* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Active Data Objects in .Net
Microsoft Access wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft SQL Server wikipedia , lookup
Functional Database Model wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
Clusterpoint wikipedia , lookup
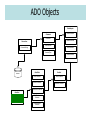
Active Data Objects Binding ASP.NET Controls to Data Jim Fawcett CSE686 – Internet Programming Summer 2004 Support for Data in .Net • Connected data access: – Use Connection object and Command to connect a DataReader object to database and read iteratively. – Use Connection object and Command to connect a DataReader and execute an SQL statement or stored procedure. • Disconnected data access: – Use a Connection and Command to connect a DataAdapter to the database and fill a DataSet with the results. – Use a Connection and Command to connect a DataAdaptor to the database and then call Update method of the DataSet. Data Provider Classes OleDbConnection OleDbCommand OleDbDataReader SqlConnection OleDbDataAdapter SqlDataAdapter DataSet SqlCommand SqlDataReader ADO Objects DataAdapter SelectCommand Command Connection UpdateCommand Connection CommandText ConnectionString InsertCommand CommandType DeleteCommand DataTable DataSet Rows Collection Tables Collection Columns Collection Relations Collection database Constraints Collection DataGrid ChildRelations Collection ParentRelations Collection Connection Object • Methods – Open() – Close() – BeginTransaction() • Properties – ConnectionString • "server=HINDENBURG\\NETSDK;Integrated Security=SSPI; database=pubs" Command Object • • Used to connect Connection Object to DataReader or a DataAdapter object and execute commands. Methods – ExecuteNonQuery() • Executes command defined in CommandText property, e.g., UPDATE, DELETE, INSERT, CREATE TABLE, ALTER COLUMN, … • Used for operations that do not return a row of data – ExecuteReader(CommandBehavior) • Returns a DataReader instance attached to the resulting rowset • Assumes you’ve defined a command that implies a query, using CommandText property – ExecuteScalar() • Executes query defined in CommandText and returns the first column of the first row of resulting rowset. Ignores the rest. • Properties – Connection – CommandText – CommandType connection string defining Server and database Text of SQL query StoredProcedure | TableDirect | Text (SQL Query) DataReader Object • Supports one-way, forward-only, access to data • Methods – Read() • Returns one row and advances current row pointer – GetBoolean, GetInt16, GetChars, GetString, GetValue – Close() • Properties – this[string] – this[int] • Normally, a DataReader is returned from a command object, ready to bind to a display control. You get one from the command method ExecuteReader(). Data Adapter Object • Used to: – extract data from data source and populate tables in a DataSet – Push changes in DataSet back to source • Methods – Fill(DataSet, Table) – FillSchema(DataSet, SchemaType) – Update() • Properties – – – – SelectCommand UpdateCommand InsertCommand DeleteCommand DataSet Object • Used for Disconnected manipulation of a source’s data. • Methods – – – – – – Clear() ReadXML(XmlReader) WriteXML(XmlWriter) AcceptChanges() HasChanges() AbandonChanges() • Properties – Tables collection • ds.Tables[tableStr].Rows[3]["Responsible Individual"] = userID; – Relations collection • Normally, you don’t fill the DataSet, a DataAdapter does that. Managing Data Coherency • DataSets support disconnect operation. When processing is complete, changes are sent back to the database. • In a multi-user environment, that obviously can cause problems. • Strategies to avoid coherency problems: – Lock records, so others can read but not update. – Build the update procedure so that it fails if the affected records where last changed after you read the data. Then go and negotiate. – Allow only one person to update any given area of the data model, partitioned in some reasonable way for the business. References • Programming Microsoft .Net, Jeff Prosise, Microsoft Press, 2002 • Access Database Design & Programming, Steven Roman, O’Reilly, 2002 • Professional C#, Robinson et. al., Wrox Press, 2002 • www.w3schools.com/sql/default.asp