* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction To Artificial Intelligence
Kevin Warwick wikipedia , lookup
Machine learning wikipedia , lookup
Incomplete Nature wikipedia , lookup
Technological singularity wikipedia , lookup
Knowledge representation and reasoning wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Philosophy of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Intelligence explosion wikipedia , lookup
Existential risk from artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
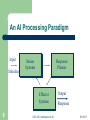
Introduction To Artificial Intelligence CSC 415-515 What Is (Artificial) Intelligence? What is intelligence? – – – – 2 CSC 415, Introduction to AI The ability to learn or understand from experience The ability to acquire and retain knowledge The ability to respond quickly and successfully to a new situation The ability to use reason to solve problems 5/1/2017 What Is Artificial Intelligence? 3 If intelligence is learning, understanding, retaining, responding, and using reason then what is AI? Is mimicking such phenomena using a machine an expression of artificial intelligence? CSC 415, Introduction to AI 5/1/2017 The Turing Test 4 Place both a human and a machine mimicking human responses outside the field of direct observation and use an unbiased interface to interrogate them. If the responses are distinguishable, the machine is not displaying intelligence. CSC 415, Introduction to AI 5/1/2017 Two Foci of AI Symbol processing – – Connectionist processing – – 5 An early thrust of AI research Stereotyped by expert systems, knowledge bases, and inference engines Typified by emergent computation Often leads to representations possessing large degrees of parallelism CSC 415, Introduction to AI 5/1/2017 An AI Processing Paradigm Input Stimulus Sensor Systems Response Planner Effector Systems 6 CSC 415, Introduction to AI Output Response 5/1/2017 Some Key Contributors: A Note on Origins 7 McCulloch and Pitts (perceptrons) Turing, von Neumann, Shannon, and McCarthy Rosenblatt (perceptron learning) Minsky and Papert Widrow and Hoff (Adaline) Zadeh (fuzzy logic) Werbos, Rumelhart, McClelland, Hinton, Parker, Le Cun Grossberg, Hopfield Holland, Goldberg, De Jong, Koza CSC 415, Introduction to AI 5/1/2017 What Will We Study? Algorithms and Representation Sensor systems – – Response planning – – Motion planning—TSP, resource allocation, scheduling Search strategies—Swarms, GAs, Neural networks Effector systems – 8 Primarily one- and two-dimensional signal sources such as sounds, image data, sunspot counts, or values in a chaotic time series Other sensor data representation such as ensemble codes and transforms Robot action control CSC 415, Introduction to AI 5/1/2017 Robot Demos Simple line following Find-and-grab Robot tag – – 9 Robot-to-robot communication (basis for cooperation) Multi-sensor processing Two sensor, line following CSC 415, Introduction to AI 5/1/2017