* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diseases of the GI System
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Foodborne illness wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Fasciolosis wikipedia , lookup
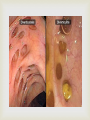
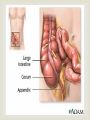
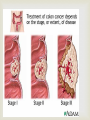
IBS Marked by a group of GI symptoms often related to stress. Symptoms often benign, sometimes showing no physical or inflammatory condition More often seen in women Usually seen between ages of 20-30 CAUSES Physiological Stress (most often) Ingested irritants as coffee, raw fruit & vegetables Lactose Intolerance Abuse of Laxatives Hormonal Changes Food Allergies S/SX N &V Lower abdominal cramping during day, relieves by passage of gas Pain- usually worst 1-2 hours after a meal Constipation alternating with diarrhea Some passage of mucous from the rectum Abdominal bloating & distension Diagnostic Imaging Barium studies reveals colon bloating and spasm Colonoscopy reveals spastic contractions of the colon without any evidence of tumors or other disease conditions Rx Stress management Avoid Food irritants Food allergy testing Heat to Abd Antispasmodics Antidepressants ULCERATIVE COLITIS Continuous inflammation of the colon & rectum. Most commonly begins in the sigmoid colon and moves upward. Begins with excessive edema leading to ulcerations In extreme cases can lead to perforation or puncture of the colon Unknown cause, but may be related to immune system response to food or bacteria in colon or possible heredity Effects women much more than men Onset of systems between ages of 15-30, and again 55-65 s/sx Weight Loss Foul- smelling stools Bloody stools, often containing excess pus & mucous Abdominal cramping weakness DIAGNOSTIC TESTS Sigmoidoscopy Colonoscopy with a biopsy Barium Enema would reveal the extent of condition Abdominal X-rays Lab Tests HGB, WBC, Bleeding time, stool specimens Rx Steroids Antidiarrheal medication Antibiotics Iron Supplements For severe cases TPN IV fluids Ileostomy Prognosis Usually good with diet and medication intervention CIRRHOSIS OF THE LIVER Chronic Disease characterized by destruction and fibrotic regeneration of liver cells. Most people live 5 years after diagnosis Twice a common in men than women, Prevalent in alcoholics, drug users over the age of 50 Other causes- Hepatitis, Autoimmune diseases Malnutrition S/Sx Early Stages Anorexia Dull abdominal ache Late Stages Respiratory difficulty Ascites Enlarged liver Jaundice, Bleeding problems, enlarged abd veins DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Abdominal X-rays CT scan and liver scan would show liver size, fibrotic areas, & masses, hepatic blood flow Esophagogastroduodenoscopy-shows bleeding and blockage Rx Vitamins Healthy diet Surgical shunt Liver Transplant PROGNOSIS Fair, depending on stage & lifestyle changes. If lifestyle does does change, less than 5 years from dx DIVERTICULITIS Pouch like structures bulge through the mucous lining of the intestines. Usually in large intestine, but can occur in ileum and other parts of the GI tract Most prevalent in men over age 40, and people who eat low fiber diets. More than half of people over the age of 60 have some diverticulitis issues Cause Exact cause unknown Low fiber diet Diminished colon mobility S/SX Moderate LLQ abd pain Low grade fever N/V Constipation, alternating with ribbon like stools In severe cases Infection, peritonitis, obstruction DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Upper GI series w/ barium Barium enema Biopsy Rx Liquid, bland diet pain medications Antibiotics Colon resection to remove pouches Prognosis Good with treatment APPENDICITIS ACUTE INFLAMMATION OF THE APPENDIX USUALLY DUE TO AN OBSTRUCTION AND INFECTION SYMPTOMS GENERALIZED ABDOMINAL PAIN THAT LATER LOCALIZES AT THE LOWER RIGHT QUADRANT N&V MILD FEVER ELEVATED WBC DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING CT Scan to confirm Dx Rx Surgery GASTROENTERITIS INFLAMMATION OF MUCOUS MEMBRANE LINING THE STOMACH AND INTESTINAL TRACT CAUSES FOOD POISONING INFECTIONS TOXINS Rx USUALLY REST AND INCREASED FLUID INTAKE IN SEVERE CASES, ANTIBOTICS, IV FLUIDS, AND MEDICATIONS TO SLOW PERISTALSIS MAY BE USED DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Usually not required, but can abd x rays are are done if symptoms last more than a few days. CROHN’S DISEASE Inflammation of any part of the GI tract, but usually in the last parts of the ileum. The inflammation extends thru all layers of the intestine. Most prevalent in adults 20-40 years of age Unknown cause, but lymphatic obstruction, allergies, genetic predisposition, infection S/Sx Steady pain in RLQ Cramping, tenderness Weight Loss Diarrhea, fatty stools, bloody stools Low grade fever Perineal Abscess DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Small bowel X-ray shows irregular mucous, ulcerations, and stiffness Barium enema shows narrowing of the bowel Sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy show patchy areas of inflammation Rx Steroids Antibiotics Stress reduction Vitamin supplemnts Diet changes. Avoid high fiber, spicy, or fatty foods, dairy products, carbonated or caffeine containing beverages COLON CANCER 2ND MOST COMMON TYPE OF CANCER IN THE US Tends to progress slowly and remain localized for a long time Equally occurs in men & women 90% curable if caught early Incidence increases over age 40 CAUSES Low fiber, high calorie diet Hx of other GI diseases Smoking Diabetes Alcohol use Sedentary lifestyle S/Sx Weakness, Fatigue Poor appetite, weight loss Rectal bleeding, dull cramps, constipation/diarrhea Vomiting Diagnostic Imaging CT scan allows good visualization Barium enema to see any obstructions Rx Surgery to remove tumor & any involved structure Chemotherapy Radiation either before or after surgery High fiber diet