* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Daily PACT Review Questions
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to genetics wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Soil food web wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
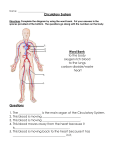
Science Grade 7 Daily PASS Review Questions DATE QUESTION 1. 2. 7-1.1 What is the proper way to carry a microscope? 3. 7-1.4 Why should you make several trials in an investigation? 4. 7-1.5 How do graphs and charts show the relationship between you independent and dependent variables? 5. 6. 7-2.1 What is a cell? 7. 8. 7-2.1 Explain the function of the mitochondria. 9. 7-2.2 What are the major structural differences between a plant and an animal cell? 10. 7-2.3 Compare the body shapes of bacteria. 11. 7-2.3 Compare the characteristics of the euglena, paramecium, and amoeba. 7-1.3 When conducting a scientific investigation, why should you test only one variable? 7-2.1 What is an organelle? 7-2.1 Describe the function of the nucleus. ANSWER A microscope should be carried by the arm and the base. An experiment will not be valid unless you control all but one variable. It will not be a fair test. You may not come up with the same results each time. You should make several trials and take the average of all the trials. Graphs and charts organize your data and provide an easy means of comparing the changes between the variables. The cell is the smallest unit of life that conducts all life functions. Organelles are smaller structures within a cell that carry out life functions. The mitochondria break down sugar and releases energy. The nucleus is the control center of the cell. It directs all of the life functions that the cell carries out. Plant cells have a cell wall for added support and protection, large vacuoles for water storage, and chloroplasts for converting light energy into food. Animal cells have no cell wall, no chloroplasts, and have smaller vacuoles. Spirilla are bacteria that have spiral shaped bodies. Cocci are bacteria that have round or sphere shaped bodies. Bacilli are bacteria that have rod shaped bodies. The euglena contains chloroplasts to make its own food. It uses a whiplike flagella to move about. The paramecium uses cilia to move about. It also has a groove that acts as a mouth opening to let food enter. The amoeba pseudopods, finger-like projections of cytoplasm, to move and obtain food. Department of Curriculum and Instruction 2/5/07 12. 7-2.4 Compare and contrast the processes of photosynthesis and respiration. 13. 7-2.4 Briefly explain the process of mitosis. 14. 7-2.5 What is heredity? 15. 7-2.5 What is the difference between a genotype and a phenotype? 16. 7-2.5 What is a dominant trait? 17. 7-2.5 In what instance will a recessive trait be expressed? 18. 7-2.6 What is a Punnett square? 19. 7-2.6 Explain the difference between a purebred organism and a hybrid. 20. 7-2.7 Distinguish between an inherited trait and an environmental trait. 21. 7-3.1 Put the following group of words in order from simplest to more complex: system, cell, organ, tissue. 22. 7-3.2 List the primary organs make up the digestive system? 23. 7-3.2 What is the function of the liver? Photosynthesis and respiration are opposite reactions. Photosynthesis uses light energy to turn water and carbon dioxide into food. Respiration takes food and breaks it down into carbon dioxide and water to release energy. Mitosis is the process of cell division that results in a parent cell making a copy of itself, resulting in two identical daughter cells. Heredity is the passing of traits (physical characteristics) from parents to offspring. The genotype is the genetic makeup of an organism. The phenotype is the outward physical appearance and behavior of an organism as a result of its genotype. A dominant trait will always be expressed even when a recessive trait is present. (TT or Tt) A recessive trait can only be expressed when there is no dominant allele present for that trait. (tt) A Punnett square is a tool used to predict the ratio of possible genes that will be expressed in an offspring based on the genes of the parents. A purebred organism has two of the same alleles for a trait. (TT, or tt). A hybrid has one dominant and one recessive trait for an allele. An inherited trait is passed genetically from parent to offspring. Some physical characteristics can be influenced or changed by environmental factors such as temperature, light, and availability of food. (i.e.: fewer leaves on a tree during a drought) Cell > tissue> organ > organ systems. A tissue is a group of specialized cells that works together. An organ is a two or more tissues that work together to perform a specific function. An organ system is two or more organs that work together to perform a specific function. Mouth> esophagus> stomach> small intestines> large intestines> rectum> anus The liver produces bile that is used to break of fat particles during digestion. Department of Curriculum and Instruction 2/5/07 24. 25. 26. 27. 7-3.2 What is the function of the pancreas? 28. 29. 30. 7-3.2 What muscle aids in the breathing process? 31. 7-3.2 What are the three main parts of the nervous system? 32. 7-3.2 What are the 3 main parts of the brain and what are their functions? 33. 7-3.2 What are the three types of muscles and their function? 34. 7-3.3 What is the function of the skeletal system? 35. 7-3.3 What is the function of skin? 36. 7-3.3 All of the body systems are dependent on the ______________________ system. 37. 7-3.3 Summarize how the respiratory system and the circulatory system work together. 38. 7-3.3 Describe how the digestive system works with the circulatory system. 