* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HEART - Wikispaces
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
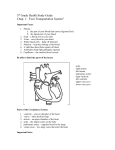
ANATOMY OF HEART Thorax • Thorax is the superior part of the trunk between the neck and abdomen. • It extends below the neck to the diaphragm. • It contains the primary organs of respiratory and cardiovascular system • A typical human rib cage consists of 24 ribs, the sternum, costal cartilages, and the 12 thoracic vertebrae. • All ribs are attached in the back to the thoracic vertebrae. • The upper seven are true ribs, are attached in the front to the sternum by means of costal cartilage. Due to their elasticity they allow movement when inhaling and exhaling. • The 8th, 9th, and 10th ribs are called false ribs, and join with the costal cartilages of the ribs above. • The 11th and 12th ribs are known as floating ribs, as they do not have any anterior connection to the sternum. • The spaces between the ribs are known as intercostal spaces; they contain the intercostal muscles, nerves, and arteries. • The thoracic cavity is divided into three major spaces. • The central/median compartment called mediastinum houses the conducting structures(esophagus,trachea,major blood vessels and most importantly heart). Pericardium There are two layers to the pericardial sac: 1. the fibrous pericardium and 2. the serous pericardium. • The serous pericardium, in turn, is divided into two layers, the parietal pericardium and visceral pericardium Heart The wall of each heart chamber consists of 1. Endocardium:thin internal layer of endothelium 2. Myocardium: thick, middle layer composed of cardiac muscle 3. Epicardium:thin external layer formed by the visceral layer of serous pericardium • The heart has four chambers: • Right and left atria • Right and left Ventricles Atrium Right atrium • The superior vena cava opens at the level of R. 3rd costal cartilage and inferior vena cava at 5th costal cartilage. • The right atrium opens into the R. ventricle thru Tricuspid valve • Receives poorly oxygeneted blood from superior vena cava, inferior vena cava and coronary sinus Left atrium • The pairs of right and left pulmonary veins enter the posterior aspect of atrium. • The left atrium opens into L. ventricle thru Bicuspid or mitral valve. • Receives rich oxygenated blood from pulmonary veins from the lungs Ventricles • • • • • Right ventricle: Receives the deoxygenated blood from the atrium And thru R. and L. pulmonary arteries pumps blood to the lungs Left ventricle: Receives the oxygenated blood from the atrium And thru Aorta pumps blood to the systemic circulation Left ventricle more thicker than the right ventricle Papillary muscles • Papillary muscles are nothing but the conical muscular projections from the myocardium of the heart • They support, strenghthen and responsible for the opening and closure of the cuspid valves. • They area attached to the cuspid valves through tendinous cords called chordae tendinae Conducting system of the heart • Conducting system of the heart consists of the cardiac muscle cells, SA and AV nodes, purkinje fibres and Bundle of His. Sinuatrial node(SA) • It is located antero-laterally just deep to epicardium at the jucnction of Superior Venacava and R.atrium. • It is the pacemaker of the heart, initiating and regulating the impulses for contraction. • It is a small collection of nodal tissue and specialized cardiac muscle fibres. • It could be stimulated or inhibited by the sympathetic or parasympathetic division Atrio-Ventricular Node(AV) • Smaller collection of nodal tissue than SA node. • Located in the posteroinferior region of the interatrial septum. Bundle of His • AV bundle- the AV node passes the signal from atrium to the ventricles thru AV bundle, which is the only bridge between the atrial and ventricular myocardium. • Av bundle divides into R. and L. bundle • These bundles proceed on each side and then ramify into purkinje fibres • These purkinje fibres on both side stimulate the papillary muscles and respective ventricles. END