* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 13 – European Explorers
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
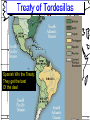
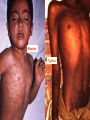
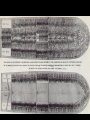
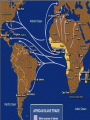
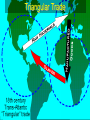
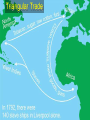
Chapter 2 – European Explorers “Age of Exploration” Chapter Summary • Europeans risked dangerous ocean voyages to discover new sea routes. • Spain and Portugal control the “New World” • Early European explorers sought gold in Africa, then began to trade slaves. Motives and Means • 1500-1800 Dynamic Energy in Europe leads to European Expansion • Why would they risk so much to explore? • The 3 G’s: • God • Gold • Glory The Portuguese • Southern coast of Africa along the Atlantic = •“The Gold Coast” The Portuguese = look to round Africa to return from India with Spices • In 1488, Bartholomeu Dias rounded the tip of Africa looking for a route to India. • Vasco da Gama rounded the tip of Africa and sailed on to the port of Calcutta in India in 1498. DIAS • He took on a cargo of spices and returned to make a profit of several thousand percent. da Gama Da Gama’s Ship What Did Columbus Look Like? Spanish – Sail West & Voyage to Americas • As the Portuguese sailed east to reach the source of the spice trade, the Spanish sailed west to find it. • Italian Christopher Columbus sails for Spain. • 4 voyages – believes he reaches the Indies • Opposing viewpoints – page 410 The Voyage Video: Age of Exploration- Race for Riches Voyages to the Americas (cont.) • Both Spain and Portugal feared the other would claim some of its newly “discovered” territories. • In the 1494 Treaty of Tordesillas, they decided on a north-to-south line through the Atlantic Ocean and the easternmost part of South America. • Portugal claimed the unexplored territories east of the line, Spain to the west. Like the modern “Space Race” – European Nations were in a race to find new territories. Spanish Win the Treaty: They get the best Of the deal Voyages to the Americas (cont.) • Amerigo Vespucci – Italian Explorer, Navigator, and Cartographer. • Wrote letters of the New World. • The European public learned about the newly discovered continent of the Americas for the first time • Led to the use of his first name Americus in Latin for “Americas” The Conquistadors - Spanish Explorers • Cortes, Pizarro examples of Conquistadors • Forced labor of Native Americans led to the cruel treatment Video: Francisco Pizzaro Voyages to the Americas (cont.) Disease Ravages Native Americans Smallpox, Measles, Typhus Hispaniola – pop. 250,000 in 1492 pop. 500 in 1538 Mexico – pop. 25 Million in 1519 pop. 1 Million in 1630 Measles Typhus Commerce & Trade • Mercantilism – set of principles that dominated economic thought in the 17th century. • Prosperity depends on supply of bullion – gold & silver • Balance of Trade – diff between what a nation imports and exports Mercantilism The prosperity of a nation is dependent upon its supply of capital, and that the global volume of international trade is "unchangeable". Economic assets (or capital) are represented by bullion (gold, silver, and trade value) held by the state, which is best increased through a positive and healthy balance of trade with other nations (exports minus imports). Europeans Needed Cheap Labor • The Middle Passage – name for the transport of slaves from Africa to America. Africans originally brought to the new world to supply labor for sugar plantations Slave Trade The Middle Passage: Drawings by Tom Feelings March 12 - December 3, 2000 Video: Slave Trade Video: The Triangular Trade: Growth of European Slave Trade Triangular Trade Triangular Trade