* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 9: Energy, Work, and Power
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
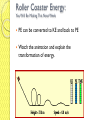
Energy Lesson Goal: Become familiar with various forms of energy. At the Bell: Pick up the worksheets at the front of class and complete the warm up. Warm Up 1) What is energy? 2) How many forms of energy can you name? 3) How do Humans get their energy? What is energy? Energy ◦ It’s the ability to do work (move something) ◦ Law of Conservation of Energy: Energy is never created or destroyed, but is changed from one form into another. ◦ Total amount of energy in a system is CONSTANT—it stays the same. What are the different forms of energy? Energy can be present in different forms of energy or a combination of forms. Mechanical Chemical Electrical Thermal Light Sound Mechanical Energy Mechanical energy: energy due to the position of something or the movement of something. Types of Mechanical Energy: Potential energy (PE): stored energy Kinetic energy (KE): energy of motion Potential Energy Potential energy is stored energy 3 types of PE ◦ Elastic Potential Energy Stored energy when a material is stretched or compressed Ex: Rubber Band or spring ◦ Chemical Potential Energy Energy stored in the bonds between atoms Ex: Energy stored in food Ex: Energy stored in batteries Gravitational Potential Energy Depends on the height and mass of an object. Stored energy due to position of an object Higher up = more potential energy More mass = more potential energy PRACTICE TIME! For the following pictures, name what type of potential energy is present: Kinetic Energy Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. If an object is moving, then it has kinetic energy. The faster an object is moving, the more kinetic energy it has. In most situations, as kinetic energy increases, potential energy decreases. PRACTICE TIME!!! In the following situation, tell me when the object will have the: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Least KE Most KE Least PE Most PE As Kinetic Increases, Potential Decreases What kind of energy does the sled have at the top of the hill before it starts moving? As the sled goes down the hill, what does that energy turn into? Roller Coaster Energy: You Will Be Making This Next Week PE can be converted to KE and back to PE Watch the animation and explain the transformation of energy. In The Real World… If a roller coaster goes down the first hill would it continue to go on forever if the track kept going? Roller Coaster Project… Electrical Energy Energy made available by the movement of electrons through a conductor (wire). We can make electric energy by converting another energy form into electricity: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Solar Panels Windmills Generators Chemical Where Does Michigan Get It’s Energy From? Chemical Energy Chemical energy is a type of energy that is stored in chemical bonds and can be converted into other forms… Examples ◦ Batteries store chemical energy ◦ Your body stores energy from food as chemical energy ◦ Photosynthesis Plants use energy from the sun to make sugar. Energy is stored in the bonds of the sugar Other Forms of Energy Thermal ◦ Heat ◦ Friction can cause KE to be converted to thermal energy Light ◦ Energy associated with electromagnetic waves Sun gives us light energy Solar Panels Sound ◦ Noise is actually a form of energy What is energy? Sci Show: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CW0 _S5YpYVo Tomorrow: Energy Transformations & Design Day for Roller Coasters Humans have created inventions to turn one form of energy into another to better our lives. Examples of these are: ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Light Bulbs Motors Air Conditioners Heaters Roller Coasters The list goes on and on… Physical Science P Energy Transformations Lesson Goal: Identify energy transformations occurring in familiar everyday situations. At the Bell: Pick up the notes at the front of class. Energy Transformations Warm Up: List the 6 main types of energy that we talked about yesterday: ◦ Mechanical ◦ Thermal (Heat) ◦ Light (Radiant) ◦ Electrical ◦ Chemical ◦ Sound The whole point of producing energy is to turn it from one form into another…these are ENERGY TRANSFORMATIONS. The ways we produce electricity are varied but all rely on energy transformations. Examples of Energy Transformations 1) Toaster 2) Fan 3) Lighter 4) Windmill Producing Electricity 5) A Dam Producing Electricity Examples of Energy Transformations 6) When you drop a book and it is falling, what kind of energy does the book have? 7) What is the energy transformation when gasoline powers a car driving down the road? Examples of Energy Transformations 8) What is the energy transformation when you eat some pasta before you run a marathon? 9) What is the energy transformation of dynamite exploding? Examples of Energy Transformations 10) A Solar Panel 11) Burning Coal for Energy Examples of Energy Transformations 12) Going Up and Down on a Skateboard Ramp? 13) What is the energy transfer of lighting a lighter?