* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Early Civilization - Edgewater School District
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
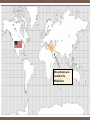
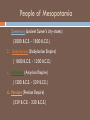
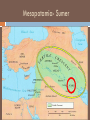
EARLY CIVILIZATION Mrs. Castaldo’s 6th Grade History Class Timeline Review Which of these years came before the year 25 B.C.E.? A 5 C.E. B 10 B.C.E. C 100 C.E. D 50 B.C.E. 50 40 30 BCE 20 10 1 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 CE Mesopotamia Video Let’s watch a video! http://www.watchknowlearn.org/Vi deo.aspx?VideoID=1565&Categor yID=5711 What will you learn? Identify the differing communities that emerged at this time Define “civilization” and describe its characteristics Describe Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent area Examine the early Mesopotamian civilizations of the Sumerians and the Babylonians CIVILIZATIONS What is a civilization? A group of people working together to create an organized society Has 3 Features: 1) A food surplus 2) A division of labor 3) Cities Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia was part of a larger region called the Fertile Crescent. This area, that stretched from the eastern edge of the Mediterranean Sea down to the Persian Gulf, had fertile soil and was where many civilizations started. The shape is somewhat similar to a crescent (think of a crescent roll, or a crescentshaped moon). Mesopotamia was located in the Middle East. Mesopotamia Mesopotamia was a place where many cities began to grow. As its name suggests, Mesopotamia was located between two rivers. The two rivers were the Tigris River and the Euphrates River. Mesopotamia was located in the Middle East, and surrounded by desert. People came to Mesopotamia because the soil between the two rivers was very fertile. Mesopotamia is located in modern-day Iraq People of Mesopotamia 1. Sumerians (ancient Sumer’s city-states) (3000 B.C.E. - 1800 B.C.E.) 2. Babylonians (Babylonian Empire) ( 1800 B.C.E. - 1200 B.C.E.) 3. Assyrians (Assyrian Empire) (1200 B.C.E. - 539 B.C.E.) 4. Persians (Persian Empire) (539 B.C.E. - 330 B.C.E.) Mesopotamia- Sumer Geography of Sumer • • • • Unpredictable rivers (Tigris and Euphrates)- flooding! Delta region extremely fertile- good soil! Flat land open to attack/invasion – no natural barriers Semi-arid climate (arid means not much moisture, dry) required many irrigation projects • Irrigation- a method of watering the land by using canals and channels. • Because of irrigation, the Sumerians did not have to depend entirely on rain to water their crops. A Growing Civilization • • • • Irrigation projects required a lot of cooperation on and leadership Farmers joined together in settlements to manage the environment and for protection These settlements became compact cities surrounded by high mud-brick walls These cities were independent from one another, so we call them city-states City States and Religion The city-states were often built around existing religious buildings/structures – creating a close relationship between government and religion The ziggurat became the focal point of these city-states Ziggurats The pictures above show a ziggurat. Ziggurats were the main temples used to worship the gods of a city. Ziggurats were built in the center of the city. They had steps and ramps, and it was believed that the gods descended to the Earth using the ziggurat as a ladder. Religion Sumerians worshipped many gods, not just one. This belief in many gods is called polytheism. “Poly” means “many” and “Theism” means gods. Sumerian myths, or stories, explained people’s beliefs. Sumerians believed that a person must keep the gods happy by going to the ziggurat and praying to them. They believed that the gods would reward them for good service. They also believed that the gods would punish the people who made them angry. •These gods were seen as powerful, but unpredictable •All land belonged to the gods and kings were their representatives •Kings and priests had special places in society •Theocracy – rule by gods or priests •By the end of Sumerian’s influence, kings were becoming separate from the priest class Cuneiform •Oldest writing system •Original purpose was economic •Used to record lists of goods, receipts, contracts, etc •One of first uses was to record beer recipe Cuneiform Scribes used a sharp point called a stylus to etch words into clay tablets. These tablets have been discovered by archaeologists and looked at by historians. Writing was reserved for the wealthy classes The Epic of Gilgamesh Like many ancient civilizations, the Sumerians also had “a flood story.” That’s not surprising given their challenging environment sitting between two unpredictable rivers…in their view, such a cataclysmic event did, indeed, destroy their “entire world.” The Epic of Gilgamesh is, perhaps, one of the oldest written story on Earth. It comes to us from ancient Sumer, and was originally written on 12 clay tablets in cuneiform script. It is about the adventures of the cruel King Gilgamesh of Uruk. In tablet XI we read about Utnapishtim, a man who built a boat and was saved from a great flood brought about by angry gods. Check out: http://www.historyforkids.org/learn/westasi a/literature/gilgamesh.htm The End of the Sumerians Each of the Sumerian city-states had a ruler, and these city-states began fighting each other. They fought over land and the use of river water. Since the Sumerians were constantly at war with each other, they became weak. By 2000 BCE, Sumer was a weakened area, and by 1759 BCE, Sumer was conquered by another group of people - the Babylonians, who were from the north. The Two Empires of Mesopotamia After the Sumerians were defeated, Mesopotamia had two main empires: Babylonia and Assyria. An empire is an area of many territories and people that are controlled by one government. The Babylonian empire lasted from around 1800 BC to 1600 BC. The Assyrian empire lasted from around 665 BC to 612 BC. Babylon - “Gate of God” As we recall from earlier, the Sumerians were conquered by the Babylonians. The king of Babylon was Hammurabi. Hammurabi united the cities of Sumer and then expanded his empire all the way to Asia Minor Babylonian Religious Beliefs Polytheistic- believed in many Gods The ancient Babylonians, who took over the land between two rivers many years after the Sumerians had disappeared, had a different language than the ancient Sumerians, but they believed in most of the same gods. If possible, the ancient Babylonian gods behaved in a manner even more unpredictable/tempermental than before. To the Sumerians, Marduk was an important god. To the Babylonians, Marduk was the most important (and most gloomy) god of all. Let’s watch a video!!!! Hammurabi’s Code Hammurabi was the king who united most of Mesopotamia and conquered the Sumerians. He developed a “code” of laws. The laws were numbered from 1 to 282. Law number 196 states: If a man put out the eye of another man, his eye shall be put out. Some people summarize Hammurabi’s code by saying “an eye for an eye.” Law number 195 states: If a son strike his father, his hands shall be hewn off. There are many, many more laws like this in Hammurabi’s Code. A statue of Hammurabi On the left is a stela, which has all 282 of Hammurabi’s laws engraved on it. This stela is located in the Louvre Museum in Paris, France. The Hammurabi stela was discovered in 1909, in Susa, Elam, which is now Khuzestan. Khuzestan is a province of southern Iran. Susa Babylonia is Conquered Hammurabi conquered many of the neighboring cities, and he kept expanding his empire. Hammurabi would often go to war against his allies as well. When the city of Elam attacked Larsa, Hammurabi helped Larsa defend themselves. Once Elam was conquered, Hammurabi turned right around and conquered Larsa! Each time that Babylon would conquer another city, Hammurabi would take the city’s chariots, weapons, tools, and all their riches. Trading helped Babylon get rich, and so did conquest. Though Hammurabi formed a large and rich empire, the people that ruled after him could not keep it together. The empire kept getting smaller and smaller until eventually it was destroyed. Please Complete the Survey Please copy and paste this web address into your browser and complete the survey in order to receive credit for viewing this ppt. You must have submit your survey by Monday, February 3rd. https://docs.google.com/forms/d/1ZBQZ5sEdGh5SgUvp6iBxO9U5tp5jluZquOf-5REAuY/viewform