* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Final Exam Review - HCC Learning Web
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Surface runoff wikipedia , lookup
Low-temperature thermal desorption wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Soil contamination wikipedia , lookup
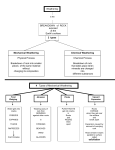
FINAL EXAM REVIEW Part 1-- Weathering, Erosion, Mass Wasting Weathering – breaking rocks down into smaller and smaller particles. The particles stay in place - not moved by wind water or ice Erosion =removal of rock particles and soils by water, wind or glacial ice. Transportation of particles is part of the erosion process (Weathering weakens the rocks, while erosion moves the weathered material.) Mass Wasting – movement of rock and soil downward due to gravity. These processes are an important part of the rock cyclecreating sediment that may become sedimentary rocks or soil By studying the effects of weathering- we can make stronger roads, and structures that last longer without costly repairs Types of weathering 1. Mechanical Weathering: Physically breaking of rocks by abrasion, impact, etc. 2.Chemical Weathering Decomposition of rock from exposure to atmospheric gases (oxygen, water vapor and carbon dioxide) or liquid water= a chemical reaction takes place Types of Mechanical Weathering 1. Frost Wedging Cold weather needed to freeze the water Water fills the cracks in the rocks Water expands when it freezes causing the crack to widen Rocks finally split/ break apart Types of Mechanical Weathering 2.Thermal Cycling Large temperature variations break rocks with due to repeated expansion and contraction 3.Pressure Release or Exfolitaion Removal of overlying rock layers, releases pressure, Underlying rocky material is pushed upward and breaks in sheets Types of Mechanical Weathering Plant Growth or Root Wedging Burrowing Animals Growing roots widen fractures in rock Mr. Gopher likes to move pieces of rock out of his way- causing rocks to chip or break Root wedging Chemical Weathering 1.Acid Rainwhen water vapor reacts with CO2, Sulfur Dioxides ,etc to produce weak acids that fall as rain- dissolving rocky materialsome rocks dissolve easier than othersEx: Limestone Statues affected by acid rain 2.Oxidation- reaction of Oxygen on a substance –ex: rust, tarnish Close view of the right hand of the Statue of Liberty Plants can cause chemical weathering Plant roots can emit chemicals that dissolve rocks and brick mortar Differential Weathering and Erosionsome rocks weather and erode faster than others Mass Wasting Factors making mass wasting likely: Over steeping or Undercutting Wave action or Human impact Thick layer(s) of loose rock , debris, soil Presence of water Lubricates moving rocks/debris/soil Lack of vegetation No roots to hold rock/soil in place Seismic (earthquake) activity Creep (or soil creep) Very slow down slope movement of soil Can be costly to maintain homes, etc., on creeping ground as foundations, walls, pipes and driveways crack and shift down slope over time Don’t usually see the movement, just the effects of the movement Not straight and upright Examples of Creep Curved tree trunks indicate creep Flow Fall A disaster waiting to happen-Why??? Ways to control Mass WastingBuild a retaining wall Build a covered Bridge Stitching Soil Horizons (Layers) Dust Bowl- Lasted 10 years- Soil Conservation Began Soil Conservation Techniques Terracing Contour plowing windbreaks Windbreaks Weathering and Erosion - Recap A. Weathering=Rocks are broken down into sediments- by Physical or Chemical means B. Erosion= The movement of rocky material and sediment by wind ,water and ice C. mass Wasting= downward movement of materials due to gravity I Types of Weathering A. Mechanical 1. Frost wedging 2. Thermal Cycling 3. Root wedging 4. Pressure release or Exfoliation 5. Burrowing Animals B Chemical 1 Acid Rain a. Carbonic Acid b. Sulfur Dioxides 2. Oxidation C. DIFFERENTIAL WEATHERING= different types of rocks weather at different rates D. Dust Bowl -1930's--- 5 most effected states= Texas, Kansas, Oklahoma, Colorado, New Mexico ---- Soil Conservation measures were developed due to the loss of top soil E. Top soil is the O Horizon (organic material) and the A Horizon(organic and mineral material) (different layers of soil are called Horizons ) RecapMass wasting is downward movement of materials due to gravity Types of Mass Wasting 1. Flow 2. Fall 3. Slide Triggers (something that makes the materials start the downward movement) 1. Saturation- too much water 2. Lack of vegetation 3. Over steeping 4. Undercutting 5. Earthquakes 6. Adding additional weight such as a house or building Slowest type of Mass Wasting is Creep Prevention – Ways to reduce or slow the amount of Mass Wasting 1.Retention Walls- must have drainage 2. Stitching rocks together with bolts 3. Build a covered area so rocky material will not fall on a roadway 4. Removal of loose materials 5.Removal(if possible) of the over steeped area 6. Terracing - used on hill sides