7-3.2 What is purpose of the gall bladder? 7-3.2 List the 3 types of blood vessels? 7-3.2 How do the blood vessels work together to complete the circulatory system? 7-3.2 What is the function of the lungs? 7-3.2 What is the function of the kidneys? Produces digestive fluids that help break down food during digestion. The gall bladder stores bile produces by the liver until it is needed. Arteries, capillaries, and veins Arteries carry oxygen rich blood away from the heart. Capillaries are very small blood vessels where the oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged. Veins carry carbon dioxide and other waste products from the body parts back to the heart. The diaphragm contracts & releases to move air in and out of the lungs. Carbon Dioxide and Oxygen are exchanged between the air and blood. The kidneys filter urea and other waste materials out of the blood. The waste materials are then eliminated as urine. The brain, the spinal chord, and the peripheral nerves are the main parts of the nervous system. The cerebrum control thoughts and voluntary actions. The cerebellum helps with balance and coordination. The brain stem controls vital involuntary actions such as breathing, heartbeat, and digestion. Skeletal muscle attaches to the bones and provides the force to move the bones. Cardiac muscle is the muscle that forms the heart. Smooth muscles control many types of involuntary movement, such as digestion. The skeletal system provides shape and support for the body, protects many organs, produces blood cells, and store some materials. Skin covers the body and prevents water loss, helps control body temperature, helps protect the body from injury and infection, and gets rid of wastes. All of the body systems are dependent upon the circulatory system to transport materials throughout the body. The respiratory system works with the circulatory system to ensure that oxygen enters the blood stream and that carbon dioxide is removed from the blood stream. The circulatory system picks up nutrients that have been made available through the digestive process and transports them throughout the body. Department of Curriculum and Instruction 2/5/07 39. 7-3.3 How does the nervous system work with the muscular system and the skeletal system? 40. 7-3.4 What is an infectious disease? 41. 7-3.4 Explain the responsibility of the immune system to the body. 42. 43. 7-3.4 What causes a cold or the flu? 44. 7-3.4 Explain how diabetes affects the body. 45. 7-3.4 How does asthma affect the body? 46. 7-4.1 How would you summarize a population? 47. 48. 7-4.1 How would you summarize a community? 49. 7-4.1 Which is larger, a biome or an ecosystem? 50. 7-4.1 Compare an organisms habitat with its niche. 51. 7-4.2 What is a food chain? 52. 7-4.2 Compare a food chain to a food web. 53. 7-4.3 What is a natural hazard? 7-3.4 How would you describe a noninfectious disease? 7-4.1 Compare a community with an ecosystem? The nervous system relays impulses to and from the muscular and skeletal systems to direct behavior and movement. Diseases that are caused by pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or protists, that is easily spread from one person to the next. The immune system recognizes a pathogen and responds to it according to its type. Colds and the flu are caused by viruses. Noninfectious diseases are not caused by pathogens. They are inherited or cause by a malfunction in a body system. Diabetes is a disorder that results in higher than normal blood sugar. It is caused by the body’s inability to produce or use insulin. Asthma affects the lungs and the air passages within the lungs. The airways become swollen and restrict airflow. This is caused by allergens such as dust, mold, and pet dander. Exercise and cold weather can also cause an asthma attack. A population is all the individuals belonging to a particular species in a given area at one time. All the different populations in an area at a particular time. A community is all the different populations in an area; whereas, an ecosystem is made up of all the communities in an area. A biome is larger. A biome is made up of all the ecosystems in area according to climate, vegetation, etc. An organism’s habitat is the place where it finds food, water, and shelter. Its niche is the role or job it plays within its environment. A food chain uses pictures or words and arrows to illustrate the energy that is transferred from one organism to another. A food web is made up of several food chains that interconnect with one another. An event that causes a change in an environment, such as a landslide, a flood, or a wildfire. Department of Curriculum and Instruction 2/5/07 54. 7-4.3 What is a limiting factor? 55. 7-4.3 Summarize how changes in a population can affect an environment. 56. 7-4.3 Explain carrying capacity. 57. 7-4.4 Why is soil quality so essential to an ecosystem? A change in the environment that affects the number of organisms an environment can support, such as climate and the availability of food, shelter, and water. The number of births or deaths in a population may affect an environment by depleting some resources. Immigration or emigration of other species into a population or community may also put stress on the number of resources available in an ecosystem. Carrying capacity is the maximum number of organisms that an environment can support. Every organism that lives on land depends on the soil either directly or indirectly. If the soil quality changes, this will directly affect the types of plants that will grow in that area, thusly affecting all the organisms that depend on those plants for food. Department of Curriculum and Instruction 2/5/07