* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classical Literacy Terms
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Early Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Augustus wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
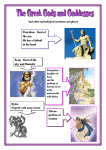
Introductory "in the year of the Lord," designating the time period after Christ's birth "before midday," in the morning, before noon “after midday” after noon : literally refers to the heel of Achilles (a character from the Iliad who killed Hector) — his heel was the only place on his body that could be pierced, thus killing him; figuratively, it refers to a weak spot "to infinity," to continue forever, without limit "to the point of sickness" - doing/saying something over and over until everyone is sick and tired of it sea to the west of Greece; named after King Aegeus after he drowned himself in the sea thinking his son Theseus was dead "the things that must be done" - a to-do list market place/business center the food of the gods; some believe it kept them immortal goddess of love god of the sun, light, reason, and the lyre literally, the apple that Eris (goddess of strife) threw in front of Hera, Aphrodite, and Athena to cause a dispute over who was the fairest; figuratively, anything which causes a dispute a system created by the Romans which carried water over long distances challenged Athena to a weaving contest and was turned into a spider for her excessive pride god of war the daughter of king Minos of Crete, who helped Theseus escape from the labyrinth after he killed the minotaur goddess of the hunt goddess of wisdom a polis (city-state) in Greece, center of art and philosophy, named after Athena (its patron goddess); the Acropolis was the hill in Athens where many temples (including the Parthenon, the temple to Athena) were located titan who had to hold up the heavens on his shoulders as punishment for rebelling against Zeus "I" "for the sake of an example" - abbreviation used when providing an example "one out of many" - found on most US minted coins and the back of the dollar bill god of wine and revelry; son of Zeus and Semele goddess of grain, the harvest, and the seasons; mother of Persephone/Proserpina the oracle of Apollo; people visited the oracle for guidance and predictions of the future one-eyed children of Ouranos/Uranus and Gaea (Mother Earth); sided with Zeus during the war with the Titans; were helpers of the smith-god Hephaestus one of the 12 Titans, father of Zeus/Jupiter, who swallowed his children in an attempt to keep from being overthrown "horn of plenty" a symbol of food and abundance Why was this called the Cornucopia in The Hunger Games? the highest political office in the Roman Republic; 2 were elected every year the arena for gladiatorial games in Rome (also known as the Flavian Amphitheater) a large horse and chariot racing track in Rome the ferryman for the river Styx going into the underworld a state of disorganized matter from which the gods and the world were created the three-headed dog that guarded the gates of the Underworld "beware of the dog" the city in Northern Africa that the Romans fought and destroyed during the Punic Wars (264-146 BC.) "seize the day" usually referring to Julius Caesar, the Roman dictator who was assassinated on the Ides of March (March 15th) 44 BCE first emperor of the Roman Empire; adopted son of Julius Caesar; member of the 2nd Triumvirate; also known as Octavian reception hall (like the living room) in a Roman house