* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fact sheet for Electricity and Magnetism Year 8 Lesson One
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
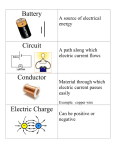
Fact sheet for Electricity and Magnetism Year 8 Lesson One Charging Up 1. Names the two types of electrical charges 2. Which charges attract 3. Which charges repel each other? 4. What charge does a proton have? 5. What charge does an electron have? 6. What charge does a neutron have? Lesson Two Circuits and Current 7. Give the definition of current 8. What does a switch do in a circuit? 9. What piece of equipment do you measure current with? 10. What is the unit of current? 11. What does a battery do? Lesson Three Potential Difference 12. Which piece of equipment do you use to measure potential difference? 13. What is the unit of potential difference 14. Give another word for potential difference Lesson Four Series and Parallel 128- 129 15. Draw a simple series circuit Kerboodle Pages 122-123 Positive and negative Positive and negative • Negative and negative • Positive and positive Positive Negative Neutral Kerboodle pages 124-125 The amount of charge flowing per second Opens and closes a gap in the circuit An ammeter Amps (A) Pushes charge around a circuit Kerboodle Pages 126-127 A voltmeter Volts Voltage Kerboodle Pages 16. Draw a simple parallel circuit 17. What happens to the current in a series It is the same everywhere circuit? 18. What happens to the current in a parallel The current in all the branches of the circuit circuit? adds up to the current at the beginning and end 19. What happens to the potential The potential difference across the difference in a series circuit? components adds up to the potential difference of the battery 20. What happens to the potential difference in a parallel circuit Lesson Five Resistance 21. What is resistance? 22. Whatis the unit of resistance? 23. How do you calculate potential difference (Ohms Law)? 24. Why are metals good conductors? 25. Why is plastic an insulator Lesson Six Magnets and Magnetic fields 26. What happens if you put two north poles of a magnet together? 27. What happens if you put a north and a south pole together? 28. Name four magnetic materials 29. Draw the field lines around two magnets attracting The potential difference across each component is the same a the potential difference across the battery Kerboodle Pages 130 -131 How easy or hard it is for charge to flow through a component Ohms (Ω) V=IR Voltage = Current x Resistance They have a low resistance as lots of electrons can move. They have a huge resistance as not many electrons can move Kerboodle Pages 132-133 They repel They attract Iron, steel , nickel and cobalt 30. Draw the field lines around two magnets repelling 31. Why does a compass work? Lesson Seven Electromagnets 32. What is special about an electromagnet? 33. Describe an electromagnet 34. How do you make an electromagnet stronger? Lesson Eight Using electromagnets 35. How can magnets be used on a train 36. What is a relay 37. Give two uses of electromagnets 38. How does a motor work? The Earth is like a huge bar magnet Kerboodle pages 134-135 It’s a magnet you can switch on and off. It is much stronger than a normal magnet It is a coil of wire with a core or iron or steel • Increase the number of turns in the coil • Increase the current • Have a magnetic material as the core. Kerboodle pages 136-137 Powerful magnets on the track repel magnets on the train A small current can turn on a much bigger current in a separate circuit • Starting a car • Sorting metal A current flows in a coil between two permanent magnets. The coil begins to spin