* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth/Space Science FINAL Review/Study Guide: Gardana DUE
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
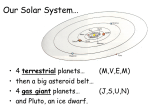
Earth/Space Science FINAL Review/Study Guide: Gardana DUE ON DAY OF MIDTERM!!!! Worth a test grade!! Use your notes and workbook to answer the following questions. Due on day of midterm. Attach the answers on a separate sheet of paper. The chapters correspond to location in workbook. Chapter 27 “Planets of the Solar System” 1.) What is the nebular hypothesis? 2.) How do the two models of the universe that were developed by Ptolemy and Copernicus compare? 3.) What are the basic characteristics of the inner planets? 4.) What are some similarities and differences between inner planets? 5.) What planetary features allow Earth to sustain life? 6.) How do the outer planets differ from terrestrial planets? 7.) How do the characteristics of the outer planets compare to one another? 8.) Why is Pluto considered a dwarf planet? Chapter 28 “Minor Bodies of the Solar System” 9.) What are four kinds of lunar surface features? 10.) What is the shape of the moon’s orbit around the Earth? 11.) Why do eclipses happen? 12.) How do movements of the moon affect tides on Earth? 13.) How are the two moons of Mars similar, and how are they different? 14.) How did scientists discover volcanoes on Io? 15.) What is one special characteristic of each of the Galilean moons? 16.) How do the rings of Saturn differ from the rings of the other outer planets? 17.) What are the physical characteristics of asteroids and comets? 18.) Where is the Kuiper Belt located? 19.) How do meteoroids, meteorites, and meteors differ? 20.) What is the relationship between the Oort cloud and comets? Chapter 29 “The Sun” 21.) How do the sun’s radiative and convective zones compare? 22.) What are the three layers of the sun’s atmosphere? 23.) How does the sun convert matter to energy in its core? 24.) How are sunspots related to powerful magnetic fields on the sun? 25.) What are the differences between prominences, solar flares, and coronal mass ejections? 26.) How can solar wind cause auroras on Earth? Chapter 30 “Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe” 27.) How do astronomers determine the composition and temperature of a star? 28.) Why do stars appear to move in the sky? 29.) How do astronomers describe the distances to stars? 30.) What is the difference between absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude? 31.) How does a protostar become a star? 32.) How does a mainsequence star generate energy? 33.) How does a star evolve after its mainsequence stage? 34.) What are the characteristics of a constellation? 35.) What are the three main types of galaxies? 36.) How is a galaxy with a quasar in it different from a typical galaxy? 37.) How did Hubble’s discoveries lead to an understanding that the universe is expanding? Chapter 2 38.) What are Earth’s compositional and structural layers? 39.) What is the difference between an open system and a closed system? 40.) What are the characteristics of Earth’s four spheres? 41.) What are the two main sources of energy in the Earth system? 42.) What are four cycles of matter on Earth? Chapter 10 43.) What is Wegner’s hypothesis of continental drift? 44.) What is seafloor spreading? 45.) How does paleomagnetism support the idea of seafloor spreading? 46.) How does seafloor spreading provide a mechanism for continental drift? 47.) What is the theory of plate tectonics? 48.) What are the three types of plate boundaries? 49.) What are three causes of plate movement? 50.) How do movements of tectonic plates change Earth’s surface? 51.) How have the movements of tectonic plates affected Earth’s climate and life? 52.) What is the supercontinent cycle? 53.) What kinds of plate collisions form mountains? 54.) What are four main types of mountains? Chapter 12 55.) Why do most earthquakes happen at plate boundaries? 56.) What tool do scientists use to measure and record earthquakes? 57.) How are tsunamis and earthquakes related? 58.) How can a large earthquake affect buildings? 59.) How can you stay safe during an earthquake? 60.) How do scientist predict earthquake risks? Chapter 13 61.) What are three tectonic settings where volcanoes can form? 62.) What are three events that may signal a volcanic eruption? Chapter 16 63.) What are two properties of aquifers? 64.) How is the water table related to the land surface? 65.) How are wells, springs, and artesian formations related? 66.) What are two features formed by hot groundwater? 67.) How does water chemically weather rock? 68.) How do caverns and sinkholes form? Study Land Formations and differences between the weather systems El Nino and La Nina.