* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The electron! Speed and energy notes
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Ultrafast laser spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
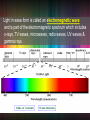
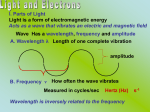
•Niels Bohr in 1913 proposed a quantum model for the hydrogen atom which correctly predicted the frequencies of the lines (colors) in hydrogen’s atomic emissions spectrum. •His model gave atoms only certain allowable energy states. •The lowest state is called the ground state. •When an atom gains energy it is said to be in an excited state. • When elements are given energy from a variety of sources (heat, light, electricity) the electrons absorb that energy, & jump up to a higher energy level, the excited state. The electrons can return to ground state by giving off the energy as a color of light, called photons of light. •Each element gives off a unique color called its atomic emission spectrum. The electrons are what give each element their unique color. •Light gives us a clue to how electrons are arranged. Light behaves like a wave & like a particle. •wave particle duality of nature – everything in the universe has properties of both waves and particles (ex. Duality of good vs. evil in man) Light in wave form is called an electromagnetic wave and is part of the electromagnetic spectrum which includes x-rays, TV waves, microwaves, radio waves, UV waves & gamma rays. Trough – low points Crest – high points Amplitude – max displacement from equilibrium (middle of wave). Wavelength – the shortest distance between points in which a wave repeats itself. (crest to crest or trough to trough) symbol - λ Rope demo Parts of a Wave length •Wavelength crest to a crest or trough to a trough lambda •Symbol = λ ( ) •Measured in meters of one wave, from a •Frequency- number of waves that pass a point in 1 second •symbol = f or v ( nu ) •Measured in Hertz (Hz) or 1/s, s-1 •All EM radiation travels at the speed of light, c = 3.00 x 108m/s in the vacuum of space Formula: c = λ v or Formula: c = λ f c is constant speed of light ν or f is frequency λ is wavelength Ex. 1) Light in the middle of the ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic radiation spectrum has a frequency of 2.73x1016s-1. Find the UV light’s wavelength. Ex. 2) Yellow light has a wavelength of 5.70x10-7m. Calculate the frequency of the yellow light. •Light as a particle is called a photon. •Light is like a particle because there are only certain amounts of energy it can have. •The minimum amount of energy a photon can have is called a quantum. •Max Planck found that this energy could be calculated with the formula E = h ν or E = h f •E is energy, measured in Joules (J) •h is Planck’s Constant = 6.626 x 10-34 Js •v or f is frequency (Hz or 1/s or s-1) same frequency as earlier •Once the minimum amount of energy is calculated, the actual energy can be a multiple of the quantum amount. (1x E, or 2 x E, or 3 x E....) Ex. 3 From examples 1 and 2, we have the frequency of UV light as 2.73x1016s-1 and the frequency of yellow light as 5.26x1014Hz. Calculate the energy in joules, of an individual photon of each. Ex. 3 From examples 1 and 2, we have the frequency of UV light as 2.73x1016s-1 and the frequency of yellow light as 5.26x1014Hz. Calculate the energy in joules, of an individual photon of each. UV light (6.626x10-34Js)(2.73x1016s-1) =1.81x10-17J yellow light (6.626x10-34Js)(5.26x1014s-1) =3.49x10-19J Which has more energy? UV light or yellow light? Ex. 3 From examples 1 and 2, we have the frequency of UV light as 2.73x1016s-1 and the frequency of yellow light as 5.26x1014Hz. Calculate the energy in joules, of an individual photon of each. UV light (6.626x10-34Js)(2.73x1016s-1) =1.81x10-17J yellow light (6.626x10-34Js)(5.26x1014s-1) =3.49x10-19J Comparing the two, UV light has more energy than yellow light •Electrons (called photoelectrons) are emitted from a metal’s surface when light of a certain frequency shines on the surface. •Example: calculators. •Photoelectric cells convert light into electric energy In Summary c = λ f or c = λ v c = speed of light = 3.00 x 108 m/s f (or v) = frequency = Hz, 1/s, s-1 λ = wavelength = m E = h f (or E = h ν ) E = Energy = J h = Planck’s Constant = 6.626 x 10-34 Js Water drops in the air disperse the white light of the sun into a rainbow. What is the energy of a photon from the violet portion of the rainbow if it has a frequency of 7.23 x 1014 Hz?