* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 406P PPT - Why Water and the Hunt for Exoplanets
Survey
Document related concepts
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Circumstellar habitable zone wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Life on Titan wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
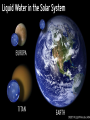
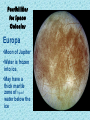
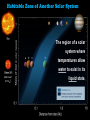
Extremophiles Live in harsh conditions we used to think could not possible support life: Extremophiles – lining the rim of a pitch-black, deep sea volcanic vent Extremophiles – can living in steaming hot springs Extremophiles –frozen in ice in an Antarctic lake. Halophilic Bacteria, Atacama Desert – or feeding off salt in the sands of the driest desert on Earth. Life can handle dark, hot, cold, and salty, but it absolutely must have… Liquid Water… …Is essential to life Kangaroo Rat vs. Salmon • Have same % of water content in cells (50 – 65 %) • Same % of salt in cells • (about 1 % on average) • 1/3 of salt in sea water (about 3.5 % on average) Frost Line Outside the frost line, water freezes into ice. Closer to the sun, water is vaporized into steam. Habitable Zone The region of the solar system where temperatures allow water to exist in its liquid state. Its nickname is the “Goldilocks Zone”. o Venus-(800 F) - Too Hot! o Mars (-67 F) - Too Cold Mars •Water is frozen. •Ice caps even have dry ice (frozen CO2). Earth - The “Blue” Planet “Just Right” Earth lies right in the middle of our solar system’s habitable zone. Only Earth has liquid water. (and it covers ¾ of it surface!!) Water Vapor (Gas) Solid Water (Ice) Liquid Water On Earth, water exists in three physical states: Liquid Water… …Is essential to life Possibilities for Space Colonies Europa •Moon of Jupiter •Water is frozen into ice. •May have a thick mantle zone of liquid water below the ice Titan Possibilities for Space Colonies • Moon of Saturn • Only moon with an atmosphere • Surface water is frozen • May have a thick mantle zone of liquid water and ammonia below the ice Habitable Zone of Another Solar System The region of a solar system where a temperatures allow water to exist in its (Red Dwarf 0.3 M )סּ liquid state. 1 Pegasi B, or Bellerophon • First exoplanet discovered orbiting around a star - found in 1995. • Its parent star, 1 Pegasi is: • about 48 ly (light years) away • Slightly bigger and brighter than the Sun (1.1 Mʘ , 1.3 Lʘ) • Gas giant – “Hot Jupiter” • ½ the mass of Jupiter • 30% larger diameter than Jupiter • Extremely close to its sun - just 5 million miles out (.05 AU) 1 Pegasi B, or Bellerophon • 20X closer to its star than the Earth is to the Sun, so much hotter than Jupiter • (Gas giants are NOT supposed to be that close to their sun!!) • Takes about 4 days to orbit its sun. • Really hot there (1300 K) hot enough to vaporize the nickel and give the planet a bluish tint. • It may be tidally locked, so the same side is always facing its sun. • NOT habitable!! – way too hot!! Possibilities for Space Colonies Ammonia – Another Polar Solvent • Ammonia (NH3) is a polar molecule just like water. • Ammonia has just one lone pair of electrons. • Water has much stronger H-bonds, so it is harder to vaporize and more likely to be a liquid at Earth temperatures (Oo C to 100o C) AMMONIA Ammonia – Another Polar Solvent • H-bonds between ammonia molecules are much weaker than the H-bonds between water molecules. • As a result, ammonia vaporizes to a gas much more easily. AMMONIA Ammonia – Another Polar Solvent • For a planet to have ammoniabased life forms, the temperature would need to be down around -33o C to -78o C! • Where does it get that cold? • Maybe on Titan?? AMMONIA Titan Possibilities for Space Colonies • May have a mixture of liquid water and ammonia in its mantle • has surface pools of liquid hydrocarbons (ethane & methane)