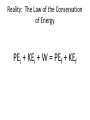* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mechanical Energy PP
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy applications of nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
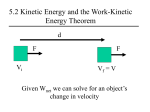
Mechanical Energy What is it? What makes it change? Mechanical Energy is… • The total amount of kinetic and (gravitational) potential energy • Changed when an external force does work on a “system” • Conserved when no external forces do work (fairly good) Examples of Mechanical energy being conserved… PEi + KEi = PEf + KEf • • • • Swinging pendulums Roller coasters Water slides Sleds on hills Reality: The Law of the Conservation of Energy PEi + KEi + W = PEf + KEf Remember… W=… PE=… KE=… W= (F)(Dr) cosq PE = mgh KE=1/2 2 mv PEi + KEi + W = PEf + KEf A Dodge Viper (1490kg) starts at rest and coasts down a 400m long incline that is tilted 5° relative to horizontal. The road then is level. a) Ignoring friction and drag, what speed will the car reach by the bottom of the hill? b) If the coefficient of static friction for the tires on the road is 0.95, how far will it take the car to stop? PEi + KEi + W = PEf + KEf A 30kg child on a 5 kg sled starts from rest at the top of a 100m long, 17m tall hill. a) Compute the speed the child would reach by the bottom of the hill if it was frictionless. b) Real hills, even icy ones have friction. When the child reaches the bottom, she is going 10.0m/s. Compute the work done by friction, and size of the friction force. What is the mathematical relationship between final speed (m/s) and amount of gravitational potential energy (J) “lost”? (Note: the initial speed is zero.) • Use the Law of the conservation of energy to predict the shape of the graph you will see when you perform this experiment. • Devise a way to perform this experiment using the set-up shown on the front board. • Compare your results to your hypothesis. Account for any differences.