* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Active Data Objects in .Net
Microsoft Access wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Functional Database Model wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
Versant Object Database wikipedia , lookup
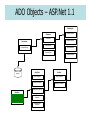
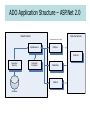
Active Data Objects Binding ASP.NET Controls to Data Jim Fawcett CSE686 – Internet Programming Summer 2005 Support for Data in .Net • Connected data access: – Use Connection object and Command to connect a DataReader object to database and read iteratively. – There are two flavors of these objects, Sql--- and OleDb---. The first are tuned to SQL Server and the second can connect to any database the provides drivers, e.g., Access, SQL, Oracle, … • Disconnected data access: – Use a SqlDataSource and GridView or DetailsView or DataList or FormView or Repeater and execute an SQL query or stored procedure. – Use a Connection and Command to connect a DataAdapter to the database and fill a DataSet with the results. – Use a Connection and Command to connect a DataAdaptor to the database and then call Update method of the DataSet. Data Provider Classes OleDbConnection OleDbCommand OleDbDataReader SqlConnection OleDbDataAdapter SqlDataAdapter DataSet SqlCommand SqlDataReader ADO Application Structure – ASP.Net 1.1 Data Providers Data Consumers Disconnected Access to Tables SqlDataAdapter DataSet WinForm Single Item or flag SqlConnection SqlCommand WebForm Connected cursor reads rows SqlDataReader database ADO Objects – ASP.Net 1.1 DataAdapter SelectCommand Command Connection UpdateCommand Connection CommandText ConnectionString InsertCommand CommandType DeleteCommand DataTable DataSet Rows Collection Tables Collection Columns Collection Relations Collection database Constraints Collection DataGrid ChildRelations Collection ParentRelations Collection ADO Application Structure – ASP.Net 2.0 Data Providers Data Consumers Disconnected Access to Tables SqlDataSource GridView WebForm Connection Property Command Properties DetailsView DataList database ADO Objects - ASP.Net 2.0 SqlDataSource Command SelectCommand(Type) Connection UpdateCommand(Type) Connection CommandText ConnectionString InsertCommand(Type) CommandType DeleteCommand(Type) Many More Properties database GridView Rows Collection Columns Collection Connection Object • Methods – – – – Open() Close() BeginTransaction() BeginTransaction().Commit() • Properties – ConnectionString • Windows, SQL, or Forms Authentication • For Windows authentication: – "server=HINDENBURG\\NETSDK;Integrated Security=SSPI; Trusted_Connection=yes; database=pubs“ – Also need impersonation code in asp application – see link on CSE686 page. – Database, Datasource, State (open | closed) are readonly properties • You can drag a connection object onto a form – Doesn’t identify a data source Command Object • • Used to connect Connection Object to DataReader or a DataAdapter object and execute commands. Methods – ExecuteNonQuery() • Executes command defined in CommandText property, e.g., UPDATE, DELETE, INSERT, CREATE TABLE, ALTER COLUMN, … • Used for operations that do not return a row of data – ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior) • Returns a DataReader instance attached to the resulting rowset • Assumes you’ve defined a command that implies a query, using CommandText property – ExecuteScalar() • • Executes query defined in CommandText and returns the first column of the first row of resulting rowset. Ignores the rest. Properties – – – – – Connection CommandText CommandType Parameters Transaction connection string defining Server and database Text of SQL query StoredProcedure | TableDirect | Text (SQL Query) Arguments for stored procedures Transaction in which command will execute DataReader Object • Supports one-way, forward-only, access to data. • Methods – – – – – – – – Once data has been read, must be closed and re-created to access data again. DataReader lasts as long as the connection is open. It can’t be persisted to session. Read() GetXXX() Returns one row and advances current row pointer GetBoolean, GetInt16, GetChars, GetString, GetValue, … 37 different methods for specific XXX types GetFieldType Returns type of specified column GetSchemaTable Returns DataTable describing structure of data NextResult Advances current row pointer Close() Closes DataReader • Properties • Normally, a DataReader is returned from a command object, ready to bind to a display control. You get one from the command method ExecuteReader(). – – – – – this[string] this[int] FieldCount Item RecordsAffected Specifies column in row by name, returns value Specifies column in row by index, returns value Number of columns in current row Value of a column Number of rows changed, inserted, or deleted Data Adapter Object • Used to: – extract data from data source and populate tables in a DataSet – Push changes in DataSet back to source • Methods – Fill(DataSet, Table) Loads data from source into DataSet – FillSchema(DataSet, SchemaType) – Update() Returns modified data to source • Properties – – – – – SelectCommand UpdateCommand InsertCommand DeleteCommand TableMappings SQL Select text SQL Update command text SQL Insert command text SQL Delete command text Map for source and DataSet columns DataSet Object • Used for Disconnected manipulation of a source’s data. – Read-write, can access tables in any order, as often as you like. – Lasts only as long as the page that created it, unless persisted to session or some other mechanism. • Methods – – – – – – AcceptChanges Clear() ReadXML(XmlReader) WriteXML(XmlWriter) HasChanges() AbandonChanges() Commits pending changes to DataSet Empties all Tables Reads XML data into DataSet Writes DataSet data to XML file boolean returns true if pending changes Reverts to unchanged state • Properties – Tables collection • ds.Tables[tableStr].Rows[3]["Responsible Individual"] = userID; – Relations collection Relationships between Tables in DataSet • Normally, you don’t fill the DataSet, a DataAdapter does that. DataTable Object • Holds records from a source per TableMapping • Properties – DataSets hold DataTable members in Table Collection. – Rows Rows collection – Columns Columns collection – TableName Name used in code • DataSet Tables Collection Methods • DataTable Rows Collection Properties and Methods • DataTable Columns Collection Properties – Tables.Add(TableName) – Tables.Add(DataTable) – Tables.AddRange(TableArray) – Item – Add(DataRow) – ColumnName – DataType Value of a specified column method to add a new row SqlDataSource • Used to connect Connection Object to GridView or DetailsView or DropDownList or … objects and execute commands. • Methods – DataBind() • Calls Select(), called by view controls DataBind() method. – Delete(), Insert(), Select(), Update() • Executes command defined DeleteCommand, InsertCommand, SelectCommand, or UpdateCommand • Properties – ConnectionString connection string defining Server and database – Commands DeleteCommand, InsertCommand, SelectCommand, UpdateCommand – CommandTypes DeleteCommandType, … StoredProcedure | Text (SQL Query) – Parameters DeleteParameters, … Arguments for stored procedures Managing Data Coherency • DataSets support disconnect operation. When processing is complete, changes are sent back to the database. • In a multi-user environment, that obviously can cause problems. • Strategies to avoid coherency problems: – Lock records, so others can read but not update. • ADO.Net does not directly provide locks • You can: SqlTransaction t = conn.BeginTransaction(IsolationLevel.Serializable); some code here t.Commit(); • Do this in a try, catch block with finalizer that does the commit so you don’t leave a bunch of records locked indefinately if your code throws an exception. – Build the update procedure so that it fails if the affected records where last changed after you read the data. Then go and negotiate. – Allow only one person to update any given area of the data model, partitioned in some reasonable way for the business. References • Pro ASP.NET 2.0 in C# 2005, MacDonald & Szpuszta, Apress, 2006 • Programming Microsoft .Net, Jeff Prosise, Microsoft Press, 2002 • Professional C#, Robinson et. al., Wrox Press, 2002 • www.w3schools.com/sql/default.asp