* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Phytoplankton - Madison County Schools
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical oxygen demand wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of electricity generation wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Blue carbon wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
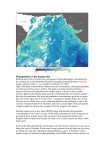
The Role of Single-Celled Organisms in the Oxygen and Carbon Cycles Phytoplankton • The name “phytoplankton” comes from the Greek word “phyto” that means “plant” and “plankton” that means to “wander or drift”. • Phytoplankton are microscopic drifting plants that live in aquatic environments, but are not restricted to the oceans. They come in lots of shapes, colors, and varieties – ranging from single-celled photosynthetic bacteria (cyanobacteria) to plantlike diatoms (a major group of algae) and armorplated cocolithophores (eukaryotes – Protista – marine plants). Phytoplankton Photosynthesis • REMEMBER – about 71% of the earth is made up of water. In this water, phytoplankton are living. That means that these single-celled organisms are going through photosynthesis and releasing oxygen back into the air. • It is hard to believe, but these organisms are producing as much or more oxygen than the trees and plants on land. How can this be? Well – land makes up about 29% of the earth and not all of it is covered with plants. Photosynthesis and the Cycles • The phytoplankton’s photosynthesis abilities impact the carbon and oxygen cycles in a big way! • There are so many of these organisms and they collect a vast amount of carbon dioxide. They use the carbon dioxide for photosynthesis and they also store it inside. They also release oxygen back into the atmosphere. • Phytoplankton are also a first link in the food chain (a primary producer). When they are consumed, some carbon makes its way back to near-surface waters. When they die, the carbon can be buried in the depths of the ocean (think fossil fuels). Phytoplankton: Small Organisms with a Massive Impact • According to scientists, phytoplankton ”have played, and continue to play, such principal roles in shaping the Earth’s biogeochemical composition. They…provide the elements necessary for all other organisms to survive.” • Science Daily says that “Phytoplankton is the fuel on which marine ecosystems run. A decline of phytoplankton affects everything up the food chain, including humans.”