* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download hot, less dense material is forced upward by the surrounding cooler
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
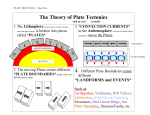
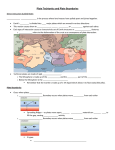
Plate tectonics combines the ideas of continental drift and seafloor spreading The Earth’s crust and part of the upper mantle are broken into sections (plates) that move on a plastic layer of the mantle Think of the plates as rafts that float Plates are made of the crust and upper mantle, the lithosphere The upper layers are less dense than the lower layers The plastic layer under the lithosphere is the Asthenosphere The rigid plates of the lithosphere float and move on the asthenosphere When plates move they can move: o Towards each other o Away from each other o Slide alongside each other Movement at any one plate boundary will result in changes at other plate boundaries Divergent Boundary the boundary between plates that are moving apart The divergent boundary in the Atlantic Ocean is called the Mid-Atlantic Ridge This divergent boundary is pushing the North American Plate and the Eurasian Plate away from each other Convergent Boundary The boundary formed when two plates push together When an oceanic plate runs into a less dense continental plate, the denser oceanic plate sinks (subducts) under the continental plate. The oceanic plate subducts into the mantle at a subduction zone This can cause volcanoes, why? When one plate enters the mantle it forces magma up along the plate boundary, forming volcanoes Subduction zones can also occur when two oceanic plates collide In this case, the denser (older) plate will subduct beneath the less dense (younger) plate Can also form volcanoes What about when two continental plates collide? Usually there is no subduction zone because both plates are less dense than the asthenosphere What happens? The plates crumple into each other and form mountain ranges Earthquakes are common at these convergent boundaries Volcanoes do not form here, why? Transform Boundary The boundary formed when two plates slide past one another The plates can move in opposite directions The plates can also move in the same direction, but at different rates When one plate slips past the other one suddenly, earthquakes occur Convection currents! What are convection currents? hot, less dense material is forced upward by the surrounding cooler material This causes a cycle of heating, rising, cooling, and sinking, called a convection current The transfer of heat inside the Earth (the inside of the Earth is very very hot!) provides the energy to move the plates When rocks break and move along surfaces, a fault forms Faults move rock layers out of place and can form mountains (fault-block mountains) Rift valleys and mid-ocean ridges can form where Earth’s crust separates At transform boundaries, two plates slide past one another without mushing together or pulling apart The plates stick and then slide, mainly in a horizontal direction, along large strike-slip faults This causes rocks on the opposite sides of the fault to move Scientists can now use GPS to measure the exact movements of Earth’s plates The latest research states that Earth’s plates are moving at a rate of 1-10cm per year!