* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 3 Student Notes
Projective plane wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Contour line wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Perspective (graphical) wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
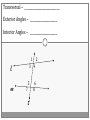
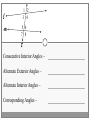
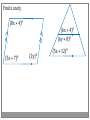
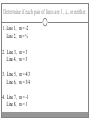
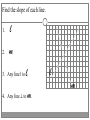
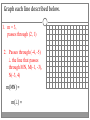
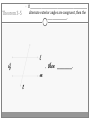
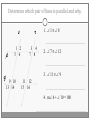
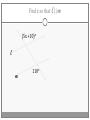
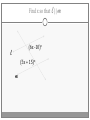
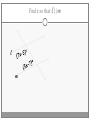
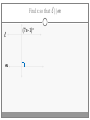
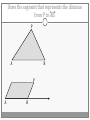
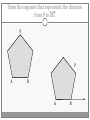
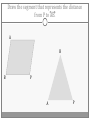
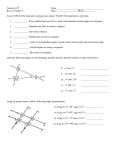
Chapter 3 Student Notes Chapter 3 Test Friday, October 12 th 3.1 Parallel Lines and Transversals Parallel Lines A C B D Skew Lines and Parallel Planes Two lines are skew if they l l and m are ________ m Examples 1. 2. 3. 4. Name all segments that are parallel to AD Name all segments that intersect AD Name all segments that are skew to AD Name all planes that are parallel to plane ABC. Answers: 1. ___________________ 2. ___________________ 3. ___________________ 4. ___________________ E H G F C D A B Transversal – ___________________________ Exterior Angles – _____________________ Interior Angles – _____________________ 1 l m 2 3 4 5 7 t 6 8 l m 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 t Consecutive Interior Angles – _____________________ Alternate Exterior Angles – _____________________ Alternate Interior Angles – _____________________ Corresponding Angles – _____________________ q p 1 2 3 4 8 7 6 5 9 10 11 12 16 17 18 19 r s Transversal 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 3 & 11 11 & 17 17 & 1 2 & 3 4 & 6 Name the transversal that forms each pair of angles. Then name the special name for each pair. ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ Special Angle Pair Name __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ __________________ 3-2 Angles and Parallel Lines 1 m 2 3 4 5 n 6 7 8 t If m ║ n , then the following relationships exists: 1 m 2 3 4 5 n 6 7 8 If m ║ n , then: t Corresponding ’s Alternate Interior ’s Alternate Exterior ’s Consecutive Interior ’s supplementary If m1 = 70o, find the others. 70o 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 More Examples 1. The value of x, if m3 = 4x + 6 and m11 = 126. If line AB is parallel to line CD and s is parallel to t, find: A 1 4 C 5 8 s 2 3 6 9 10 12 11 13 14 16 15 7 t 2. The value of x, if m1 = 100 and m8 = 2x + 10. 3. The value of y, if m11 = 3y – 5 and m16 = 2y + 20. B D Important Notes: •When the lines are parallel; •The acute angles ____________________. •The obtuse angles ___________________. •One acute angle is _______________ to one obtuse angle. 1 m 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 n t 30o 1 36o Find the measure of angle 1. 140o 1 30o Find the measure of angle 1. Find the value of x and y. (5x)o Find x and y. (8x + 4)0 (6x + 4)0 (6y + 8)0 (5x + 7)0 (2y)0 (5x + 12)0 3-3 Slopes of Lines Slope of ǁ, and⊥ lines Determine if each pair of lines are ǁ , ⊥, or neither. 1. Line 1, m = -2 Line 2, m = ½ 2. Line 3, m = 3 Line 4, m = 3 3. Line 5, m = 4/3 Line 6, m = 3/4 4. Line 7, m = -1 Line 8, m = 1 Find the slope of each line. 1. l 2. m l 3. Any line ǁ to . 4. Any line ⊥ to m. l m Slope of a Line The slope of the non-vertical line through the points and is m= The slope of a vertical line ____________. The slope of a horizontal line is _______. Examples Find the slope of the line through the given points. (-4, 7) and (3, 7) Examples Find the slope of the line through the given points. (3, -1) and (3, 2) Examples Find the slope of the line through the given points. (1, -4) and (2, 5) Examples Find the slope of the line through the given points. (-2, 5) and (1, -1) Given each pair of points, Determine if AB ǁ CD, AB ⊥ CD, or neither. 1. A(-3, -2) B(9, 1) C(3, 6) D(5, -2) 2. A(5, -4) B(10, 0) C(9, -8) D(5, -13) m(l) = m(m) = m(s) = m(r) = l s m r Graph each line described below. 1. m = 3, passes through (2, 1) 2. Passes through (-4, -5) the line that passes through MN, M(-1, -3), N(-3, 4) m(MN) = m() = 3-5 Proving Lines Parallel If ___________________________________________________ Postulate 3-4 corresponding angles are congruent, then the _________________. l if m t , then ______. If ________________________________________________________ Theorem 3-5 alternate exterior angles are congruent, then the ___________________. l if m t , then ______. If __________________________________________________________ consecutive interior angles are supplementary, Theorem 3-6 then ____________________. 1 if 2 t l m , then ______. If ____________________________________________________ alternate interior angles are congruent, then ________________. Theorem 3-7 l if m t , then ______. Theorem 3-8 l if m t , then ______. Determine which pair of lines is parallel and why. s p q 1 2 5 6 r 1. 1 8 4 2. 7 12 3 7 8 3. 11 9 9 10 13 14 11 12 15 16 4. m 6 + 10 = 180 Find x so that (5x +10)o l m 110o l || m Find x so that (6x -10)o l (5x + 15)o m l || m Find x so that l m l || m Find x so that l m (7x–1)o l || m 3.6 Perpendiculars and Distance How would you measure the distance from Fishersville to the Beach? Fishersville Beach Draw the segment that represents the distance from P to AB. P A B P A B Draw the segment that represents the distance from P to AB. P P A B A B Draw the segment that represents the distance from P to AB. A B B P A P