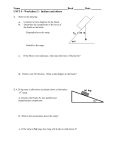
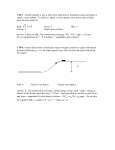
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dissipative Forces
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatic generator wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup