the flight of stairs in 3 seconds. Step 3: The girl climbs the ladder with the painting in 5 seconds. Height of ladder = 2 m Step 2: The girl lifts a painting to a height of 0.5 m in 0.75 seconds. Height of stairs = 3 m Force necessary to lift painting = 60 N The unit for power is the watt (W). One watt (W) is equal to 1 J of work done for 1 second. Use the data given in the diagram below to determine how much work and power are involved in each step. Remember to show your work. EQUATION: Work is closely related to the concept of power. Power is a measure of how much work is done in a certain time. The faster work is done, the more power is produced. Part 2: Work and Power N ame SCIENCE: PHYSICAL SCIENCE IN M ATH 4 ! ! ! If it’s green, it’s biology. If it smells Graded by: ___________________________________________________________________ score:______ LAB: Work & Power PURPOSES ๏ to describe power and its measurements ๏ to explain the units of power ๏ to calculate power, work, and time using the formulas work = force x distance power= work ÷ time HYPOTHESIS(4 pts) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------MATERIALS ! Stopwatch, meter stick, pencil,calculator PROCEDURES round all to 0.01, include the correct UNITS for each DATA TABLE (2 pts each box): 1. Determine your weight in newtons, this will be the force (Multiply your weight in pounds by 4.5.) 2. Determine how many seconds it takes you to walk up a flight of stairs. 3. Determine how many seconds it takes you to walk up a flight of stairs backwards 4. Determine how many seconds it takes you to run up the flight of stairs (no skipping steps). 5. Determine how many seconds it takes you to run up the flight of stairs (skipping allowed) 6. Determine the vertical height of the stairs in meters If it’s green, it’s biology. If it smells 5 its chemistry. If it doesn’t work its physics. 7. Determine how much work was done to walk up the stairs. 8. Determine how much work was done to walk up the stairs backwards. 9. Determine how much work was done to run up the stairs. 10.Determine how much work was done to run up the stairs with skipping. 11.Determine how much power was produced to walk up the stairs. 12.Determine how much power was produced to walk up the stairs backwards. 13.Determine how much power was produced to run up the stairs. 14.Determine how much power was produced to run up the stairs with skipping. Questions(complete sentences): 1. Why was work the same for all tests? 1pt 2. When did you produce the most power and why? 2pts If it’s green, it’s biology. If it smells 6 its chemistry. If it doesn’t work its physics. If it’s green, it’s biology. If it smells 7 its chemistry. If it doesn’t work its physics. G. F. E. D. C. B. A. Copyright 2003 _____ Screw _____ Lever _____ Inclined plane _____ Wedge _____ Wheel and axle _____ Gear _____ Pulley Write the letter of the picture below next to the name of the simple machine it matches. Your Name ___________________ Teacher’s name _____________________ Simple Machines Pre-Test | Wheel and Axle | Screw | Pulley | Inclined Plane | Lever Copyright 2003 A heavy object could be rolled up this simple machine, instead of lifting it straight up. Using this simple machine can save effort, although the object must usually cover more distance if this simple machine is used. _______________________ Examples of this simple machine are used to hold things together. It is made up of an inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder. ________________________ This simple machine can be used to split things apart or hold a door open. _______________ These simple machines are wheels with teeth on them that fit together when the simple machines are turned. These simple machines are used to increase or decrease turning power by changing their size. ____________________ This simple machine can be used to lift a weight. It has a fulcrum, or pivot point, which can be located in the center, near the end or at the end of this simple machine. ________________ A rope, a wheel with a groove in it and a weight make up this simple machine. You can pull down on the rope to lift the weight. __________________ These two parts act as one simple machine. They roll and are found on cars, bikes and wheelbarrows. ________________ Wedge | Gear Word Bank: Write the name of the simple machine that is described in the sentences below: Simple Machines Overview If it’s green, it’s biology. If it smells 8 its chemistry. If it doesn’t work its physics. Use the EdHeads Link on Mr. Satoʼs Links Page Circle One Kitchen or Garage Object Machine(s) Circle One Bedroom or Bathroom Object Machine(s) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 If it’s green, it’s biology. If it smells 9 its chemistry. If it doesn’t work its physics. Eureka! Simple Machines (inclined plane, lever, pulley) 1. When you use a machine to use less force you must increase the ___________________ that you apply the force. 2. Machines allow you to use less energy. True or False 3. The sloping flat thing is called an _________________________. 4. The pivot point on a lever is called the ____________________. 5. The name of the “teeter-totter” simple machine is a _________________. 6. The principle of the lever states “the longer the arm of the lever to which force is applied the less that ______________ need be. 7. Mechanical advantage can be determined by dividing the __________ force by the ___________ force. 8. Pulleys that stay in one place are called _________________ and those that change position are called _____________________. If it’s green, it’s biology. If it smells 10 its chemistry. If it doesn’t work its physics. THREE CLASSES OF LEVERS If it’s green, it’s biology. If it smells 11 its chemistry. If it doesn’t work its physics. Notes on Mechanical Advantage If it’s green, it’s biology. If it smells 12 its chemistry. If it doesn’t work its physics. Graded by:_____________________________________________________________ LAB: Mechanical Advantage score: Purpose (1pt): Information (1pt): Materials: Legos, scale, ruler, calculator Build A (1 pt) B (1pt) C (1pt) D (1pt) E (1pt) F (1pt) Simple Machines Completed? Inclined plane with a mechanical advantage of 5. height=______ hyp. length= ________ MA=_______ Inclined plane with a mechanical advantage of 40. height=______ hyp. length= ________ MA=_______ Lever with a mechanical advantage of 2. Input Dist. =_____ Output Dist.= _______ MA=______ Lever with a mechanical advantage of 10. Input Dist. =_____ Output Dist.= _______ MA=______ Lever with a mechanical advantage of 0.1 Input Dist. =_____ Output Dist.= _______ MA=______ What is the MA of the Pulley System? MA=_________ G (2pt) Build a lever with the most MA possible (must be >10) H (2pt) What is the weight of the load? ____________ Input Dist. =_____ Output Dist.= _______ MA=______ (round to 0.1, minus 1 pt if you ask Mr. Sato how to do this) Questions: SHOW WORK (round to 1st significant figure, ex: 0.0154 becomes 0.02) 1.How much force would be needed to push(input force) the load(output force) up your inclined plane in build A(use MA=5)? (2pt) Show work answer:________________ If it’s green, it’s biology. If it smells 13 its chemistry. If it doesn’t work its physics. 2. How much force would be needed to push the load up your inclined plane in build B? (use MA=40) (2pt) Show work answer:________________ 3. How much input force would be needed to lift the load up with your lever in build C? (use MA=2) (2pt) Show work answer:________________ 4. How much input force would be needed to lift the load up with your lever in build D? (use MA=10)(2pt) Show work answer:________________ 5. How much input force would be needed to lift the load up with your lever in build E? use MA=0.1)(2pt) Show work answer:________________ 6. How much input force would be needed to move our red load up with the pulley system? (2pt) Show work answer:________________ 7. How would you set up to lift a load with the least amount of input force?, draw a picture or explain with words. (2pt) Input Force Load Fulcrum Bar Draw or explain If it’s green, it’s biology. If it smells 14 its chemistry. If it doesn’t work its physics. Graded by:________________________________________________________ LEGO Madness Card Number Point value score: Type(s) of Machine(s) open 2 1st class lever, MA=4 open 2 2nd class lever, MA = 2 open 2 3rd Class lever, MA = 0.5 open 2 wheel and axle open 2 Inclined Plane with height of 5 cm and a MA= 4 open 4 fixed pulley open 4 movable pulley 6 back top 1 6 back bottom 1 7 inside top or bottom 1 7 back 3 8 inside to #5 1 8 back 1 9 inside to #6 1 If it’s green, it’s biology. If it smells 15 ____/22 Completed? its chemistry. If it doesn’t work its physics. Card Number Point Type(s) of Machine(s) value 9 back 6 10 back top 1 10 back bottom 1 11 inside 1 11 back 1 12 back 1 13 inside to #6 1 13 back 4 14 back 3 15 inside to #6 1 15 back 1 16 inside to #6 2 16 Back 3 17 inside to #6 2 18 inside to #5 1 18 back 2 19 back 3 If it’s green, it’s biology. If it smells 16 Completed? its chemistry. If it doesn’t work its physics. If it’s green, it’s biology. If it smells 17 its chemistry. If it doesn’t work its physics. Mind Map Use Word Processing and the following terms to create a concept map: machine, mechanical advantage, lever, input force, output force, work If it’s green, it’s biology. If it smells 18 its chemistry. If it doesn’t work its physics.