* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Viking
Sample-return mission wikipedia , lookup
Heliosphere wikipedia , lookup
Earth's rotation wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Standard solar model wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Space: 1889 wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
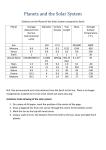
Astronomy Chapter 2 The Solar System Observing the Solar System Section 1 Vocabulary Geocentric: A description of the solar system in which all of the planets revolve around Earth Ellipse: An elongated circle, or oval shape; the shape of the planets’ orbits Heliocentric: A description of the solar system in which all of the planets revolve around the sun Intertia: the tendency of a moving object to continue in a straight line or a stationary object to remain in place Main Ideas Ptolemy thought that Earth is at the center of the system of planets Copernicus thought that the sun is at the center of the planets. Galileo’s observations supported Copernicus’s theory. Kepler discovered that the orbits of the planets are ellipses Newton concluded that two factors—inertia and gravity—combine to keep the planets in orbit Guiding Questions How is Copernicus’s description of the system of planets different from Ptolemy’s description? How did Galileo’s observations of Jupiter’s moons help to show that the geocentric explanation is incorrect? What shape are the orbits of the planets? How was the discovery of this orbit shape made? What two factors act together to keep the planets in orbit around the sun? The Sun Section 2 Vocabulary Nuclear fusion: the process by which hydrogen atoms join together to form helium, releasing energy Core: the central part of the sun, where nuclear fusion occurs Photosphere: the inner layer of he sun’s atmosphere Chromosphere: the middle layer of the sun’s atmosphere Corona: the outer layer of the sun’s atmosphere Vocabulary Solar wind: a stream of electrically charged particles produced by the sun’s corona Sunspot: A dark area of gas on the sun that is cooler than surrounding gases Prominence: a loop of gas that protrudes from the sun’s surface, linking parts of sunspot regions Solar flare: an explosion of hydrogen gas from the sun’s surface that occurs when lops in sunspot regions suddenly connect Main Ideas The sun’s energy comes from nuclear fusion The sun’s atmosphere has three layers: the photosphere, the chromosphere, and the corona Features on or above the sun’s surface include sunspots, prominences, and solar flares Guiding Questions How is energy produced in the sun’s core? Name the layers of the sun’s atmosphere. What is the solar wind? Describe three features found on or above the surface of the sun. Why do sunspots look darker than the rest of the sun’s photosphere? How does the number of sunspots change over time? The Inner Planets Section 3 Vocabulary Terrestrial planets: the name given to the four inner planets, Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars Retrograde rotation: The spinning motion of a planet from east to west, opposite to the rotation of most planets and moons Greenhouse effect: the trapping of heat by a planet’s atmosphere Main Ideas The four inner planets—Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars—are small and have rocky surfaces. They are often called the terrestrial planets Guiding Questions What features do all of the inner planets have in common? What is Mercury’s atmosphere like? Explain Why can astronomers see the surface of Mars clearly, but not the surface of Venus? How have astronomers been able to study the surface of Venus? What evidence do astrnomomers have that water once flowed on Mars? The Outer Planets Section 4 Vocabulary Gas Giant: the name given to the first four outer planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune Main Ideas Four outer planets—Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune—are much larger than Earth Pluto and Charon have solid surfaces and masses much less than that of Earth Guiding Questions How are the gas giants similar to each other? How are they different? How is Pluto different from the gas giants? What is the most prominent feature of Jupiter’s surface? What cuases this feature? Why do astrnomoers think Uranus may have been hit by another object billions of years ago? Comets, Asteroids, and Meteors Section 5 Vocabulary Comet a ball of ice and dust whose orbit is a long narrow ellipse Asteroid: objects revolving around the sun that are too small and too numerous to be considered planets Asteroid belt: the region of the solar system between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, where many asteroids are found Meteoroid: a chunk of rock or dust in space Meteor: a streak of light in the sky produced by the burning of a meteoroid in Earth’s atmosphere Meteorites: a meteoroid that has hit Earth’s surface Main Ideas Comets are chunks of ice and dust that usually have long, elliptical orbits Most asteroids revolve around the sun between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter Guiding Questions What is a comet made of? Where are most asteroids found? What are the main sources of meteoroids? What is the difference between a meteor and a meteorite? Is There Life Beyond Earth? Section 6 Vocabluarly Extraterrestrial Life: life that arises outside of Earth Main Ideas Earth has liquid water and a suitable temperature range and atmosphere for living things to survive. Since life as we know it requires water, scientists hypothesize that mars may have once had the conditions for life to exist Guiding Questions What conditions does life on Earth need to survive? Why do astronomers think there could be life on Europa? How did the Viking missions search fro life on Mars?