* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Temperature
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
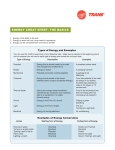
Do Now Give an example for each of the following energy conversions. 1. 2. 3. 4. Electrical → Thermal Chemical → Mechanical Electrical → Mechanical Mechanical → Sound Write your answers in your science journal. Do now The temperature of boiling water is 100° on the Celsius scale and 212° on the Fahrenheit scale. Look at each of the following temperatures and decide whether you think that it is hot or cold: 60°F, 60°C, 37°F, 37°C, 0°C,100°F, 70°F Write your responses in your science journal. •Objectives: Describe how temperature relates to kinetic energy. Compare temperatures on different temperature scales. Give examples of thermal expansion. Learning Target Today I will: learn about temperature and how it related to kinetic energy. So that I can: explain and describe how temperature is determined. I will know I got it if: I can clearly explain how temperature is determined and its relation to kinetic energy. Vocabulary Temperature Thermal expansion Agenda Today we will: Learn how heat is transferred by taking notes. Complete a group and individual activity exploring heat transfer. Exit ticket Anticipatory Set https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yXT012us9ng What Is Temperature? • Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in an object. • Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. All moving objects have kinetic energy. • The amount of kinetic energy that an object has depends on the object’s mass and speed. What Is Temperature?, continued • Temperature and Kinetic Energy All matter is made of atoms or molecules that are always moving. • The faster the particles are moving, the more kinetic energy they have. The more kinetic energy the particles of an object have, the higher the temperature of the object is. What Is Temperature?, continued • The gas particles on the right have a higher average kinetic energy than those on the left. So, the gas on the right is at a higher temperature. What Is Temperature?, continued • Average Kinetic Energy of Particles The motion of particles in matter is random, so individual particles have different amounts of kinetic energy. • When you measure an object’s temperature, you are measuring the average kinetic energy of the particles in the object. Measuring Temperature • Using a Thermometer Thermometers can measure temperature because of a property called thermal expansion. • Thermal expansion is the increase in volume of a substance in response to an increase in temperature. As a substance’s temperature increases, its particles move faster and spread out. Measuring Temperature, continued • Temperature Scales Three common temperature scales are the Celsius scale, the Fahrenheit scale, and the Kelvin scale. • The Kelvin scale is the official SI temperature scale. 9 F C 32 5 5 C F 32 9 Transferred Thermal Energy • Heat is the energy transferred between objects that are at different temperatures. • When two objects at different temperatures come into contact, energy is always transferred from the object that has the higher temperature to the object that has the lower temperature. Transferred Thermal Energy, continued • Heat and Thermal Energy Heat is transferred in the form of thermal energy. Thermal energy is the total kinetic energy of the particles that make up a substance. • Thermal energy depends partly on temperature. Thermal energy also depends on how much of a substance there is. Transferred Thermal Energy, continued • Reaching Thermal Equilibrium The point at which two object that are touching reach the same temperature is called thermal equilibrium. • When objects that are touching have the same temperature, they are at thermal equilibrium and no net change in the thermal energy of either one occurs. Exit Ticket